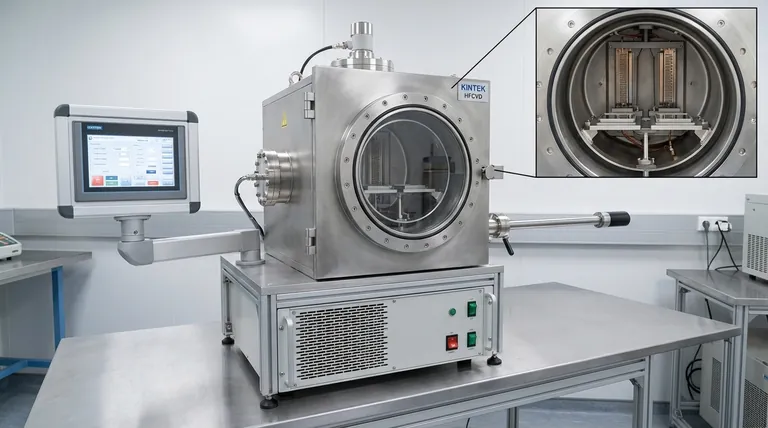
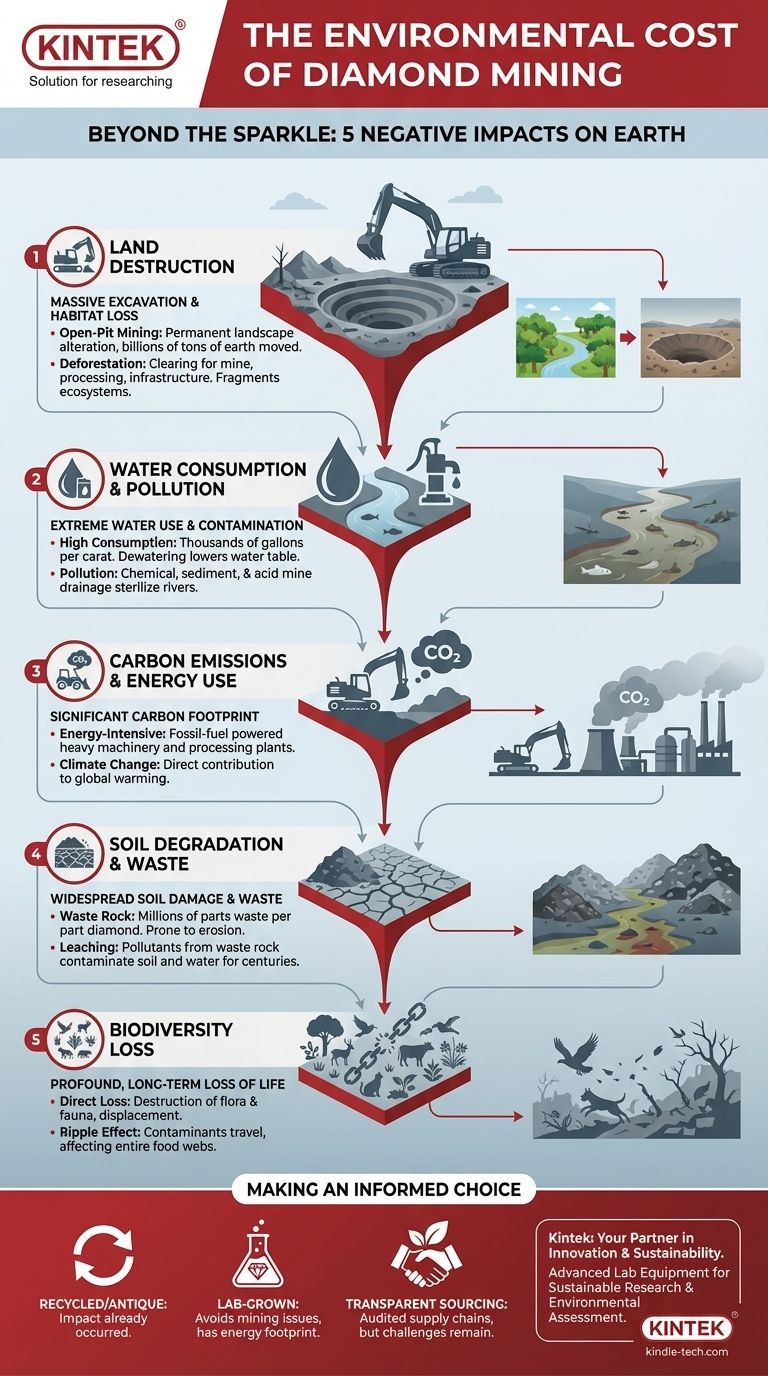
Beyond the sparkle, the process of extracting natural diamonds from the earth carries a significant and often irreversible environmental toll. The five primary negative impacts are massive land excavation and habitat destruction, extensive water consumption and pollution, significant carbon emissions from energy use, widespread soil degradation, and profound, long-term biodiversity loss. These issues are not isolated; they create a cascade of ecological damage that extends far beyond the mine's perimeter.
The core issue with diamond mining is one of scale and permanence. To find a few carats of diamonds, hundreds of millions of tons of earth must be moved, consuming vast resources and leaving behind a permanently altered landscape that struggles to recover.

The Immense Physical Footprint of Mining
The most visible impact of diamond mining is the sheer physical alteration of the land. The methods used are inherently destructive and require clearing enormous tracts of earth.
Open-Pit Mining and Land Disturbance
Most diamonds are extracted from kimberlite pipes via massive open-pit mines. These operations can create some of the largest holes on Earth, with a single mine often displacing billions of tons of rock and soil over its lifetime.
This process permanently transforms the landscape, creating vast craters and enormous piles of waste rock that are difficult, if not impossible, to fully remediate.
Deforestation and Habitat Fragmentation
To establish a mine, vast areas of land must be cleared of all vegetation. This deforestation extends beyond the pit itself to include space for processing facilities, waste rock storage, and infrastructure like roads and worker housing.
This activity not only destroys habitats directly but also fragments larger ecosystems. It cuts off migration routes and isolates animal populations, reducing genetic diversity and making them more vulnerable.
Water: Consumption and Contamination
Diamond mining is a profoundly thirsty industry, both consuming and polluting local water resources at an alarming rate. This dual impact threatens entire watersheds.
Extreme Water Consumption
Water is essential for separating diamonds from the ore and for suppressing dust. A single carat of diamond can require thousands of gallons of water for its processing.
Furthermore, miners must constantly pump groundwater out of the pit to keep it from flooding, a process called dewatering. This can drastically lower the local water table, drying up wells and springs that nearby communities and ecosystems depend on.
Chemical and Sediment Pollution
Water discharged from a mine site is often heavily contaminated. It carries fine particles of rock, known as sediment, which can smother riverbeds and destroy aquatic habitats.
More dangerously, this water can also contain heavy metals and other toxins leached from the excavated rock. In some mines, the exposure of sulfide minerals to air and water creates acid mine drainage, a highly toxic and acidic runoff that can sterilize rivers for decades.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Energy and Waste
The environmental cost is not limited to land and water. The energy required to operate a mine and the sheer volume of waste it produces create a significant, lasting burden.
The Carbon Footprint of Extraction
Diamond mining is incredibly energy-intensive. Heavy machinery—including massive excavators, haul trucks, and crushers—runs almost exclusively on fossil fuels, releasing enormous quantities of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases.
The energy needed to power the sorting and processing plants further contributes to the mine's substantial carbon footprint, directly fueling climate change.
The Problem of Waste Rock
For every one part diamond recovered, millions of parts of waste rock are excavated. The ratio of waste to product is one of the highest of any mining activity.
These immense piles of waste rock are not benign. They take up vast amounts of land, are prone to erosion, and can leach pollutants into the soil and water for centuries after a mine has closed.
The Lasting Impact on Biodiversity
The cumulative effect of habitat destruction, water pollution, and land degradation is a severe and often permanent loss of biodiversity.
Direct Loss of Flora and Fauna
When a habitat is destroyed for a mine, the plants and animals that lived there are either killed or displaced. The displaced wildlife is often forced into smaller, less suitable territories where it must compete for limited resources, leading to population decline.
The Ripple Effect of Contamination
The impact is not confined to the mine's immediate footprint. Contaminants that enter rivers can travel hundreds of miles downstream, poisoning fish and the birds and mammals that feed on them.
This creates a toxic ripple effect throughout the food web, leading to widespread ecological decline far from the source of the pollution.
Making an Informed Choice
Understanding the environmental consequences of diamond mining allows you to evaluate your options with clarity. Your choice depends on which impact you prioritize mitigating.
- If your primary focus is preventing new environmental damage: Consider recycled, antique, or heirloom diamonds, as their environmental impact has already occurred and is not new.
- If your primary focus is avoiding the issues of mining altogether: Investigate lab-grown diamonds, which bypass the land and water issues of mining but have their own energy footprint to consider.
- If your primary focus is promoting better mining practices: Look for retailers who provide transparent, third-party audited reports on their supply chain, though achieving true environmental neutrality at a mine remains a significant challenge.
Ultimately, knowing the true environmental cost behind a diamond empowers you to make a decision that aligns with your values.
Summary Table:
| Impact Area | Key Negative Effect |
|---|---|
| Land | Massive habitat destruction and permanent landscape alteration from open-pit mining. |
| Water | Extreme water consumption and pollution from chemicals, sediment, and acid mine drainage. |
| Air & Climate | Significant carbon emissions from fossil fuel-powered heavy machinery and processing plants. |
| Soil | Widespread degradation and contamination from waste rock and leaching pollutants. |
| Biodiversity | Profound, long-term loss of plant and animal life due to habitat fragmentation and pollution. |
Make an Informed, Sustainable Choice
Understanding the full environmental impact of your materials is the first step toward a more sustainable operation. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables that empower researchers and industries to analyze material properties, develop cleaner alternatives, and ensure supply chain transparency.
Whether you are researching sustainable materials, developing lab-grown gemstone technologies, or conducting environmental impact assessments, having the right tools is critical.
Let KINTEK be your partner in innovation. Contact our experts today to find the precise equipment you need to support your sustainability goals and laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production








