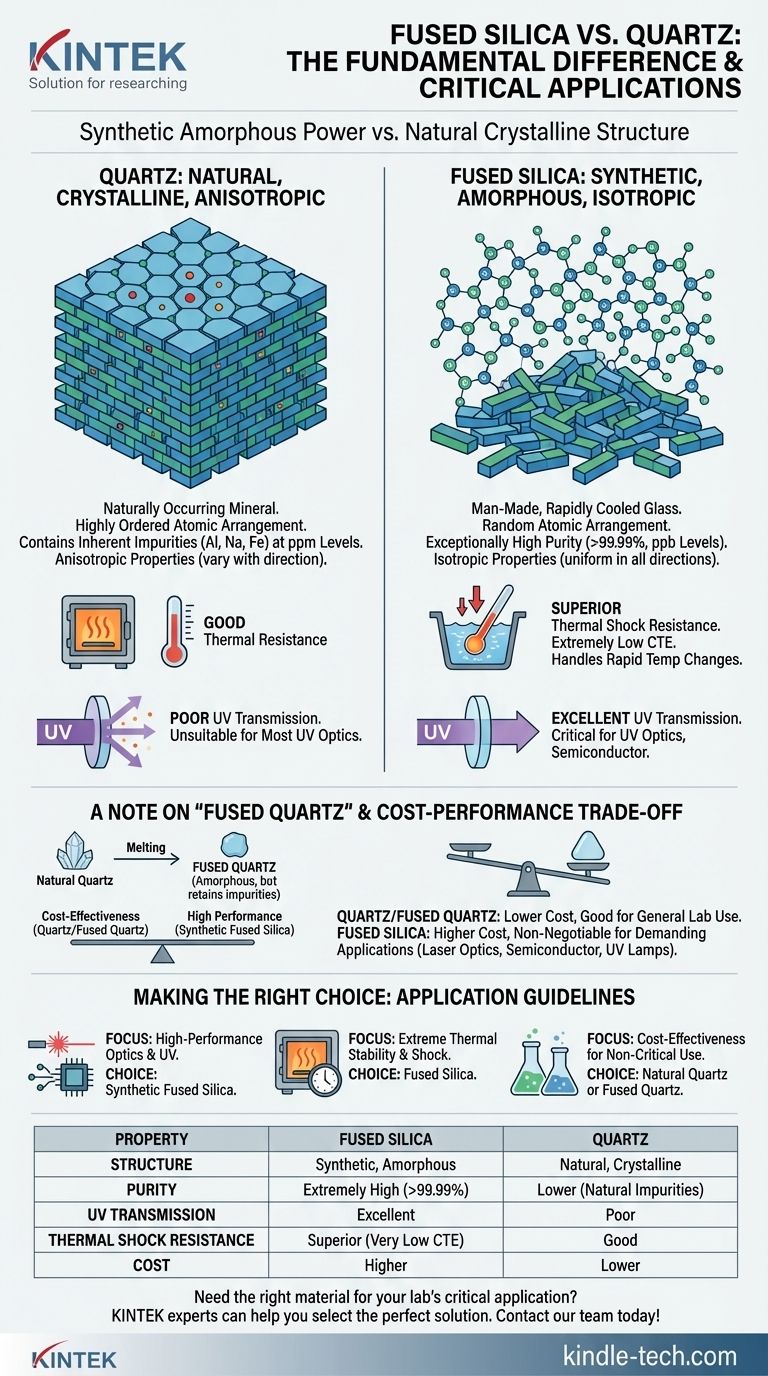
While often used interchangeably, fused silica and quartz are not the same material, though they are chemically related. Quartz is a naturally occurring mineral with a crystalline structure, while fused silica is a man-made, non-crystalline (amorphous) glass. This fundamental structural difference gives fused silica superior optical and thermal properties that are critical for high-performance applications.
The core distinction lies in structure and purity: Quartz is a natural crystal with inherent impurities, whereas fused silica is a synthetic, amorphous solid of exceptionally high purity. This makes fused silica the superior choice for demanding optical and high-temperature environments.

The Fundamental Difference: Crystalline vs. Amorphous
The performance gap between quartz and fused silica originates from their atomic arrangement. Understanding this is key to selecting the right material.
Quartz: The Crystalline Structure
Natural quartz is a crystalline material. Its silicon and oxygen atoms are arranged in a highly ordered, repeating, three-dimensional pattern, much like bricks in a perfectly built wall.
This structure forms naturally as magma cools over geological time. However, this natural process incorporates impurities—like aluminum, sodium, and iron—into the crystal lattice.
Fused Silica: The Amorphous Structure
Fused silica is amorphous, meaning it lacks any long-range atomic order. It is made by melting an extremely pure silicon dioxide (SiO₂) source and cooling it rapidly enough that crystals cannot form.
Its atoms are arranged randomly, like a pile of bricks rather than a wall. This synthetic process allows for extreme control over purity, resulting in a material that is almost 100% pure SiO₂.
Why This Structural Difference Matters
The uniform, amorphous structure of fused silica gives it isotropic properties, meaning its characteristics (like refractive index and thermal expansion) are the same in all directions.
In contrast, the crystalline structure of quartz is anisotropic, causing properties to vary depending on the direction of measurement. The impurities in quartz also degrade its optical and thermal performance.
Comparing Key Properties for Application
For an engineer or scientist, the choice between these materials comes down to specific performance requirements.
Optical Transmission (Especially UV)
This is the most significant differentiator. Fused silica offers excellent optical transmission from the deep ultraviolet (UV) through the visible and into the near-infrared (IR) spectrum. Its purity is the reason it excels in UV applications.
Natural quartz, due to metallic impurities, strongly absorbs UV light, making it unsuitable for most UV optics or sterilization applications.
Thermal Performance
Fused silica has an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE). It barely changes size with temperature fluctuations, giving it outstanding resistance to thermal shock. You can heat it to over 1000°C and plunge it into cold water without it cracking.
While quartz has good thermal resistance, it is nowhere near the level of fused silica. Its higher and more variable CTE makes it vulnerable to fracture under rapid temperature changes.
Purity and Contamination
Synthetic fused silica is one of the purest materials manufactured today, with impurity levels measured in parts per billion (ppb). This is critical for semiconductor manufacturing, where even trace metallic ions can ruin a microchip.
Natural quartz contains impurities at the parts per million (ppm) level, which is thousands of times less pure.
A Note on "Fused Quartz"
To add to the confusion, a third material exists: fused quartz. This is made by melting natural quartz crystals instead of using a synthetic chemical precursor. It is amorphous like fused silica but retains the impurities of its natural source material. It sits between natural quartz and synthetic fused silica in both performance and cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Performance
Your decision will ultimately balance application demands against budget constraints.
The Cost Factor
Natural quartz is mined directly from the earth and is relatively abundant, making it a much cheaper raw material.
The Manufacturing Process
Creating synthetic fused silica requires transforming a pure chemical gas (like SiCl₄) into solid SiO₂ in a highly controlled, energy-intensive process. This complex manufacturing drives its significantly higher cost.
When to Justify the Cost
For general lab equipment, furnace windows, or applications where ultimate optical clarity and thermal shock are not required, quartz or fused quartz are often sufficient and highly cost-effective.
For demanding applications—such as laser optics, semiconductor processing, UV lamps, and high-end analytical instruments—the superior performance of synthetic fused silica is non-negotiable and worth the investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material prevents costly failures and ensures your project's success. Use these guidelines to make a clear decision.
- If your primary focus is high-performance optics or UV transmission: You must use synthetic fused silica for its essential purity and clarity in the UV spectrum.
- If your primary focus is extreme thermal stability and shock resistance: Fused silica's near-zero coefficient of thermal expansion is the only reliable choice for environments with rapid temperature cycling.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for non-critical applications: Natural quartz or fused quartz offers good performance for a fraction of the price.
By understanding that fused silica's synthetic, amorphous purity is the source of its power, you can confidently choose the right material for your specific technical goal.
Summary Table:
| Property | Fused Silica | Quartz |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Synthetic, Amorphous | Natural, Crystalline |
| Purity | Extremely High (>99.99%) | Lower (Natural Impurities) |
| UV Transmission | Excellent | Poor |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Superior (Very Low CTE) | Good |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Need the right material for your lab's critical application? Choosing between fused silica and quartz is essential for the success of your optical systems, semiconductor processes, or high-temperature equipment. KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables. Our experts can help you select the perfect material to ensure superior clarity, thermal stability, and contamination control for your specific needs. Contact our team today to discuss your application and get a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Resistant Optical Quartz Glass Sheet
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Single Double Sided Coated K9 Quartz Sheet
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
- CF Ultra-High Vacuum Observation Window Window Flange High Borosilicate Glass Sight Glass
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- How does the design of a sample mesh or support affect gas-solid reaction efficiency? Optimize Flow-Type Synthesis
- What is the purpose of using a 0.45μm microporous filter membrane? Ensure Accurate Mine Wastewater Analysis
- What material is used for furnace insulation? Key Materials for Maximum Efficiency & Performance
- How do you clean Rotavapor? A Step-by-Step Guide to Maintain Analytical Purity
- How does a gas ballast valve function? Balancing Vacuum Performance with Pump Longevity
- What is the function of combining an ultrasonic disperser and a mechanical stirrer? Achieve Flawless Slurry Dispersion
- What are the functional requirements for graphite molds used in B4C/Al sintering? Optimize High-Pressure Performance
- What are quartz glass tubes used for? Essential for High-Temp, High-Purity Applications










