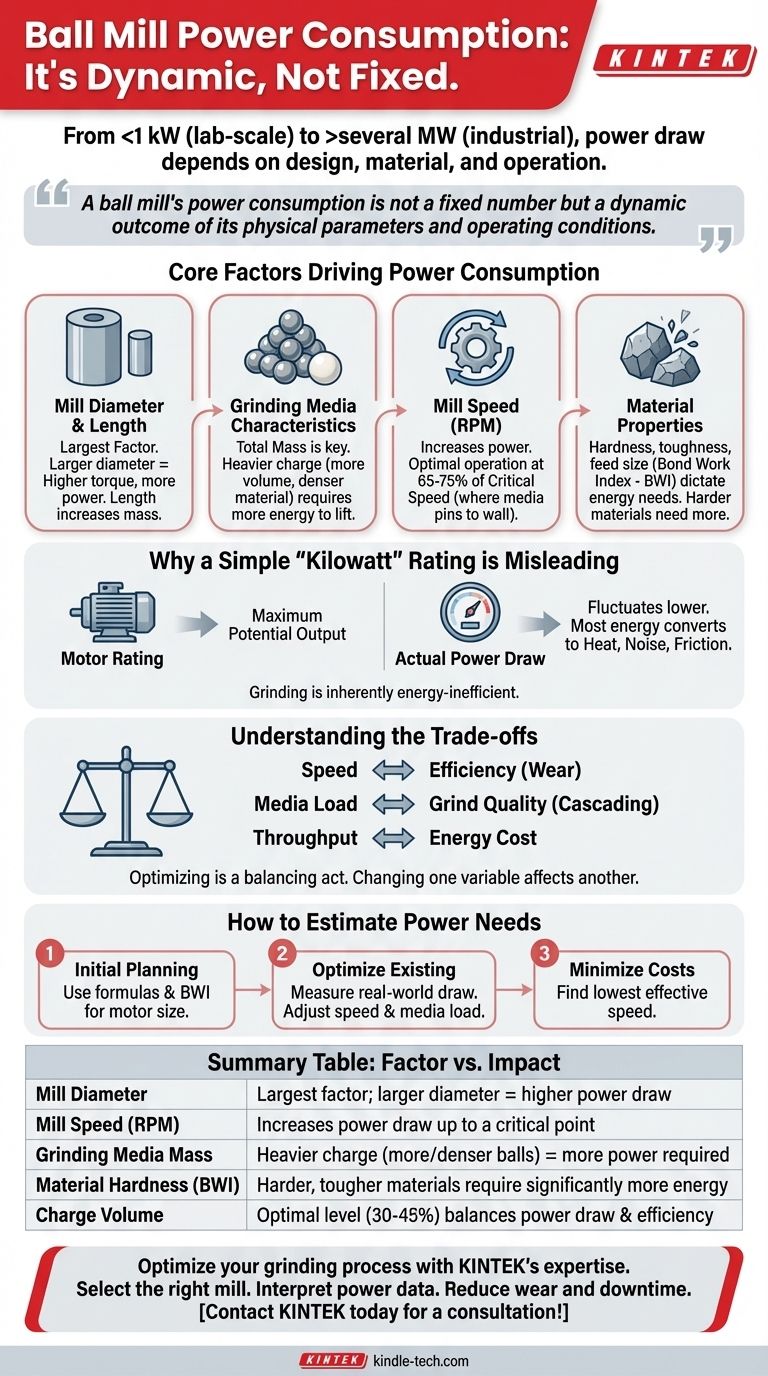
It is impossible to state a single power figure for a ball mill. Instead, the power a ball mill consumes is a calculated value that depends entirely on its design, the material it is grinding, and how it is operated. A small lab-scale mill might use less than a kilowatt, while a large industrial mill used in mining operations can draw several megawatts.
The central takeaway is that a ball mill's power consumption is not a fixed number but a dynamic outcome of its physical parameters and operating conditions. Understanding these variables is the key to estimating and controlling energy costs.

The Core Factors Driving Power Consumption
To understand a ball mill's power draw, you must look at the physics of its operation. The primary use of energy is to continuously lift the grinding media (the balls) and the material charge, allowing them to fall and create the impacts and abrasion that cause size reduction.
Mill Diameter and Length
The diameter of the mill is the most significant factor in its power consumption. A larger diameter means the grinding media must be lifted higher on each revolution, which requires more torque and therefore more power. The length of the mill also increases the total mass of the media and material, contributing directly to the power draw.
Grinding Media Characteristics
The total mass of the grinding media is a primary driver of energy use. This is determined by the charge volume (typically 30-45% of the mill volume), the size of the individual balls, and their material density (steel is much denser than ceramic). A heavier charge requires more energy to lift.
Mill Speed (RPM)
A mill's rotational speed is critical. As speed increases, power draw increases. However, there is a "critical speed" at which centrifugal force will cause the grinding media to be pinned against the mill's inner wall, stopping the grinding action. Most mills operate at 65-75% of this critical speed to maximize power application for effective grinding.
Material Properties
The characteristics of the material being ground have a profound impact. The hardness, toughness, and feed size of the material dictate how much energy is required to achieve the desired particle size. Harder materials require more energy input, a concept often quantified by the Bond Work Index (BWI) in mineral processing.
Why a Simple "Kilowatt" Rating is Misleading
Looking at a motor's nameplate is only the first step and can be deceptive if taken as the sole indicator of energy use.
Motor Rating vs. Actual Power Draw
The kilowatt or horsepower rating on a mill's motor represents its maximum potential power output, not its constant operational consumption. The actual power drawn from the grid will fluctuate based on the factors above and is almost always lower than the motor's maximum rating.
The Inefficiency of Grinding
Ball milling is an inherently energy-inefficient process. A vast majority of the electrical energy supplied to the motor is converted into heat, noise, and mechanical friction. As the reference notes, especially in nano-grinding, the energy required becomes very large because only a tiny fraction of the power input results in the creation of new surface area on the particles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing a ball mill is a balancing act. Changing one variable to reduce power consumption can negatively affect another aspect of the operation.
Speed vs. Efficiency
Running a mill faster increases throughput but often at the cost of decreased energy efficiency. It also dramatically increases the wear rate on the grinding media and the mill liners, leading to higher maintenance costs and more frequent downtime.
Media Load vs. Grind Quality
A higher media charge (more balls) increases power draw and can increase grinding action, but overfilling the mill can impede the cascading motion of the charge, reducing grinding efficiency. The optimal charge level provides the best balance between power draw and effective size reduction.
Throughput vs. Energy Cost
The ultimate trade-off is economic. A business must decide whether the value of increased production (higher throughput) is worth the corresponding increase in electricity costs. Finding the "sweet spot" where the mill operates most cost-effectively is a key goal of process engineering.
How to Estimate Power Needs for Your Goal
Rather than seeking a single number, focus on the variables you can control to meet your objective.
- If your primary focus is initial project planning: Rely on manufacturer specifications and established empirical formulas, such as those using the Bond Work Index, to estimate the motor size required for your specific material and throughput goals.
- If your primary focus is optimizing an existing mill: Install power meters to measure real-world energy draw. Experiment by methodically adjusting variables like mill speed and media load to find the most energy-efficient operating point for your desired output.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational costs: Avoid running the mill at maximum speed unless absolutely necessary. Focus on finding the lowest speed that still produces the required particle size and throughput, as this will significantly reduce both energy consumption and mechanical wear.
Ultimately, managing a ball mill's power consumption comes down to controlling the variables of the grinding process itself.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Power Consumption |
|---|---|
| Mill Diameter | Largest factor; larger diameter = higher power draw |
| Mill Speed (RPM) | Increases power draw up to a critical point |
| Grinding Media Mass | Heavier charge (more/denser balls) = more power required |
| Material Hardness (BWI) | Harder, tougher materials require significantly more energy |
| Charge Volume | Optimal level (30-45%) balances power draw and grinding efficiency |
Optimize your grinding process with KINTEK's expertise.
Whether you are planning a new project with a lab-scale ball mill or seeking to reduce the operational costs of an industrial system, understanding and controlling power consumption is key to your success and profitability.
KINTEK specializes in supplying high-quality lab equipment, including ball mills, and providing the technical support to help you:
- Select the right mill for your specific material and throughput goals.
- Interpret power data to find the most energy-efficient operating point.
- Reduce wear and downtime with optimal process settings.
Let our experts help you balance performance with cost. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation tailored to your laboratory's grinding needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why use ball milling for NMC cathode materials? Achieve Precision Particle Sizing for Composite Cathodes
- What is the product size of a ball mill? Achieve Micron-Level Precision for Your Materials
- What are the disadvantages of a ball mill? High Energy Use, Noise, and Contamination Risks
- What is the purpose of ball milling? A Versatile Tool for Material Synthesis and Modification
- What is the function of ball milling equipment in NZSSP electrolyte preparation? Optimize NASICON Solid-State Synthesis



















