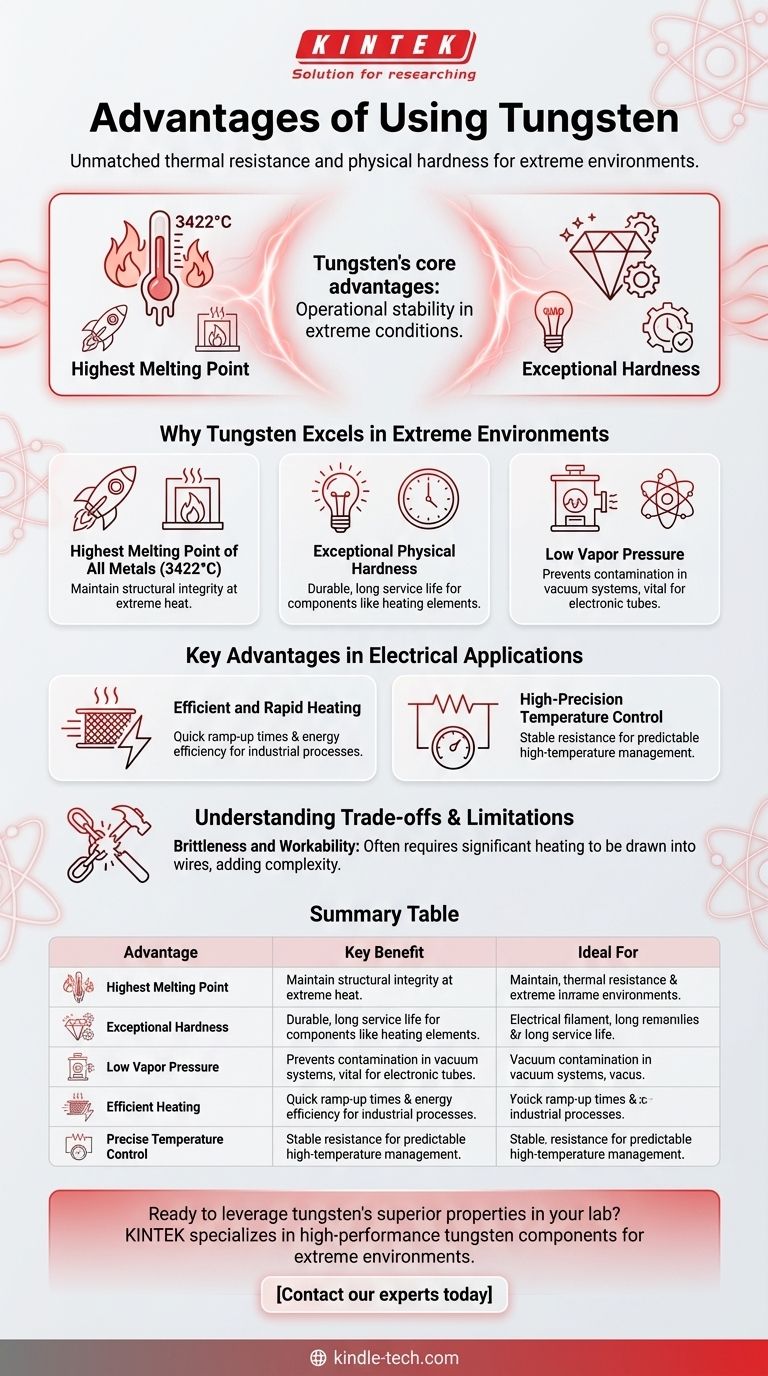
Tungsten's core advantages are its unmatched thermal resistance and physical hardness. This combination of properties makes it the premier material for components that must function under extreme heat and physical stress, particularly in specialized electrical and electronic equipment.
The decision to use tungsten is a decision for operational stability in extreme environments. Its unique ability to withstand immense heat without melting or degrading makes it indispensable for high-performance applications where other metals would fail.
Why Tungsten Excels in Extreme Environments
Tungsten's value is most apparent when conditions become too severe for common metals. Its fundamental properties make it uniquely suited for high-temperature and high-stress roles.
The Highest Melting Point of All Metals
Tungsten has a melting point of 3422°C (6192°F), the highest of any pure metal.
This exceptional thermal stability allows it to maintain its structural integrity at temperatures that would vaporize steel or copper, making it essential for applications like rocket nozzles and furnace windings.
Exceptional Physical Hardness
It is an extremely hard and dense metal, contributing to the durability and longevity of components made from it.
This inherent toughness translates to a long service life for parts like electrical filaments and heating elements, which must endure constant thermal cycling without breaking down.
Low Vapor Pressure
A critical and often overlooked advantage is tungsten's very low vapor pressure.
This means it does not easily turn into a gas, even when heated to thousands of degrees. This property is vital for components used in vacuum furnaces, as it prevents the metal from contaminating the vacuum environment.
Key Advantages in Electrical Applications
While its thermal properties are paramount, tungsten also possesses characteristics that make it highly effective in demanding electrical and electronic systems.
Efficient and Rapid Heating
Components like tungsten mesh are known for their fast heating speed.
This allows for quick ramp-up times in industrial processes and ensures energy is converted to heat efficiently, without being wasted.
High-Precision Temperature Control
Tungsten's stable electrical resistance at high temperatures allows for a high degree of precision in temperature management.
This makes it an ideal material for high-temperature resistors, where predictable and repeatable performance is crucial for process control in environments up to 2,000°C.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect, and tungsten's strengths come with important considerations. Understanding these trade-offs is key to using it effectively.
Brittleness and Workability
In its raw form at room temperature, tungsten can be quite brittle and difficult to machine.
It often must be heated significantly simply to be drawn into wires or formed into other shapes, adding complexity and cost to the manufacturing process.
System-Level Constraints
The theoretical performance of tungsten can be limited by the other materials in the system.
For example, a tungsten resistor's maximum operating temperature might not be dictated by the tungsten itself, but by the refractory materials used to support it, which may fail at lower temperatures.
When to Choose Tungsten
Selecting tungsten is appropriate when your design requirements push beyond the limits of conventional materials.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability: Tungsten is the definitive choice for applications like vacuum furnace elements and filaments where temperatures consistently exceed the limits of other metals.
- If your primary focus is durability under thermal stress: Its hardness and resistance to wear make it ideal for electrical contacts and emitters that must endure repeated, intense heating and cooling cycles.
- If your primary focus is maintaining a pure vacuum: Its low vapor pressure ensures it will not sublimate and contaminate sensitive processes, making it essential for high-vacuum electronic tubes and equipment.
Ultimately, tungsten is the material you specify when operational failure due to heat or physical degradation is not an option.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Highest Melting Point | Maintains integrity at 3422°C (6192°F) | Rocket nozzles, furnace elements |
| Exceptional Hardness | Superior durability & long service life | Electrical filaments, heating elements |
| Low Vapor Pressure | Prevents contamination in vacuum systems | Vacuum furnace components, electronic tubes |
| Efficient Heating | Fast ramp-up times & energy efficiency | Industrial heating processes |
| Precise Temperature Control | Stable resistance at high temperatures | High-temperature resistors (up to 2000°C) |
Ready to leverage tungsten's superior properties in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including tungsten components designed for extreme environments. Whether you need durable furnace elements, precise heating solutions, or vacuum-compatible parts, our expertise ensures reliability and peak performance for your most demanding applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss how tungsten can solve your high-temperature challenges and enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hydrothermal Synthesis Reactor Polytetrafluoroethylene Carbon Paper and Carbon Cloth Nano-growth
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Ball Valve Seat
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Etching Flower Basket ITO FTO Developing Glue Removal
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Corrosion Resistant Cleaning Rack Flower Basket
People Also Ask
- Why is Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) preferred as a lining material for reactors? Ensure Maximum Chemical Resistance
- Is PTFE corrosion resistant? Discover the Ultimate Chemical Resistance for Your Lab
- What are the advantages of using PTFE jars for RuTi alloy mixing? Ensure Chemical Purity and High Yield
- Why are PTFE laboratory consumables required when testing stainless steel against organic acids? Ensure Data Integrity
- What is the difference between PPF and coating? Armor vs. Slick Shell for Your Car



















