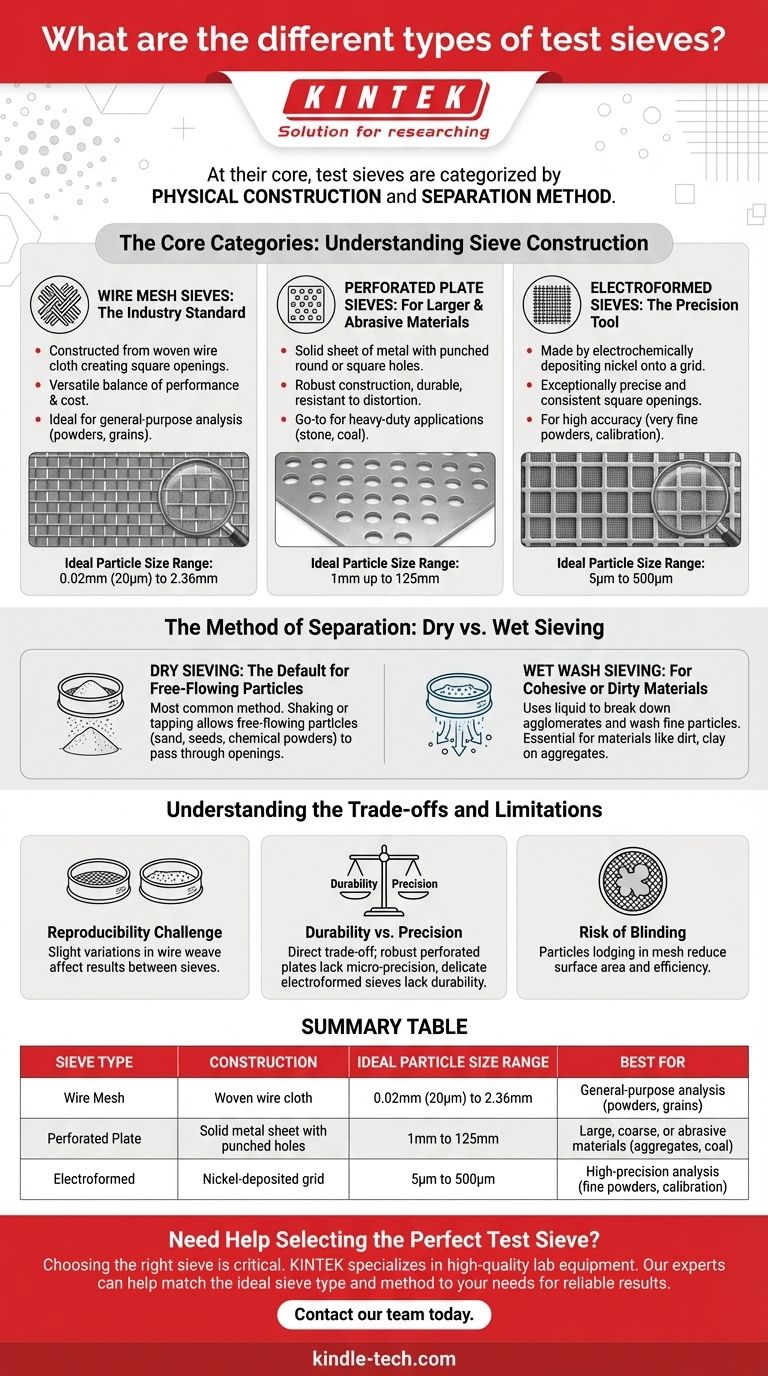
At their core, test sieves are categorized in two distinct ways: by their physical construction and by the method used for separation. The construction—whether wire mesh, perforated plate, or electroformed—defines the sieve's precision and application, while the method—dry or wet sieving—describes the process used to separate the particles.
Choosing the right test sieve goes beyond simply matching the opening size to your particles. The fundamental decision lies in matching the sieve's physical construction to the material you are analyzing and the level of precision your work demands.
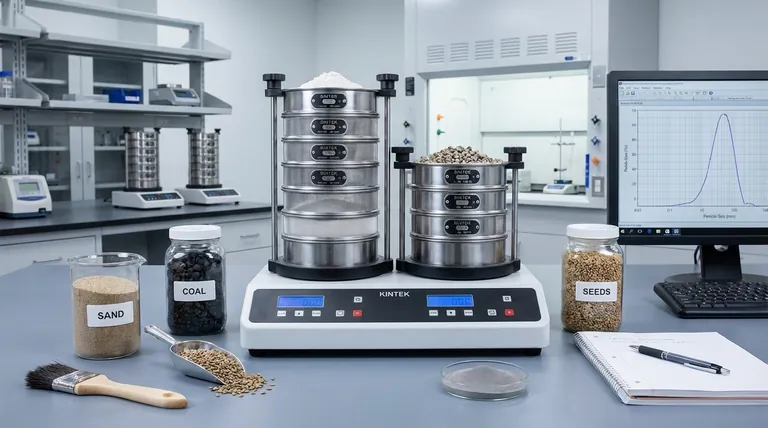

The Core Categories: Understanding Sieve Construction
The most fundamental way to classify a test sieve is by how its separation medium is manufactured. This directly impacts its accuracy, durability, and ideal use case.
Wire Mesh Sieves: The Industry Standard
Wire mesh sieves are the most common type, constructed from a woven wire cloth. The wires are interlaced to create square openings of a specific size.
They offer a versatile balance of performance and cost, making them the workhorse for a huge range of industries, from agriculture to pharmaceuticals.
These sieves are ideal for general-purpose analysis of powders, grains, and other granular materials, typically covering a size range from 0.02mm (20 microns) to 2.36mm.
Perforated Plate Sieves: For Larger & Abrasive Materials
Instead of woven wire, these sieves use a solid sheet of metal (usually steel) with round or square holes punched into it.
This robust construction makes them far more durable and resistant to distortion than wire mesh. They are the go-to choice for heavy-duty applications.
Perforated plate is used for sizing large, coarse, or abrasive materials like stone, coal, and other aggregates. Their measurement range is much larger, typically from 1mm up to 125mm.
Electroformed Sieves: The Precision Tool
Electroformed sieves represent the pinnacle of accuracy. They are made by electrochemically depositing nickel onto a flat, photosensitized grid pattern, creating exceptionally precise and consistent square openings.
Due to their high precision and cost, they are used for applications demanding the highest degree of accuracy, such as analyzing very fine powders or for calibrating other sieves.
Their strength is in the micro-particle range, with standard sizes from a very fine 5µm (microns) up to 500µm.
The Method of Separation: Dry vs. Wet Sieving
Once you have a sieve, the method you use to perform the test is the second key classification. This is determined by the nature of your sample material.
Dry Sieving: The Default for Free-Flowing Particles
This is the most common method, involving shaking or tapping the sieve stack to allow particles to pass through the openings under the force of gravity.
Dry sieving is effective for any material that is free-flowing and does not clump or stick together, such as dry sand, seeds, or chemical powders.
Wet Wash Sieving: For Cohesive or Dirty Materials
Wet wash sieving is used when water or another liquid is required to help separate the particles. The liquid helps break down agglomerates and wash fine particles through the mesh.
This technique is essential in industries like civil engineering, where it's used to wash away dirt and clay from rock aggregates to get an accurate measurement of the rock itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No single sieve type is perfect for every task. Understanding their inherent limitations is critical for producing reliable data.
The Challenge of Reproducibility
With woven wire mesh sieves, slight variations in the weave are unavoidable during manufacturing. This means two sieves with the same nominal opening size can produce slightly different results.
This is a well-understood factor in particle size analysis and must be considered when comparing data from different labs or different sieve sets.
Durability vs. Precision
There is a direct trade-off between how durable a sieve is and how precise it can be. Perforated plate sieves can withstand heavy, abrasive materials but cannot be made with micro-sized openings.
Conversely, highly accurate electroformed sieves are delicate and can be easily damaged by abrasive materials or improper handling.
The Risk of Blinding and Clogging
During testing, particles that are very close to the size of the sieve openings can become lodged in the mesh. This phenomenon, known as blinding, reduces the available surface area and impairs the efficiency of the separation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice depends entirely on your material and your analytical goals. Use these points as a guide.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose analysis of powders or grains: Use standard wire mesh sieves, as they offer the best balance of cost and broad applicability.
- If your primary focus is sizing large, coarse, or abrasive materials like aggregates: Opt for the superior durability of perforated plate sieves to ensure a long service life.
- If your primary focus is high-precision analysis of very fine particles or instrument calibration: Invest in electroformed sieves for their unmatched accuracy and consistency.
- If your material contains fine particles that adhere to larger ones (like clay on gravel): You must employ a wet wash sieving method to ensure an accurate and complete separation.
By aligning the sieve's construction and testing method with your specific needs, you ensure the accuracy and reliability of your particle size analysis.
Summary Table:
| Sieve Type | Construction | Ideal Particle Size Range | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wire Mesh | Woven wire cloth | 0.02mm (20µm) to 2.36mm | General-purpose analysis of powders, grains, and granular materials |
| Perforated Plate | Solid metal sheet with punched holes | 1mm to 125mm | Large, coarse, or abrasive materials like aggregates, coal, and stone |
| Electroformed | Nickel-deposited grid | 5µm to 500µm | High-precision analysis of fine powders and sieve calibration |
Need Help Selecting the Perfect Test Sieve?
Choosing the right sieve is critical for accurate particle size analysis. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of test sieves for every application. Our experts can help you match the ideal sieve type and method to your specific material and precision requirements, ensuring reliable and reproducible results for your laboratory.
Contact our team today to discuss your needs and enhance your analytical processes with the right equipment from KINTEK!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Precision Wire Saw Laboratory Cutting Machine with 800mm x 800mm Workbench for Diamond Single Wire Circular Small Cutting
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of sieving machines? Choose the Right Motion for Your Material
- What are the applications of sieving machine? From Mining to Pharmaceuticals
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- What are the components of a sieving machine? Unlock the Anatomy of Precision Particle Separation
- What is powder sieving? A Guide to Accurate Particle Size Separation



















