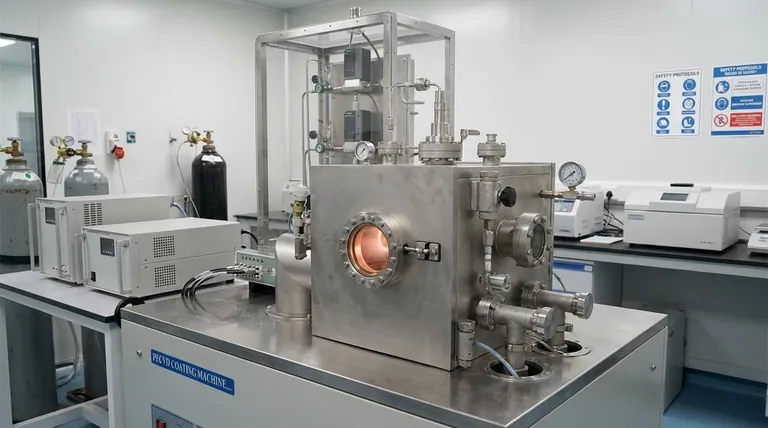
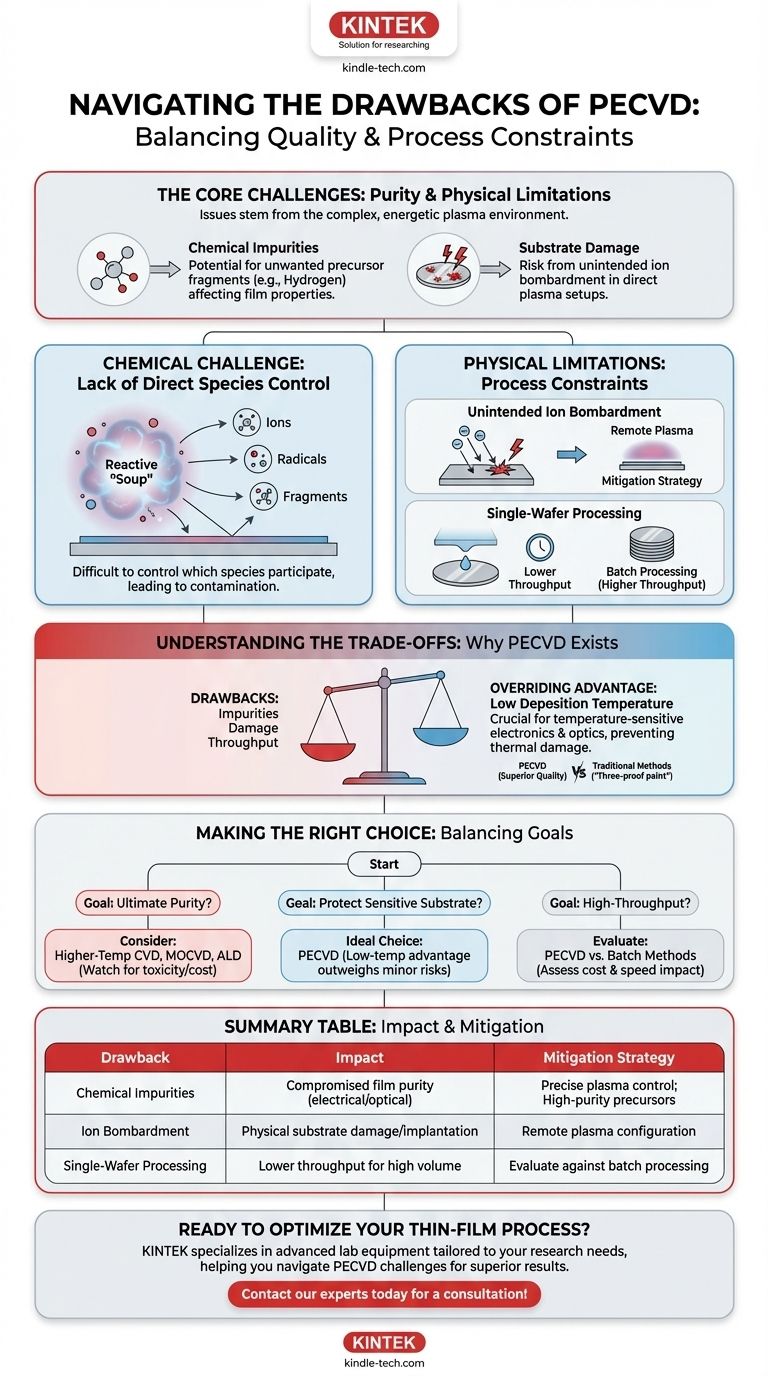
The primary drawbacks of PECVD are the potential for chemical impurities in the final film and the risk of substrate damage from ion bombardment. These issues stem directly from the use of a plasma, which, while enabling low-temperature deposition, creates a complex and highly energetic chemical environment that can be difficult to control precisely.
PECVD offers the significant advantage of depositing high-quality films at low temperatures, but this benefit comes with inherent trade-offs: a higher risk of chemical contamination and process-induced physical limitations compared to some higher-temperature or non-plasma methods.

The Core Chemical Challenge: Purity Control
The plasma at the heart of the PECVD process is a double-edged sword. While it provides the energy for reactions to occur at low temperatures, it also creates a complex mix of reactive species that can compromise the final film.
Lack of Direct Species Control
In a conventional PECVD reactor, the plasma creates a reactive "soup" of ions, radicals, and precursor fragments. It is difficult to precisely control which of these species are created and which ones ultimately participate in film growth on the substrate surface.
Contamination from Precursor Fragments
A direct consequence of this limited control is the incorporation of unwanted precursor fragments into the growing film. For example, if hydrogen-containing precursors are used, residual hydrogen can be embedded in the film, affecting its stoichiometric purity and altering its electrical or optical properties.
The Physical and Process Limitations
Beyond chemical purity, the physical nature of the plasma process introduces its own set of constraints on device fabrication and manufacturing throughput.
Unintended Ion Bombardment
In a standard "direct" plasma setup, the substrate is immersed in the plasma. Energetic ions can accelerate toward the substrate and strike its surface, causing physical damage or unintended ion implantation. This can be detrimental to sensitive electronic devices. This specific drawback can, however, be mitigated by using a remote plasma configuration, where the plasma is generated away from the substrate.
Single-Sided, Single-Wafer Processing
PECVD is typically a single-wafer process that coats only one side of the substrate at a time. While this allows for excellent uniformity on that single surface, it can be a significant limitation for high-volume manufacturing, where batch processing methods might offer higher throughput and lower cost-per-unit.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The drawbacks of PECVD do not exist in a vacuum. They are accepted because the technology solves critical problems that other methods cannot, particularly for temperature-sensitive materials.
The Overriding Low-Temperature Advantage
The single most important benefit of PECVD is its low deposition temperature. This prevents thermal damage to underlying components, reduces stress caused by thermal expansion mismatch, and minimizes diffusion between layers, making it indispensable for many modern electronics and optics applications.
Superior Film Quality vs. Traditional Methods
When compared to traditional methods like applying "three-proof paint," PECVD offers vastly superior results. It produces thin, uniform, and highly adherent films that do not interfere with heat dissipation or electrical performance, overcoming the major limitations of older coating technologies.
A Practical Choice Among Advanced Methods
While other advanced techniques like Metal-Organic CVD (MOCVD) may offer higher purity, they often come with their own significant drawbacks. MOCVD typically uses sources that are expensive, highly toxic, or flammable, presenting major safety and environmental challenges. In this context, the drawbacks of PECVD are often seen as the more manageable engineering compromise.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right deposition method requires balancing the need for film quality against process constraints and substrate limitations.
- If your primary focus is ultimate chemical purity and crystalline perfection: The risk of contamination and ion damage in PECVD may be a critical flaw, pushing you toward higher-temperature CVD, MOCVD, or ALD.
- If your primary focus is depositing a high-quality protective film on a temperature-sensitive product: PECVD is often the ideal choice, as its low-temperature advantage far outweighs the minor risk of impurities.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput manufacturing: The single-wafer nature of PECVD may be a bottleneck, and you must evaluate if its benefits justify the potential impact on production speed and cost.
Ultimately, understanding these limitations empowers you to select PECVD for the applications where its unique strengths provide the greatest value.
Summary Table:
| Drawback | Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Impurities | Compromised film purity and properties (e.g., electrical, optical) | Precise control of plasma parameters; use of high-purity precursors |
| Ion Bombardment | Physical substrate damage or unintended implantation | Use of remote plasma configuration |
| Single-Wafer Processing | Lower throughput for high-volume manufacturing | Evaluate against batch processing methods for cost-effectiveness |
Ready to optimize your thin-film deposition process?
While PECVD has its trade-offs, it remains a critical technology for low-temperature applications. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific research and production needs. Whether you're working on sensitive electronics, optics, or other advanced materials, our expertise can help you navigate these challenges and achieve superior results.
Let's discuss how we can support your laboratory's goals. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application


















