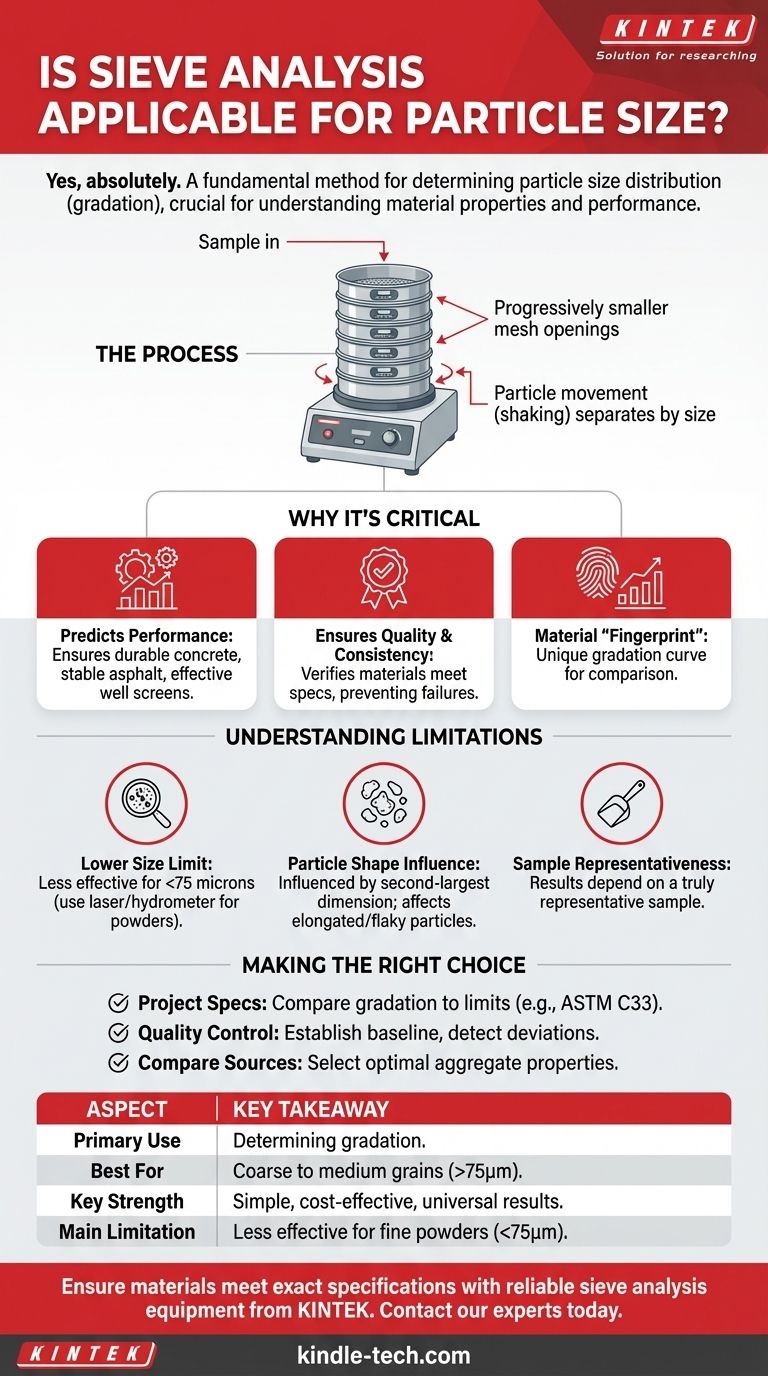
Yes, absolutely. Sieve analysis is one of the most fundamental and widely used methods for determining the particle size distribution of granular materials. It is a trusted technique in many industries due to its simplicity, low cost, and the straightforward, universally understood nature of its results.
Sieve analysis is not merely about measuring particles; it is about understanding a material's "gradation"—the full spectrum of particle sizes within a sample—which directly dictates its physical properties and performance in real-world applications.

Why Particle Size Distribution Is a Critical Parameter
Sieve analysis provides the data needed to understand a material's physical makeup. This data is essential for predicting behavior, ensuring quality, and making correct design choices.
It Predicts Material Performance
The distribution of particle sizes is a critical factor that determines how a material will perform. A well-graded aggregate, for instance, has a mix of particle sizes that pack together densely, creating a strong, stable structure.
This is why sieve analysis is essential for designing durable concrete mixes, stable asphalt pavements, and effective water production well screens.
It Ensures Quality and Consistency
For engineers and manufacturers, consistency is key. Performing sieve analysis on incoming raw materials or finished products verifies that they meet the required specifications batch after batch.
This simple test prevents costly failures acessórios to out-of-spec materials.
It Provides a "Fingerprint" of the Material
The results of a sieve analysis, often plotted as a gradation curve, act as a unique fingerprint for a granular material. This allows for quick comparison between different sources or batches.
The process works by passing a sample through a stack of sieves with progressively smaller mesh openings. Particle movement, induced by shaking or tapping, is crucial for ensuring particles have the opportunity to pass through the apertures and be retained on the correct sieve, leading to an accurate separation by size.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, sieve analysis is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is crucial for interpreting results correctly.
The Lower Size Limit
Sieve analysis palavras with very fine particles, typically those smaller than 75 microns (or a No. 200 sieve). Forces like static electricity and cohesion can cause fine particles to clump together, preventing them from passing through the mesh.
For powders, silts, and clays, other methods like laser diffraction or hydrometer analysis are more appropriate.
The Influence of Particle Shape
Sieves measure a particle's size based on its ability to pass through a square opening. This means the result is most influenced by a particle's second-largest dimension.
Highly elongated or flat, flaky particles may be classified in a way that doesn't fully represent their true geometry, which can affect性能 in some applications.
Sample Representativeness is Paramount
The analysis is only as good as the sample provided. If the small sample used for the test is not truly representative of the entire stockpile or batch, the results will be misleading. Proper sampling técnica is non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use the results of sieve analysis to make data-driven decisions based on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is meeting a project specification: Compare your material's gradation curve directly against the upper and lower specification limits required for the application (e.g., ASTM C33 for concrete aggregate).
- If your primary focus is quality control and consistency: Establish a baseline gradation for your ideal material and use sieve analysis to quickly detect any deviation in new batches.
- If your primary focus is choosing between material sources: Use sieve analysis results to compare the gradation of different aggregates to select the one ženy has the optimal properties for your design.
Ultimately, sieve analysis empowers you to move from guessing about a material's quality to knowing its character with certainty.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Determining particle size distribution (gradation) of granular materials. |
| Best For | Coarse to medium-grained materials (down to ~75 microns). |
| Key Strength | Simple, cost-effective, and provides universally understood results. |
| Main Limitation | Less effective for fine powders (<75 microns) where particle shape affects results. |
Ensure your materials meet exact specifications with reliable sieve analysis equipment from KINTEK.
Whether you're working in construction, manufacturing, or research, accurate particle size data is critical for quality and performance. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab sieves, shakers, and accessories designed for durability and precise results.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieving solution for your laboratory's needs and achieve consistent, data-driven quality control.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
- What is the primary purpose of using standard sieves? Master Particle Uniformity for High-Quality Catalyst Preparation



















