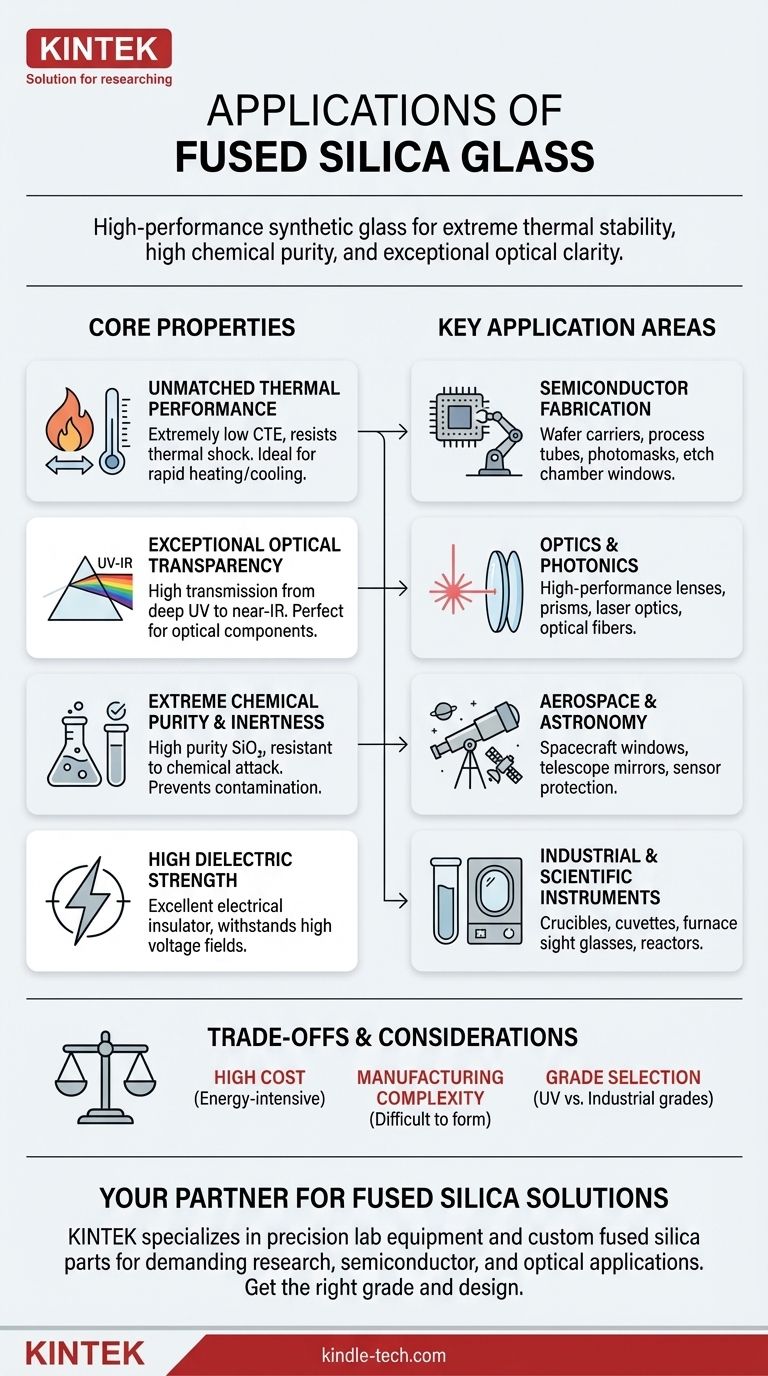
In short, fused silica is a high-performance synthetic glass used in applications where extreme thermal stability, high chemical purity, and exceptional optical clarity are non-negotiable. Its unique properties make it the material of choice for demanding roles in semiconductor manufacturing, high-power optics, scientific instrumentation, and aerospace.
Fused silica is not simply a stronger type of glass. It is a specialized material chosen specifically when conventional glasses like borosilicate would fail due to thermal shock, chemical contamination, or an inability to transmit ultraviolet light. Understanding its core properties is the key to understanding its applications.
The Core Properties Driving Fused Silica's Use
The applications of fused silica are a direct result of its unique and superior material properties compared to other types of glass. It is an engineered material, not a naturally occurring one, prized for its purity and performance under stress.
Unmatched Thermal Performance
Fused silica has an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE). This means it barely expands or contracts when its temperature changes dramatically.
This property makes it indispensable for applications involving rapid heating and cooling, where other materials would crack from thermal shock. Think of furnace windows, rapid thermal processing equipment, and large telescope mirrors that must maintain a perfect shape despite temperature fluctuations.
Exceptional Optical Transparency
Unlike most glasses that absorb ultraviolet (UV) light, fused silica offers excellent transmission from the deep UV through the visible spectrum and into the near-infrared.
This is why it is the default choice for optical components in UV sterilization systems, excimer lasers, spectrophotometry, and photolithography steppers used in chip manufacturing. It is also the foundational material for most optical fibers due to its clarity.
Extreme Chemical Purity and Inertness
Fused silica is composed of amorphous silicon dioxide (SiO₂) in a very pure form, lacking the metallic ions and other additives found in common glass.
This high purity makes it highly resistant to chemical attack and ensures it does not leach contaminants. This is critical in semiconductor fabrication, where it is used for wafer carriers, process tubes, and crucibles to prevent even parts-per-billion contamination of silicon wafers.
High Dielectric Strength
Fused silica is an excellent electrical insulator, meaning it can withstand very high voltage fields without breaking down. This makes it a valuable material for insulators in high-voltage equipment and components in electronic systems where electrical isolation is crucial.
Key Application Areas in Detail
These fundamental properties enable fused silica to excel in some of the world's most advanced industries.
Semiconductor Fabrication
This is one of the largest markets for fused silica. Its thermal stability and purity are essential for creating the pristine environment needed to manufacture integrated circuits. It is used for process tubes, wafer boats, etch chamber windows, and the photomask substrates that define circuit patterns.
Optics and Photonics
Due to its broad transmission range, fused silica is used for high-performance lenses, prisms, beam splitters, and windows. It is especially critical for applications involving high-energy lasers, where its ability to resist laser-induced damage is paramount.
Aerospace and Astronomy
The material's ability to withstand thermal shock and its radiation resistance make it ideal for spacecraft windows and sensor protection. Its dimensional stability is why it was used to create the massive primary mirror blanks for the Hubble Space Telescope and other major observatories.
Industrial and Scientific Instruments
In industrial settings, fused silica serves as sight glasses for high-temperature furnaces and reactors. In laboratories, it is used for high-purity crucibles, test tubes, and the cuvettes that hold samples inside spectrophotometers, where optical clarity is essential for accurate measurements.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, fused silica is not the solution for every problem. Its selection requires a clear understanding of its trade-offs.
High Cost
The primary drawback of fused silica is its cost. The energy-intensive process required to melt pure silica at extremely high temperatures (~2000°C) makes it significantly more expensive than standard borosilicate or soda-lime glass.
Manufacturing Complexity
The same high melting point that provides thermal stability also makes fused silica very difficult to form and shape. This specialized fabrication process adds to the overall cost and limits the complexity of parts that can be economically produced.
Not All Fused Silica is Equal
Different manufacturing methods produce various grades of fused silica. For example, "UV grade" has superior deep-UV transmission but is more expensive, while "industrial grade" is suitable for thermal applications but not for precision optics. Selecting the wrong grade can lead to unexpected failures or poor performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision to use fused silica should be driven by a specific performance requirement that other materials cannot meet.
- If your primary focus is withstanding extreme temperature changes: Fused silica is the clear choice for components like furnace windows, thermal insulators, or telescope mirrors.
- If your primary focus is performance in the deep UV spectrum: You must use a UV-grade fused silica for applications like laser optics or UV sterilization equipment.
- If your primary focus is preventing all chemical contamination: Fused silica is essential for semiconductor processing, high-purity chemical handling, and trace-element analysis.
- If your project is cost-sensitive and does not require extreme thermal or UV performance: A less expensive material like borosilicate glass is likely a more practical choice.
Ultimately, choosing fused silica is a deliberate engineering decision to overcome the limitations of conventional materials in highly demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Properties Utilized | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Semiconductor Fabrication | Chemical Purity, Thermal Stability | Wafer carriers, process tubes, photomasks |
| Optics & Photonics | UV Transparency, Laser Damage Resistance | Lenses, prisms, laser optics, optical fibers |
| Aerospace & Astronomy | Thermal Shock Resistance, Dimensional Stability | Spacecraft windows, telescope mirrors |
| Scientific Instruments | Chemical Inertness, Optical Clarity | Crucibles, cuvettes, furnace sight glasses |
Need high-performance fused silica components for your laboratory? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, including custom fused silica parts for semiconductor, optical, and research applications. Our expertise ensures you get the right grade and design to meet your extreme thermal, chemical, and optical demands. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your project with pure, reliable solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Resistant Optical Quartz Glass Sheet
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Single Double Sided Coated K9 Quartz Sheet
- 400-700nm Wavelength Anti Reflective AR Coating Glass
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range of quartz glass? Master Its Thermal Limits for Demanding Applications
- Does quartz have a high melting point? Discover Its Superior High-Temperature Performance
- What is optical quartz? The Ultimate Material for UV and High-Temp Optics
- What is the high temperature of quartz? Key Thresholds for Crystalline vs. Fused Silica
- What temperature does quartz glass melt at? Understanding Its Softening Point and Practical Limits












