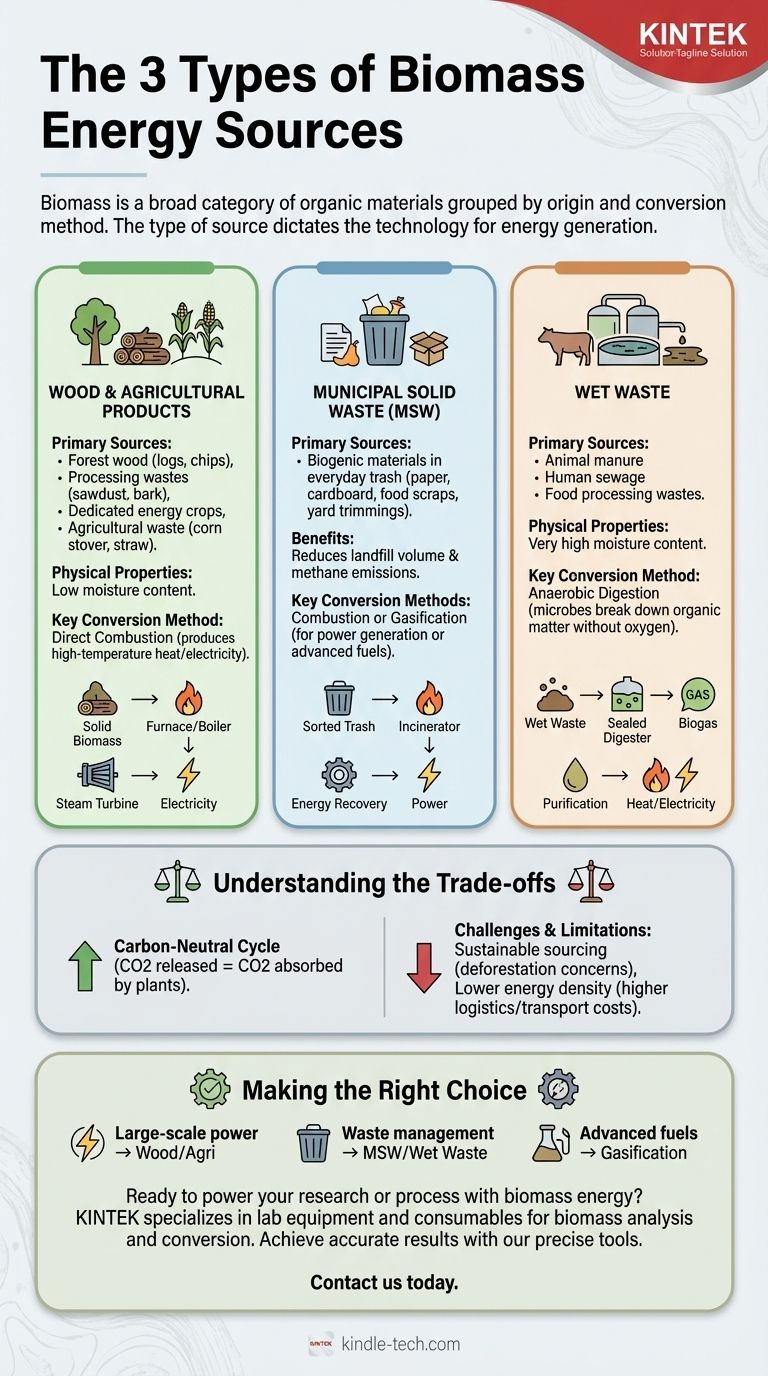
The three primary types of biomass energy sources are wood and agricultural products, municipal solid waste, and wet waste. These categories group organic materials based on their origin and how they are typically converted into energy, ranging from direct burning of wood to the bacterial decomposition of sewage to create biogas.
Biomass is not a single fuel but a broad category of organic materials. The key is to understand that the type of biomass source you use dictates the technology required to convert it into useful energy.

A Closer Look at Each Biomass Category
To truly grasp the potential of biomass, we must analyze each source type individually. Their physical properties, moisture content, and origin stories are fundamentally different.
Category 1: Wood and Agricultural Products
This is the most traditional and widely used category of biomass. It includes materials that are directly harvested or are byproducts of industrial processing.
The primary sources are wood from forests, such as logs and chips, and wood processing wastes, like sawdust and bark. It also includes dedicated energy crops and agricultural waste materials like corn stover or straw.
These materials are typically low in moisture and are ideal for direct combustion to produce heat and electricity.
Category 2: Municipal Solid Waste (MSW)
This category leverages the biogenic (plant- or animal-based) materials found in everyday trash. It represents an opportunity to turn a disposal problem into an energy source.
Sources include paper, cardboard, food scraps, yard trimmings, and other organic items discarded by homes and businesses.
Converting MSW to energy not only generates power but also significantly reduces the volume of waste sent to landfills, mitigating methane emissions from decomposition.
Category 3: Wet Waste
Wet waste consists of organic materials with very high moisture content, making them unsuitable for direct burning.
This includes animal manure from farms, human sewage from wastewater treatment plants, and certain food processing wastes.
The primary conversion method for this category is anaerobic digestion, where microbes break down the organic matter in an oxygen-free environment to produce biogas.
How Biomass is Converted into Energy
The type of biomass dictates the conversion process. The goal is always the same—to release the stored chemical energy—but the methods vary significantly.
Direct Combustion
This is the most straightforward method. Solid biomass, primarily wood and agricultural products, is burned in a furnace to produce high-temperature heat.
This heat can be used directly for industrial processes or to boil water, creating steam that drives a turbine to generate electricity.
Anaerobic Digestion
This biological process is ideal for wet waste. Bacteria break down the material in a sealed container called a digester.
The process releases biogas, which is mostly methane—the primary component of natural gas. This biogas can be purified and used for heating, cooking, or electricity generation.
Thermal Conversion (Gasification & Pyrolysis)
These are more advanced processes that use heat and limited oxygen to break down solid biomass.
Instead of simply burning the material, gasification converts it into a flammable gas mixture called synthesis gas (syngas). Pyrolysis converts it into a liquid known as bio-oil. Both products can be refined into fuels or used to generate power.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While biomass is a renewable resource, its application is not without challenges. An objective assessment requires looking at both sides of the ledger.
The Benefit: A Carbon-Neutral Cycle
In principle, biomass is carbon-neutral. The carbon dioxide (CO2) released during combustion is equivalent to the CO2 absorbed by the plants during their growth.
This creates a closed-loop system, unlike fossil fuels, which release carbon that was sequestered millions of years ago.
The Challenge: Sourcing and Sustainability
The primary concern is ensuring that the biomass is sourced sustainably. This means not contributing to deforestation or competing with land and resources needed for food production.
Responsible biomass energy relies on using waste streams or growing dedicated non-food energy crops on marginal land.
The Limitation: Energy Density and Logistics
Biomass is bulky and has a lower energy density than fossil fuels. This means larger quantities are needed to produce the same amount of energy.
Transporting large volumes of wood chips, straw, or manure from their source to a power plant can be costly and energy-intensive, potentially offsetting some of the environmental benefits.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal biomass strategy depends entirely on the available resources and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, stable power generation: Wood and agricultural waste are the most established sources for direct combustion plants.
- If your primary focus is waste management and localized energy: Municipal solid waste and wet wastes like manure are perfect for turning a disposal liability into an energy asset.
- If your primary focus is creating advanced liquid fuels or chemicals: Gasification and pyrolysis of solid biomass offer the most versatile conversion pathway.
Understanding these distinct categories allows you to see biomass not as a single solution, but as a versatile portfolio of renewable resources tailored to specific needs.
Summary Table:
| Biomass Category | Primary Sources | Key Conversion Method |
|---|---|---|
| Wood & Agricultural Products | Forest wood, sawdust, energy crops, corn stover | Direct Combustion |
| Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) | Paper, food scraps, yard trimmings from trash | Combustion or Gasification |
| Wet Waste | Animal manure, sewage, food processing waste | Anaerobic Digestion |
Ready to power your research or process with biomass energy? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for biomass analysis and conversion. Whether you're developing new biofuels or optimizing waste-to-energy processes, our precise, reliable tools help you achieve accurate results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's biomass energy goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions



