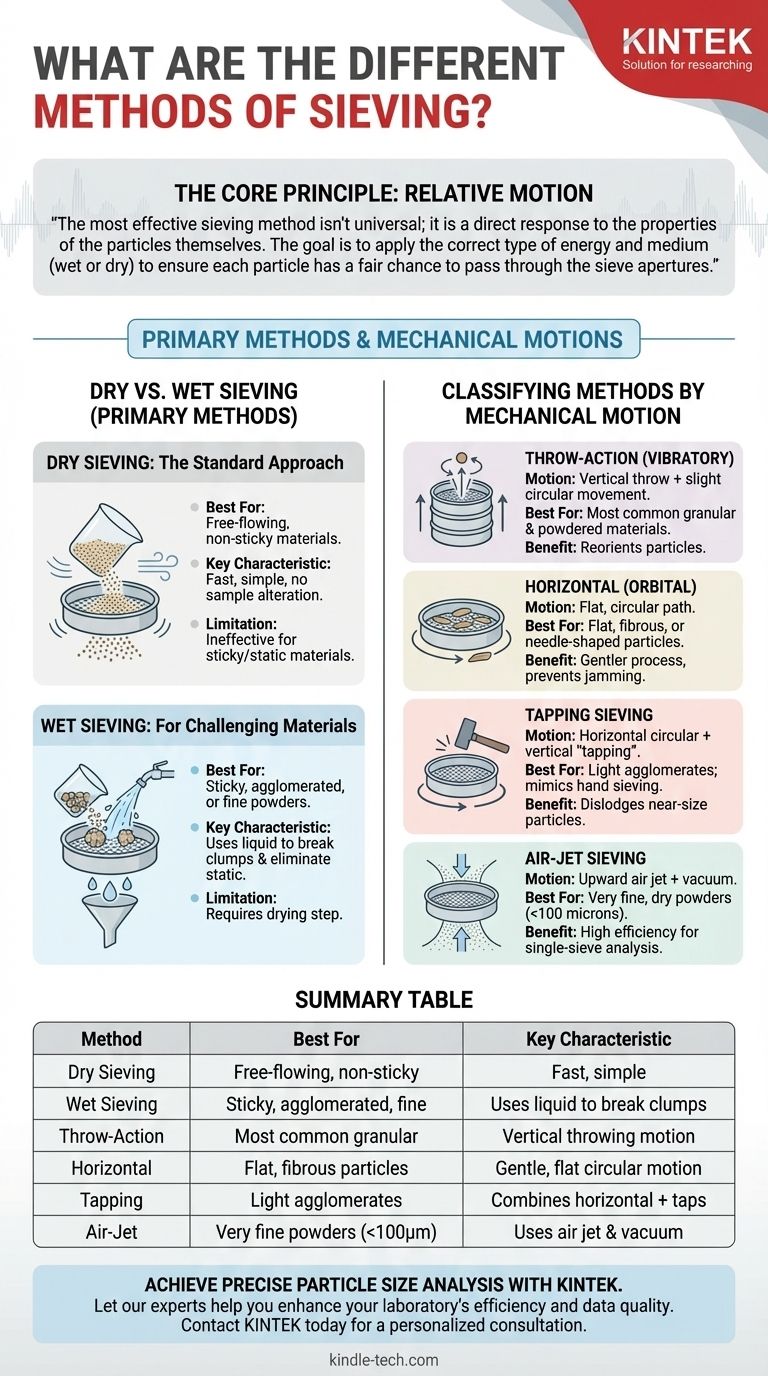
At its core, sieving separates particles using two primary methods: dry sieving and wet sieving. The choice between them, and the specific type of mechanical motion used—such as vibratory, horizontal, or tapping—is determined entirely by the physical characteristics of the material you need to analyze, including its size, shape, and tendency to clump together.
The most effective sieving method isn't universal; it is a direct response to the properties of the particles themselves. The goal is to apply the correct type of energy and medium (wet or dry) to ensure each particle has a fair chance to pass through the sieve apertures.
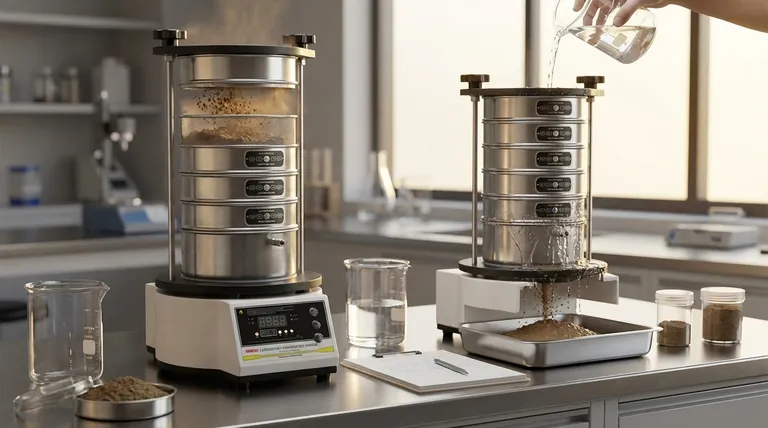

The Core Principle: Relative Motion
Sieving works by creating relative movement between a sample's particles and a sieve mesh. This motion, whether vertical or horizontal, gives particles the opportunity to either pass through the mesh openings or be retained on the surface.
However, simple agitation is often not enough. Factors like static electricity, moisture, and inter-particle cohesion can cause particles to clump together (agglomerate), preventing an accurate size separation. Advanced sieving methods are designed specifically to overcome these forces.
Classifying Methods by Mechanical Motion
The type of motion a sieve shaker imparts is critical for handling different particle shapes and sizes. Each motion profile is engineered to solve a specific separation challenge.
Throw-Action (Vibratory) Sieving
This is the most common method. A drive system creates a vertical throwing motion, often combined with a slight circular movement. This lifts the particles up and lets them fall back onto the sieve, reorienting them to present a different face to the mesh.
It is a versatile, all-purpose method suitable for most common granular and powdered materials.
Horizontal (Orbital) Sieving
In this method, the sieves move in a flat, circular path. Particles slide across the surface of the mesh, which is ideal for long, flat, fibrous, or needle-shaped particles that might otherwise get stuck in the mesh in a vertical orientation.
Horizontal sieving minimizes the impact energy, making it a gentler process for more delicate materials.
Tapping Sieving
This technique combines a horizontal, circular motion with a vertical "tapping" impulse. The tap helps to break up light agglomerates and dislodge near-size particles that may be wedged in the mesh openings.
It closely mimics the action of traditional hand sieving and is often specified in older industry standards.
Air-Jet Sieving
This highly specialized method is designed for single-sieve analysis of very fine, dry powders that are prone to static charge and agglomeration (typically below 100 microns). A rotating nozzle inside the sieve blows a jet of air upward through the mesh.
This air current fluidizes the particle bed, deagglomerating the powder and clearing the mesh. A vacuum draws the fine particles down through the sieve, providing a very efficient separation.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Dry vs. Wet Sieving
The choice between using a liquid medium or not is a fundamental decision that depends entirely on the material's tendency to stick together.
Dry Sieving: The Standard Approach
Dry sieving is the default method for the vast majority of applications. It is used for any material that is free-flowing and does not agglomerate when agitated.
Its primary advantages are speed, simplicity, and the fact that the sample is not altered by a liquid. However, it is ineffective for materials that are sticky, oily, or prone to strong electrostatic charges.
Wet Sieving: For Challenging Materials
Wet sieving is the solution for materials that cannot be separated dry. This includes suspensions, sludges, and fine powders that clump together due to moisture or static.
The sample is placed on the top sieve, and a liquid (usually water) is sprayed over it. The liquid washes the fine particles down through the sieve stack, breaking up agglomerates and eliminating static forces in the process. While highly effective, it requires the extra step of drying the separated fractions before weighing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the best method, you must first characterize your material. The strategy you choose will directly impact the accuracy and repeatability of your results.
- If your primary focus is standard granular materials: A throw-action (vibratory) shaker using dry sieving is your most reliable and efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is separating flat, elongated, or fibrous particles: Horizontal sieving provides the best chance for these particles to align with and pass through the mesh.
- If your primary focus is very fine, dry powders prone to static: Air-jet sieving offers the highest efficiency for single-sieve analysis.
- If your primary focus is accuracy with sticky, clay-like, or heavily agglomerated materials: Wet sieving is the definitive method to break clumps and ensure complete separation.
By matching the sieving method to your material's unique properties, you transform a simple separation into a precise analytical process.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Dry Sieving | Free-flowing, non-sticky materials | Fast, simple, no sample alteration |
| Wet Sieving | Sticky, agglomerated, or fine powders | Uses liquid to break clumps & eliminate static |
| Throw-Action (Vibratory) | Most common granular & powdered materials | Vertical throwing motion for particle reorientation |
| Horizontal (Orbital) | Flat, fibrous, or needle-shaped particles | Gentle, flat circular motion to prevent jamming |
| Tapping Sieving | Light agglomerates; mimics hand sieving | Combines horizontal motion with vertical taps |
| Air-Jet Sieving | Very fine, dry powders (<100 microns) | Uses air jet & vacuum for efficient separation |
Achieve precise and repeatable particle size analysis with the right sieving equipment from KINTEK.
Whether your lab works with standard granules, delicate fibers, or challenging fine powders, selecting the correct sieving method is critical for accurate results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab sieving equipment and consumables designed to meet the specific needs of your materials and applications.
Let our experts help you enhance your laboratory's efficiency and data quality. We provide the right tools and support to ensure your sieving process is optimized for success.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and discover the ideal sieving solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
People Also Ask
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- Why is powder classification using standard sieves essential for SHS reactions? Unlock Superior Nitriding Results
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance



















