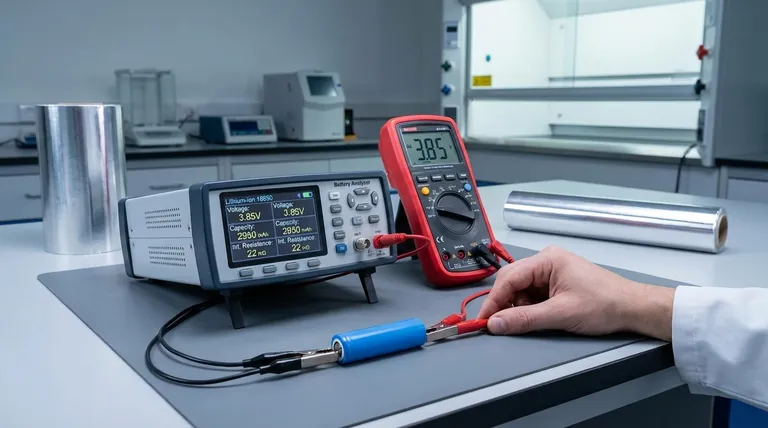
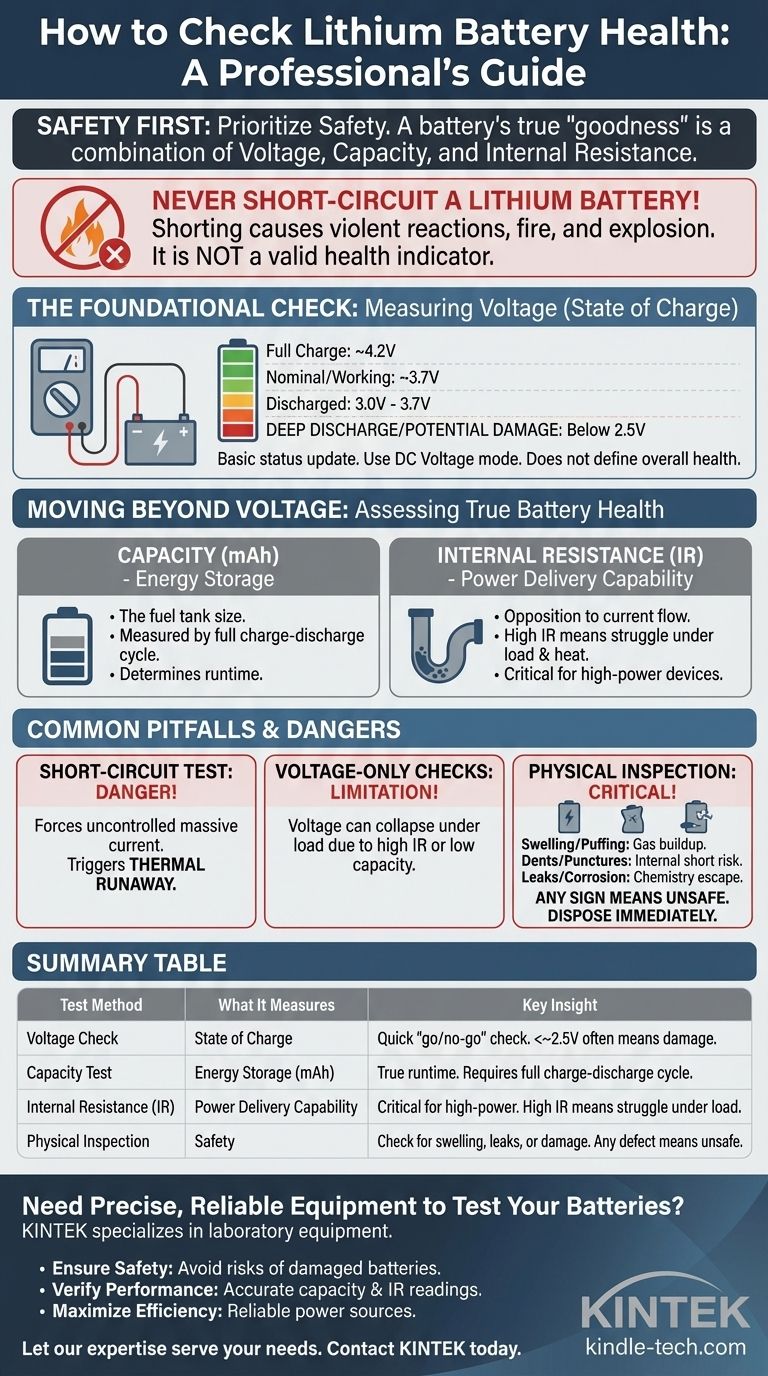
The single most important rule when testing a lithium battery is to prioritize safety. While a simple voltage check can give you a quick status update, a popular but dangerously incorrect method involves short-circuiting the battery to test its current. Never do this. Shorting a lithium battery can cause a violent reaction, including fire and explosion, and is not a valid indicator of its health.
A battery's true "goodness" cannot be determined by a single test. It is a combination of its voltage (state of charge), capacity (energy storage), and internal resistance (power delivery capability). A simple voltage check is a starting point, but a definitive answer requires the right tools.

The Foundational Check: Measuring Voltage
The most basic and accessible test is measuring the battery's open-circuit voltage with a multimeter. This tells you its current state of charge, not its overall health.
Why Voltage Matters
Voltage is the electrical potential of the battery. A fully charged lithium-ion cell will typically be around 4.2 volts, while its "nominal" or working voltage is usually 3.7 volts. A reading significantly below the nominal voltage indicates it is discharged.
How to Safely Measure Voltage
- Set your multimeter to the DC Voltage mode (V with a straight line, or VDC).
- Choose a range that is higher than the battery's maximum voltage (e.g., the 20V setting is suitable for most consumer lithium batteries).
- Touch the red probe to the positive (+) terminal of the battery.
- Touch the black probe to the negative (-) terminal.
- Observe the reading on the multimeter's screen.
Interpreting the Voltage Reading
A healthy, fully charged 3.7V nominal battery should read close to 4.2V. If it reads between 3.0V and 3.7V, it is simply in a discharged state and needs charging.
However, if the voltage has fallen below a certain threshold (often between 2.0V and 2.5V), the battery may have entered a "deep discharge" state. At this point, internal chemical damage can occur, making it unable to hold a charge reliably or safely again.
Moving Beyond Voltage: Assessing True Battery Health
A battery can have a perfect voltage reading but still be "bad." True health is determined by its ability to store and deliver energy, which is measured by capacity and internal resistance.
The Concept of Capacity (mAh)
Capacity, measured in milliamp-hours (mAh), is the equivalent of the battery's fuel tank size. A new battery should have a capacity close to its advertised rating. An old, degraded battery might show a full 4.2V charge but have a tiny capacity, meaning it will die very quickly when used.
The Importance of Internal Resistance (IR)
Internal Resistance (IR) is a measure of how much the battery opposes the flow of current. Think of it as a clog in a fuel line. A battery with low IR can deliver large amounts of power effortlessly. As a battery ages, its IR increases, causing it to struggle and heat up under load, even if its capacity is still reasonable. High IR is a primary indicator of a worn-out battery.
Common Pitfalls and Dangers
Understanding what not to do is as important as knowing the correct methods. Certain tests are not only inaccurate but also extremely hazardous.
The Extreme Danger of the "Short-Circuit Test"
The idea of shorting a battery with a multimeter to measure amperage is a dangerously flawed concept. This forces an uncontrolled, massive current draw from the battery, which can trigger thermal runaway. This is an unstoppable chemical chain reaction that generates intense heat, causing the battery to swell, vent flammable gas, and potentially explode.
This test does not accurately measure battery health; it only proves the battery can deliver a destructive amount of current for a brief moment before it is potentially damaged or destroyed. It must never be attempted.
The Limitation of Voltage-Only Checks
Relying solely on a voltage reading is a common mistake. A battery can show a full voltage when resting but collapse to a very low voltage the moment a device tries to draw power from it. This behavior is a classic symptom of high internal resistance or diminished capacity.
The Critical Role of Physical Inspection
Before performing any electrical test, always inspect the battery visually. Look for:
- Swelling or "puffing": This indicates gas buildup inside and is a sign of critical failure.
- Dents or punctures: Any damage to the casing can lead to an internal short circuit.
- Leaks or corrosion: Any sign that the internal chemistry is escaping means the battery is compromised.
If you see any of these signs, the battery is unsafe and should be removed from service and disposed of properly immediately.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To truly determine if a battery is good, use the right method for the information you need.
- If your primary focus is a quick "go/no-go" check: Measure the voltage with a multimeter. A reading below 2.5V for a standard Li-ion cell often means it's permanently damaged.
- If your primary focus is ensuring performance in a high-power device (like a drone or power tool): You must assess the internal resistance. A dedicated IR meter or advanced hobby charger can provide this reading.
- If your primary focus is knowing the true runtime you can expect: The only definitive method is to perform a full charge-discharge cycle with a battery analyzer or smart charger that measures capacity (mAh).
- If your primary focus is safety: Immediately recycle any battery that shows physical swelling, leaking, or damage, regardless of its voltage reading.
A truly good battery is one that not only holds a charge but can deliver that charge safely and effectively when you need it most.
Summary Table:
| Test Method | What It Measures | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Check | State of Charge | A quick 'go/no-go' check. Reading below ~2.5V often indicates permanent damage. |
| Capacity Test | Energy Storage (mAh) | Determines the true runtime. Requires a full charge-discharge cycle. |
| Internal Resistance (IR) | Power Delivery Capability | Critical for high-power devices. High IR means the battery struggles under load. |
| Physical Inspection | Safety | Check for swelling, leaks, or damage. Any defect means the battery is unsafe. |
Need precise, reliable equipment to test your batteries?
Accurately assessing battery health requires the right tools. KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables, providing the analyzers, testers, and safety gear you need for dependable results.
We help you:
- Ensure Safety: Avoid the risks of damaged or degraded batteries.
- Verify Performance: Get accurate readings on capacity and internal resistance.
- Maximize Efficiency: Keep your devices running reliably with properly tested power sources.
Let our expertise in lab equipment serve your laboratory needs. Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect solution for your battery testing requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Aluminum Foil Current Collector for Lithium Battery
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Button Battery Case for Battery Lab Applications
- Nickel Aluminum Tabs for Soft Pack Lithium Batteries
- Customizable XRD Sample Holders for Diverse Research Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the recommended storage environment conditions for carbon materials? Preserve Performance and Value
- How to tell if a lithium-ion battery is bad? Spot the critical signs of failure before it's too late.
- What parameters are analyzed using an electrochemical workstation for LATP stability? Optimize Your Interface Research
- What is the role of magnetic stirring and ultrasonic treatment in Zn–WO3? Achieve Perfect Nanoparticle Dispersion
- How do heating or UV curing devices influence solid-state batteries? Expert Insights on In-Situ Polymerization
- What are the advantages of using a thermostatic control chamber for flow batteries? Achieve Superior Data Integrity
- Why must the drying of PEO-TPP composite layers be in an argon glove box? Ensure Peak Battery Performance
- Is there a way to test lithium batteries? Understand Voltage vs. True Health















