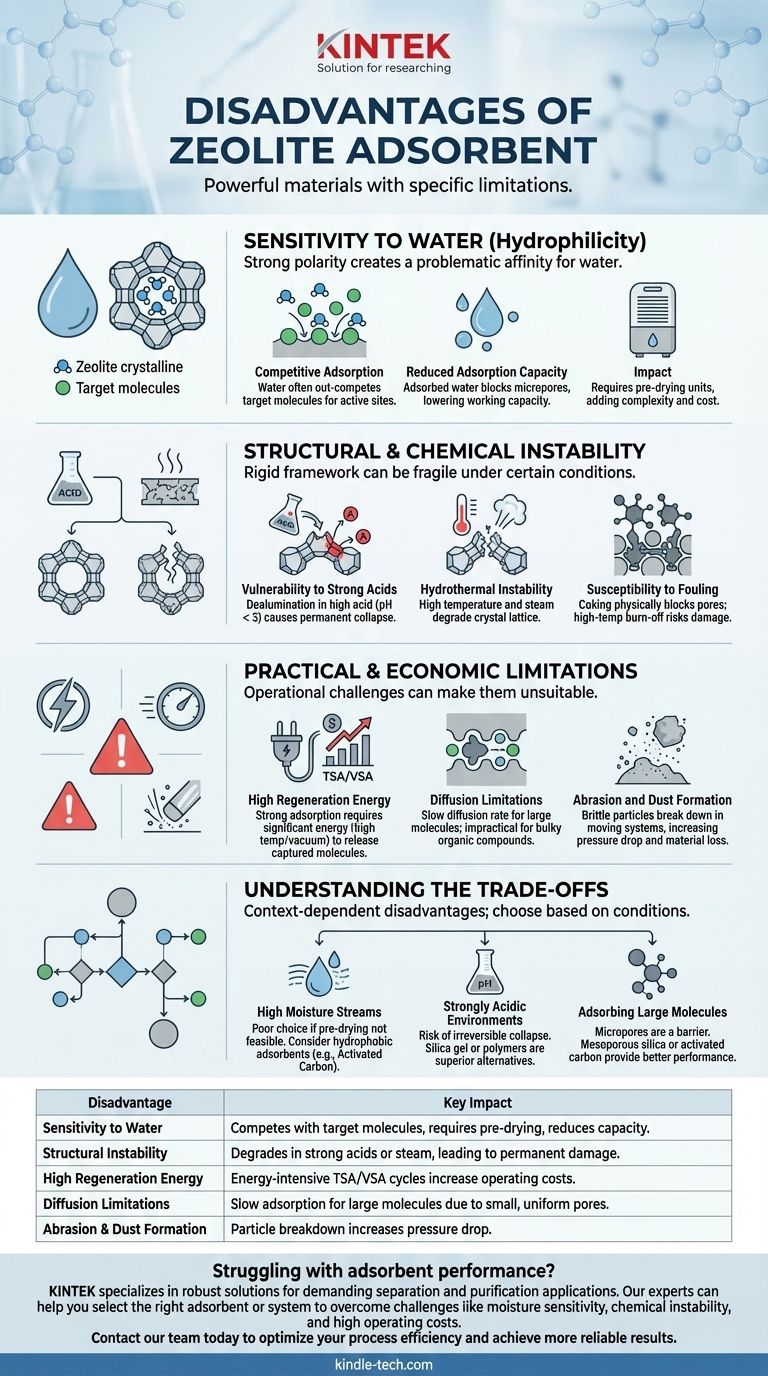
While incredibly powerful, the primary disadvantages of zeolite adsorbents are their strong sensitivity to moisture, their structural vulnerability in acidic or high-temperature steam environments, and the high energy cost required for their regeneration. These limitations stem directly from their rigid, crystalline structure and the chemical properties that also make them so effective.
The core challenge with zeolites is that their greatest strengths—uniform micropores and strong surface polarity—are also the source of their most significant weaknesses. They are specialized, high-performance materials that fail when used outside of their ideal operating conditions, particularly in the presence of water or harsh chemicals.

Sensitivity to Water (Hydrophilicity)
Zeolites are aluminosilicates, and the aluminum sites create a strong polarity across the structure. This gives them a powerful, often problematic, affinity for water.
Competitive Adsorption
Water is a highly polar molecule that is readily and strongly adsorbed by most common zeolites (e.g., Zeolite 3A, 4A, 5A, 13X). If water vapor is present in a gas or liquid stream, it will often out-compete the target molecule for a spot on the zeolite's active sites.
This forces the implementation of an upstream drying unit or "guard bed" to remove moisture, adding complexity and cost to the overall process.
Reduced Adsorption Capacity
Even in small amounts, adsorbed water can block access to the zeolite's micropores. This effectively reduces the available surface area and lowers the adsorbent's working capacity for the molecule you actually want to capture.
Structural and Chemical Instability
The rigid, crystalline framework of a zeolite is precise but can be fragile under certain chemical conditions.
Vulnerability to Strong Acids
In highly acidic environments (typically pH < 3), the acid can attack and leach aluminum atoms directly from the zeolite framework. This process, known as dealumination, causes the crystalline structure to collapse, permanently destroying the adsorbent.
Hydrothermal Instability
The combination of high temperatures and steam is particularly damaging. Under these hydrothermal conditions, the zeolite structure can degrade, again through the loss of aluminum atoms and a breakdown of the crystal lattice. This is a critical concern during steam-based regeneration cycles.
Susceptibility to Fouling
In applications like hydrocarbon processing, heavy organic molecules or polymers can deposit within the pores, a process known as coking. This physically blocks the pores and deactivates the adsorbent. Removing this coke often requires high-temperature burn-offs, which can risk hydrothermal damage to the zeolite itself.
Practical and Economic Limitations
Beyond chemical vulnerabilities, zeolites present operational and cost challenges that can make them unsuitable for certain applications.
High Regeneration Energy
The same strong forces that make zeolites excellent adsorbents also mean that it takes a significant amount of energy to release the captured molecules. Regeneration typically requires either high temperatures (Temperature Swing Adsorption, TSA) or deep vacuums (Vacuum Swing Adsorption, VSA), both of which are energy-intensive and drive up operating costs.
Diffusion Limitations
Zeolites have extremely small and uniform pores (micropores). While this is excellent for size-selective separations of small molecules, it severely slows down the rate at which larger molecules can diffuse into the adsorbent. This can make them impractical for adsorbing bulky organic compounds.
Abrasion and Dust Formation
As a crystalline material, zeolites can be brittle. In moving or fluidized bed systems, the particles can rub against each other and the vessel walls, breaking down and creating fine dust. This dust can increase pressure drop and lead to material loss.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When to Reconsider Zeolites
The disadvantages of zeolites are not absolute; they are context-dependent. They are the wrong choice when the process conditions directly conflict with their inherent properties.
For Streams with High Moisture Content
If your process stream is saturated with water and pre-drying is not feasible, a zeolite is a poor choice. A more hydrophobic adsorbent like activated carbon may be more effective, even if its capacity for the target molecule is lower in dry conditions.
For Strongly Acidic Environments
If the fluid being treated is highly acidic, the risk of irreversible dealumination and structural collapse is too high. Materials like silica gel or certain polymers, which are stable at low pH, are superior alternatives.
For Adsorbing Large Molecules
If you need to remove large organic molecules (e.g., color bodies from a liquid), the micropores of a zeolite will present a significant barrier. A material with a wider pore size distribution, such as activated carbon or a mesoporous silica, will provide much better performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct adsorbent requires matching the material's properties to your specific process conditions and goals.
- If your primary focus is high-purity separation of small molecules in a dry stream: Zeolites are often the best possible choice due to their exceptional selectivity.
- If your process stream is wet or contains polar impurities: You must either budget for a pre-drying unit or select a more hydrophobic adsorbent.
- If you are operating under harsh pH conditions or with high-temperature steam: Prioritize structurally robust materials and carefully evaluate the chemical compatibility of any zeolite.
- If minimizing operational energy cost is your main driver: Carefully model the regeneration energy, as it can make zeolites economically unviable compared to weaker adsorbents that regenerate under milder conditions.
Ultimately, understanding these limitations is the key to successfully harnessing the unique and powerful capabilities of zeolite adsorbents.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity to Water | Competes with target molecules, requires pre-drying, reduces capacity |
| Structural Instability | Degrades in strong acids or steam, leading to permanent damage |
| High Regeneration Energy | Energy-intensive TSA/VSA cycles increase operating costs |
| Diffusion Limitations | Slow adsorption for large molecules due to small, uniform pores |
| Abrasion & Dust Formation | Particle breakdown in fluidized beds increases pressure drop |
Struggling with adsorbent performance in your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing robust solutions for demanding separation and purification applications. Our experts can help you select the right adsorbent or system to overcome challenges like moisture sensitivity, chemical instability, and high operating costs. Contact our team today to optimize your process efficiency and achieve more reliable results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Single Double Sided Coated K9 Quartz Sheet
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Conductive Carbon Cloth Carbon Paper Carbon Felt for Electrodes and Batteries
People Also Ask
- What is the main difference between soldering and brazing? Choose the Right Metal Joining Method
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of brazing? A Guide to Strong, Clean Metal Joining
- What are the classification of ceramic materials? A Guide to Oxides, Non-Oxides, and Composites
- What are the disadvantages of brazing? Understanding the key limitations and trade-offs.
- What can carbon nanotubes be used for? Unlock Superior Performance in Batteries & Materials



















