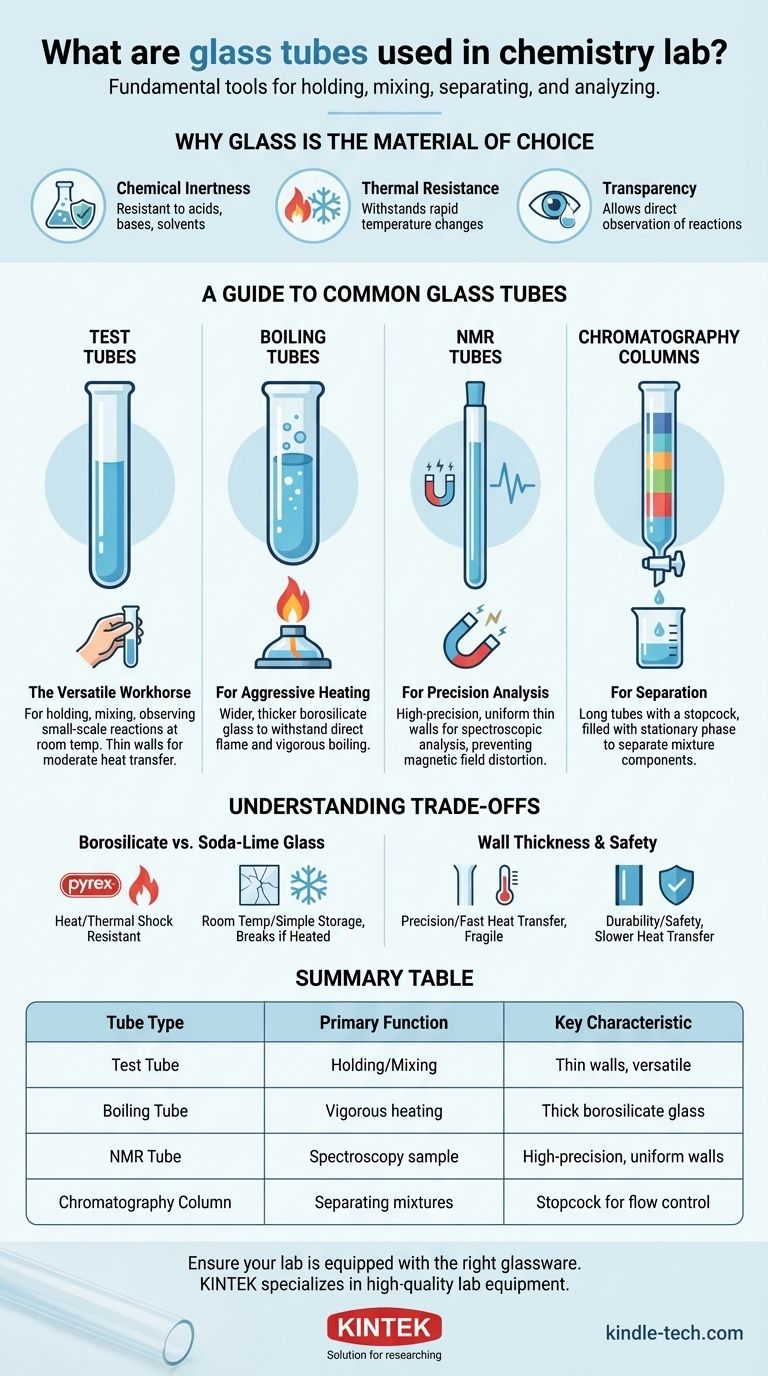
In a chemistry lab, glass tubes are fundamental tools used for a wide range of tasks, from simply holding and mixing chemicals to performing complex separations and analyses. The most common types you will encounter are test tubes, boiling tubes, NMR tubes, and chromatography columns, each with a specific design tailored to its function.
The critical insight is that not all glass tubes are interchangeable. Their material composition, wall thickness, and shape are precisely engineered for specific tasks, making the choice of tube a crucial factor in the safety and success of an experiment.

Why Glass is the Material of Choice
Before examining specific tubes, it's essential to understand why glass is ubiquitous in the laboratory. Its properties make it uniquely suited for handling a vast array of chemical substances and processes.
Chemical Inertness
Glass is highly resistant to chemical attack from acids, bases, solvents, and other reactive substances. This ensures that the tube itself does not contaminate the experiment or degrade during use.
Thermal Resistance
Specific types of glass, like borosilicate glass, have very low coefficients of thermal expansion. This allows them to withstand rapid temperature changes and direct heating without cracking, a critical safety feature.
Transparency
The clarity of glass allows for direct observation of chemical reactions, color changes, and phase transitions. This visual feedback is fundamental to both qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis.
A Guide to Common Glass Tubes
While they may look similar at a glance, each type of glass tube has a distinct purpose dictated by its construction.
Test Tubes: The Versatile Workhorse
The test tube is the most common glass tube, designed for holding, mixing, and observing small-scale chemical reactions at or near room temperature.
Their walls are relatively thin to allow for moderate heat transfer, such as when warming the contents in a water bath. They are typically made of less expensive soda-lime or borosilicate glass.
Boiling Tubes: For Aggressive Heating
A boiling tube is essentially a heavy-duty version of a test tube. It is wider and made from thicker borosilicate glass (like Pyrex).
This construction allows it to be heated directly in a Bunsen burner flame and to withstand the mechanical stress of vigorous boiling without shattering.
NMR Tubes: For Precision Analysis
NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) tubes are highly specialized tools used to hold samples for spectroscopic analysis.
They are manufactured to extremely high tolerances with thin, perfectly uniform walls. This precision is necessary to ensure the magnetic field within the spectrometer is not distorted, which would ruin the analytical results.
Chromatography Columns: For Separation
These are long glass tubes equipped with a stopcock or valve at the bottom. They are filled with a stationary phase material (like silica gel or alumina).
A mixture is applied to the top and a solvent is allowed to flow through, separating the mixture's components based on their different affinities for the stationary phase. The stopcock allows for precise control over the flow rate and collection of the separated fractions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong tube can lead to failed experiments or dangerous accidents. Understanding the key differences in their design is paramount.
Borosilicate vs. Soda-Lime Glass
Borosilicate glass (e.g., Pyrex, Kimax) is the standard for any application involving heating. Its low thermal expansion prevents it from cracking under thermal shock.
Soda-lime glass is cheaper and perfectly suitable for simple storage or room-temperature reactions, but it will likely break if heated rapidly. Never heat a tube unless you are certain it is borosilicate glass.
Wall Thickness and Safety
Thin walls, found in standard test tubes and NMR tubes, allow for rapid heat transfer and high precision, respectively. However, they are more fragile.
Thick walls, characteristic of boiling tubes, prioritize durability and safety under aggressive heating and pressure changes, at the cost of slower heat transfer.
Choosing the Right Tube for Your Experiment
Your experimental goal dictates your choice of equipment. A methodical approach ensures safety and reliable results.
- If your primary focus is observing a small-scale reaction at room temperature: A standard test tube is your ideal and most economical choice.
- If your primary focus is vigorously heating a liquid over a flame: You must use a boiling tube made of borosilicate glass to prevent shattering.
- If your primary focus is separating a chemical mixture based on polarity: A chromatography column provides the necessary structure and flow control.
- If your primary focus is preparing a sample for molecular structure analysis: A specialized NMR tube is required for its precision and dimensional uniformity.
Understanding the specific design of each tube transforms it from a simple container into a precise scientific instrument.
Summary Table:
| Tube Type | Primary Function | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Test Tube | Holding, mixing, observing reactions | Thin walls, versatile |
| Boiling Tube | Vigorous heating over a flame | Thick borosilicate glass |
| NMR Tube | Sample holder for spectroscopy | High-precision, uniform walls |
| Chromatography Column | Separating chemical mixtures | Equipped with a stopcock for flow control |
Ensure your lab is equipped with the right glassware for every application. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of chemical-resistant and heat-tolerant glass tubes. Our products are designed to meet the precise demands of your laboratory, ensuring safety, accuracy, and reliability in all your experiments.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs and let our experts help you select the perfect tools for your research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Beaker and Lids
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a magnetic stirring hot plate in zirconia-alumina synthesis? Master Solution Combustion Prep
- What measures should be taken to prevent cross-contamination when using different sizes of alumina powder?
- What are the advantages of using zirconia milling jars for sulfide electrolytes? Enhance Purity and Conductivity
- What role do multi-layer tantalum and tungsten cylindrical heat shields play in KEMS? Boost Thermal Stability Now
- What causes the severe thermal-shock load on a pusher plate in a sintering furnace? The Trade-Off for High-Efficiency Manufacturing
- What is the purpose of using a magnetic stirrer in a fuel cell electrolyte system? Enhance Stability and Accuracy
- Can you run a pellet stove without a vacuum switch? The Critical Safety Risks Explained
- What are the advantages of using Rotary Vane Vacuum Pumps? The Versatile Workhorse for Laboratory Efficiency



















