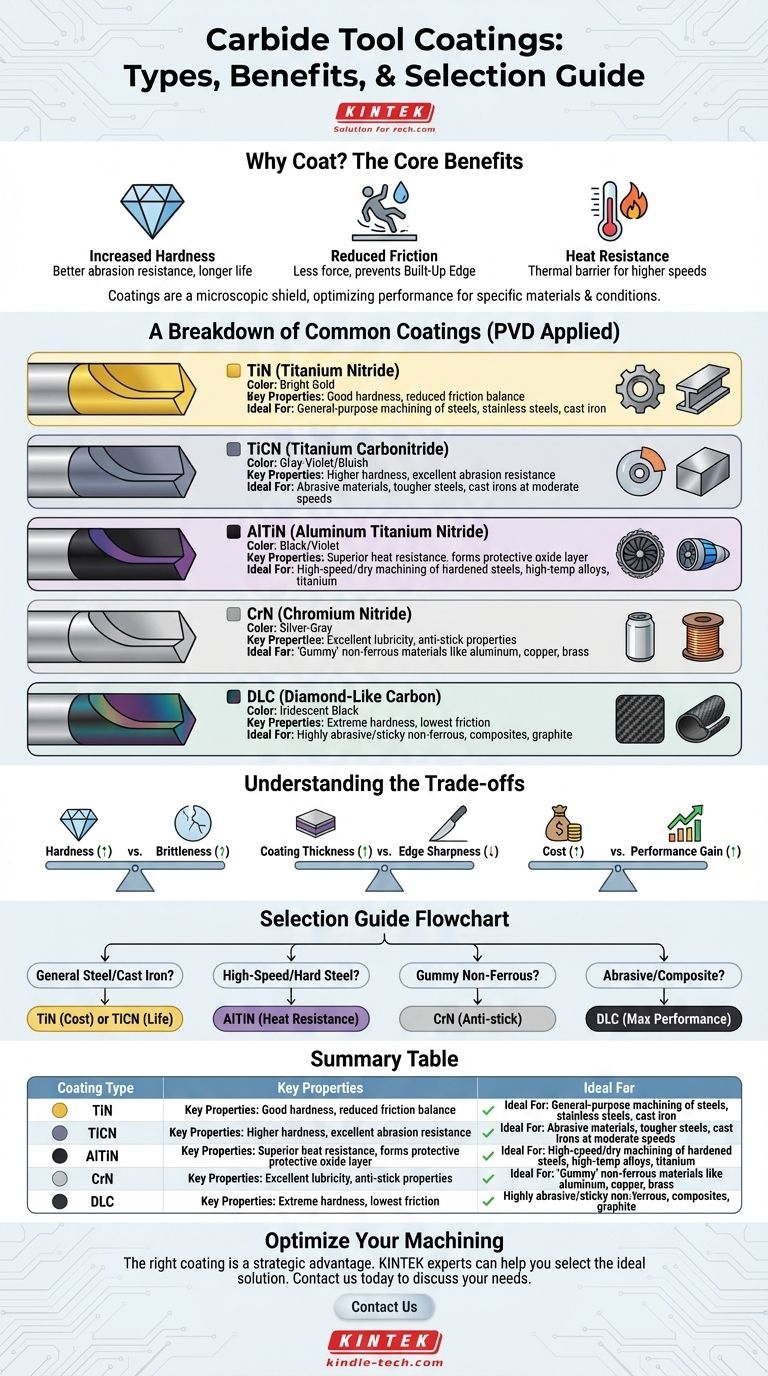
In short, the most common carbide tool coatings are families of materials based on Titanium Nitride (TiN), Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN), and Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN). Each offers a unique combination of hardness, heat resistance, and lubricity designed to optimize tool life and performance for specific materials and cutting conditions.
The core principle is not to find the single "best" coating, but to match the coating's specific properties to the material you are cutting and the demands of the machining operation. The right coating acts as a shield, fundamentally changing how the tool interacts with the workpiece.
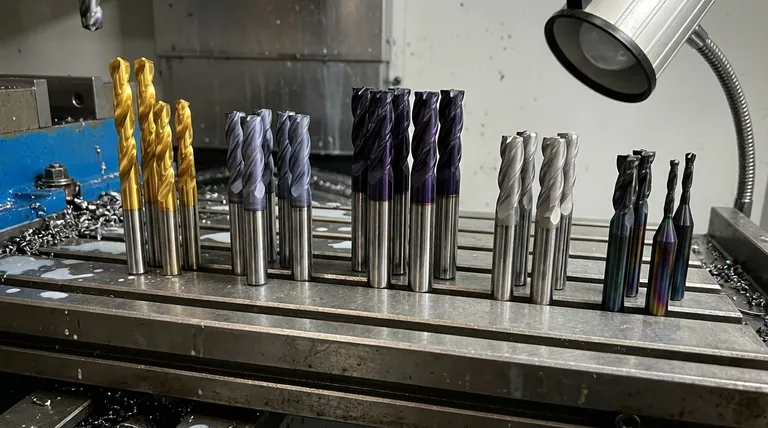

Why Coat a Carbide Tool in the First Place?
Before comparing coatings, it's essential to understand what they do. An uncoated carbide tool is already very hard, but a microscopic layer of coating adds critical performance advantages.
### The Three Core Benefits
A coating enhances a tool's performance in three primary ways:
- Increased Hardness: The coating is often significantly harder than the carbide substrate itself. This directly translates to better abrasion resistance and a longer-lasting cutting edge.
- Reduced Friction: A smoother, more lubricious surface reduces the forces required to cut and helps prevent material from sticking to the tool, an issue known as built-up edge (BUE).
- Heat Resistance: Coatings act as a thermal barrier, protecting the carbide tool from the extreme temperatures generated at the cutting edge. Some coatings even use that heat to their advantage by forming protective oxide layers.
A Breakdown of Common Tool Coatings
While there are many proprietary variations, most coatings fall into a few key families. They are typically applied via a process called Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), which bonds a layer just a few microns thick to the tool's surface.
### TiN (Titanium Nitride)
TiN is the classic, general-purpose coating, easily identified by its bright gold color. It was one of the first PVD coatings to gain widespread use and remains a reliable, cost-effective choice.
It offers a good balance of increased hardness and reduced friction, making it a significant upgrade over an uncoated tool for general machining of steels, stainless steels, and cast iron.
### TiCN (Titanium Carbonitride)
Think of TiCN as a step up from TiN in terms of hardness. The addition of carbon into the material matrix makes it noticeably more resistant to abrasive wear.
This extra hardness makes TiCN (often gray-violet or bluish in color) ideal for cutting abrasive materials or when you need longer tool life in tougher steels and cast irons, particularly at moderate cutting speeds.
### AlTiN / TiAlN (Aluminum Titanium Nitride)
This family of coatings represents a major leap in thermal performance and is a top choice for high-performance machining. The key ingredient is aluminum, which forms a microscopic layer of aluminum oxide at the cutting edge as temperatures rise.
This self-forming ceramic layer is incredibly hard and acts as an excellent thermal barrier, allowing AlTiN (black/violet) to excel in high-speed and dry machining of hardened steels, high-temperature alloys, and titanium. The higher the aluminum content (as in AlTiN vs. TiAlN), the better the high-temperature performance.
### CrN (Chromium Nitride)
CrN (silver-gray) is not as hard as the titanium-based coatings, but its primary advantage is excellent lubricity and anti-stick properties.
This makes it the preferred choice for machining "gummy" materials that tend to cause built-up edge, most notably non-ferrous materials like aluminum, copper, and brass.
### DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon)
DLC coatings are a family of advanced carbon-based films that offer extreme hardness combined with an exceptionally low coefficient of friction—even lower than CrN.
This unmatched lubricity makes DLC coatings (typically iridescent black) the ultimate solution for machining highly abrasive and sticky non-ferrous materials, such as high-silicon aluminum, graphite, and composites.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a coating involves balancing competing factors. There is no single coating that is superior in all situations.
### Hardness vs. Brittleness
Generally, as a coating's hardness increases, so does its brittleness. An extremely hard coating like TiCN is excellent for a smooth, continuous cut but may be more prone to chipping than a tougher, more ductile coating in operations with heavy interruptions.
### Coating Thickness vs. Edge Sharpness
Coatings add thickness, even if only by a few microns. For materials that require an extremely sharp cutting edge, like aluminum, a thicker coating can slightly round the edge, negatively impacting performance. This is why thin DLC or CrN coatings are often preferred for these applications.
### Cost vs. Performance Gain
Advanced coatings like AlTiN and DLC cost more than standard TiN. You must weigh whether the increased tool life and productivity justify the higher initial investment. For a one-off job in mild steel, TiN is sufficient. For a high-volume production run in a difficult material, AlTiN will almost certainly pay for itself.
Selecting the Right Coating for Your Application
Use this as a starting point for matching the coating to your job.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose machining of steels and cast iron: Start with TiN for cost-effectiveness or upgrade to TiCN for longer tool life in more abrasive conditions.
- If your primary focus is high-speed or dry machining of hard steels and superalloys: AlTiN is the clear choice due to its superior heat resistance.
- If your primary focus is machining aluminum, copper, or other non-ferrous materials: CrN or DLC are your best options to prevent built-up edge and achieve a superior finish.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance in non-ferrous and composite materials: DLC provides the ultimate combination of hardness and lubricity.
Ultimately, understanding these coating properties empowers you to select a tool not just based on its shape, but on its engineered surface.
Summary Table:
| Coating Type | Key Properties | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| TiN (Titanium Nitride) | Good hardness, reduced friction, cost-effective | General-purpose machining of steels, stainless steels, cast iron |
| TiCN (Titanium Carbonitride) | Higher hardness than TiN, excellent abrasion resistance | Machining abrasive materials, tougher steels, cast irons at moderate speeds |
| AlTiN (Aluminum Titanium Nitride) | Superior heat resistance, forms protective oxide layer | High-speed/dry machining of hardened steels, high-temperature alloys, titanium |
| CrN (Chromium Nitride) | Excellent lubricity, anti-stick properties | Machining 'gummy' non-ferrous materials like aluminum, copper, brass |
| DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) | Extreme hardness, lowest friction, high lubricity | Machining highly abrasive/sticky non-ferrous materials, composites, graphite |
Ready to optimize your machining process with the perfect tool coating? The right coating isn't just an upgrade—it's a strategic advantage that dramatically increases tool life, improves finish quality, and boosts productivity. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including precision tools engineered for your specific challenges. Our experts can help you select the ideal coating for your materials and operations. Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss your needs and discover how KINTEK solutions can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
People Also Ask
- How does a high-precision carbon heating block contribute to the formation of hierarchical structures in an AACVD reactor?
- What is the difference between CVD and sputter coating? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What type of power source is used in RF sputtering? High-Frequency AC Solutions for Insulating Materials
- What is the difference between PVD and CVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is physical vapor deposition for jewelry? A Durable, High-Tech Finish for Modern Wear
- What is deposition in nanotechnology? Build High-Performance Materials Atom by Atom
- What is the process of film deposition? A Step-by-Step Guide to Thin-Film Creation
- What are the applications of Lpcvd? Key Uses in Semiconductor & MEMS Manufacturing



















