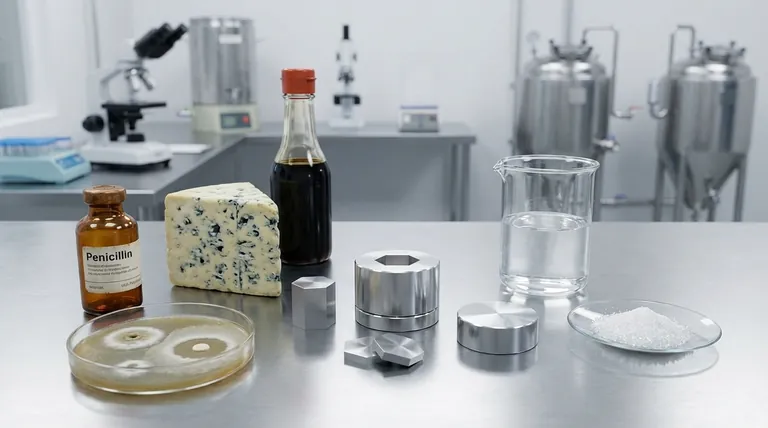
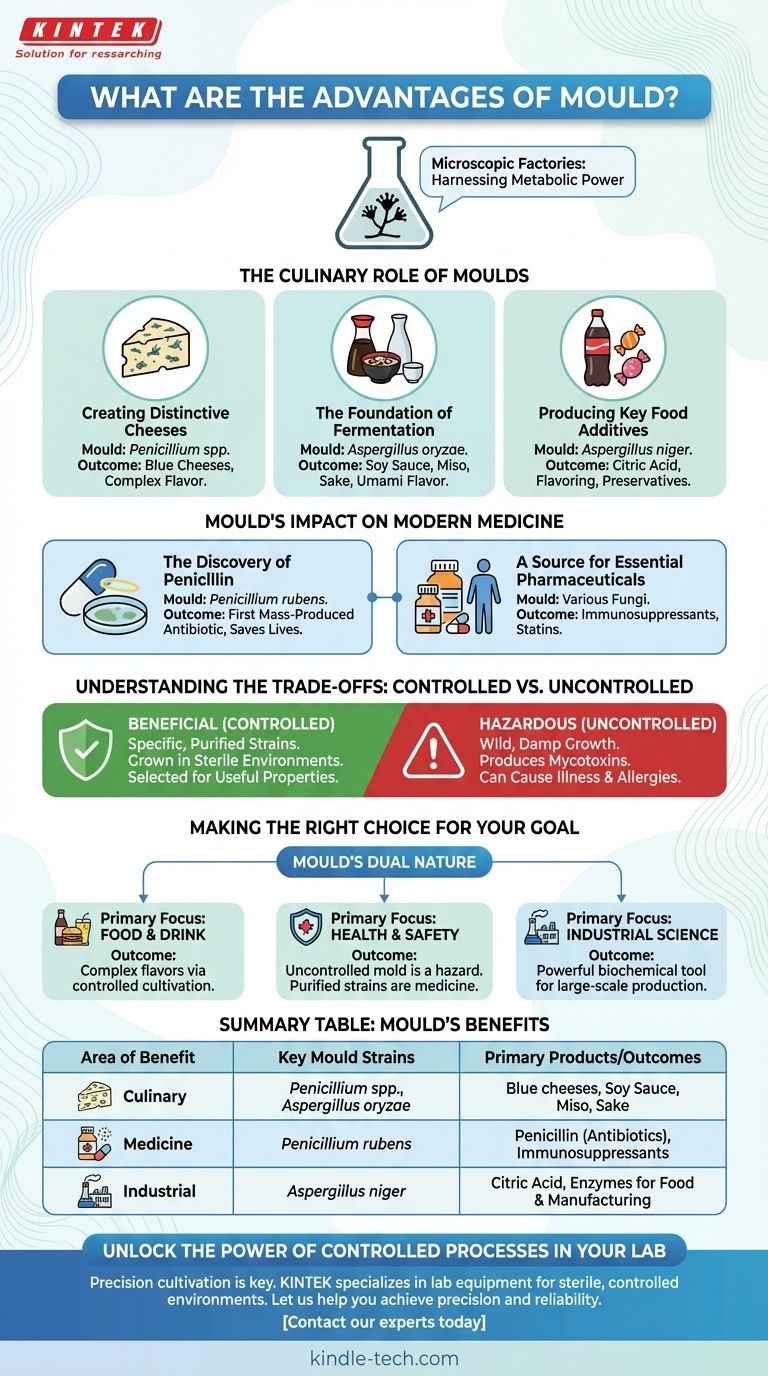
While often seen as a sign of decay, certain types of mold are incredibly beneficial and have been harnessed by humans for centuries. These specialized molds are fundamental to producing life-saving medicines like penicillin, creating the distinct flavors in many foods and cheeses, and manufacturing common ingredients used in everyday products.
The core advantage of mold lies in its metabolic power. Humans have learned to cultivate specific, non-toxic mold strains in controlled environments to act as microscopic factories, producing everything from powerful antibiotics to the complex enzymes that give foods like blue cheese and soy sauce their character.

The Culinary Role of Molds
Many of the world's most complex and prized flavors would not exist without the careful application of specific mold species. This is not the same as spoilage; it is a deliberate and controlled cultivation process.
Creating Distinctive Cheeses
The sharp, tangy flavor and characteristic blue veins of cheeses like Roquefort, Gorgonzola, and Stilton are created by introducing Penicillium molds. These molds break down fats and proteins in the cheese, developing a deep, complex flavor and creamy texture as it ages.
The Foundation of Fermentation
In many culinary traditions, mold is essential for fermentation. For instance, Aspergillus oryzae (koji) is a vital mold used to make soy sauce, miso, and sake. It produces enzymes that break down starches and proteins in soybeans and rice, unlocking rich, savory (umami) flavors.
Producing Key Food Additives
Molds are also used on an industrial scale to create ingredients we consume daily. Citric acid, a common preservative and flavoring agent in soft drinks and candy, is commercially produced using the mold Aspergillus niger.
Mold's Impact on Modern Medicine
The single most significant contribution of mold to human history is arguably in the field of medicine. Its natural properties have been leveraged to save countless lives.
The Discovery of Penicillin
The age of antibiotics began with an observation of the mold Penicillium rubens. This mold naturally produces a substance that inhibits bacterial growth, which was isolated to create penicillin, the world's first mass-produced antibiotic. This discovery revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections.
A Source for Essential Pharmaceuticals
Beyond penicillin, various fungi and molds are a source for other critical medications. These include immunosuppressant drugs essential for organ transplant patients and cholesterol-lowering statins, highlighting their ongoing importance in pharmaceutical development.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Controlled vs. Uncontrolled Mold
It is critical to distinguish between the beneficial molds used in industry and the unwanted mold that can grow in a damp environment.
The Importance of Specific Strains
The molds used to make cheese or medicine are specific, purified strains grown in highly controlled, sterile conditions. They have been selected over generations for their useful properties and lack of toxicity.
The Dangers of Mycotoxins
Conversely, uncontrolled mold growth in homes or on spoiled food can be hazardous. These wild molds can produce mycotoxins, which are toxic compounds that can cause illness and allergic reactions. This is why harnessing mold's benefits requires precise scientific control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding mold requires appreciating its dual nature. Its value is entirely dependent on the species, the strain, and the context in which it grows.
- If your primary focus is food and drink: Recognize that the complex flavors in many cheeses, soy sauce, and fermented beverages are the direct result of controlled mold cultivation.
- If your primary focus is health and safety: Treat any uncontrolled mold growth in your environment as a potential hazard, while appreciating that specific, purified mold strains are the foundation for life-saving medicines.
- If your primary focus is industrial science: View mold as a powerful and efficient biochemical tool capable of producing valuable enzymes, acids, and pharmaceuticals at a massive scale.
Ultimately, mold is a powerful natural tool whose benefits depend entirely on human intention and scientific control.
Summary Table:
| Area of Benefit | Key Mould Strains | Primary Products/Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Culinary | Penicillium spp., Aspergillus oryzae | Blue cheeses, Soy Sauce, Miso, Sake |
| Medicine | Penicillium rubens | Penicillin (Antibiotics), Immunosuppressants |
| Industrial | Aspergillus niger | Citric Acid, Enzymes for Food & Manufacturing |
Unlock the Power of Controlled Processes in Your Lab
The precise cultivation of specific strains is key to harnessing biological power, whether for research or development. At KINTEK, we specialize in the lab equipment and consumables needed to maintain the sterile, controlled environments essential for this work.
Let us help you achieve precision and reliability. Contact our experts today to find the right solutions for your laboratory's unique needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Cylindrical Press Mold for Lab Applications
- Assemble Lab Cylindrical Press Mold
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How do custom graphite molds contribute to Al-20% Si/graphite flake composites? Optimize Microstructure & Conductivity
- What role do high-temperature pressure molds play in SiCp/Al fabrication? Enhancing Densification and Thermal Uniformity
- What is the core function of high-strength graphite molds? Master Vacuum Hot Press Sintering Efficiency
- Is it fitting the mould or mold? A Guide to Correct Spelling by Region
- What is the physical role of graphite molds in vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Cu-Al2O3 Composite Densification



















