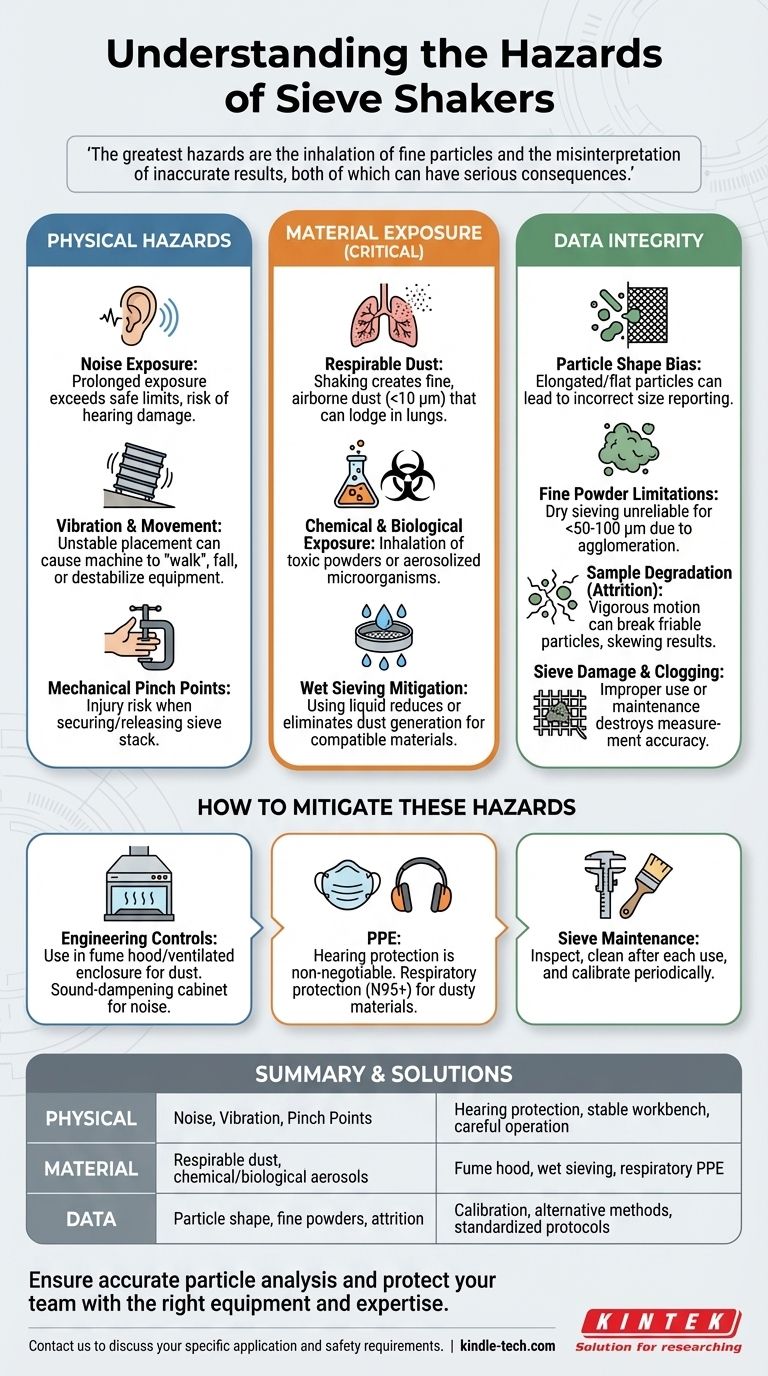
The primary hazards of sieve shakers fall into three distinct categories: physical risks from machine operation, exposure risks from the material being tested, and data integrity risks from the method's inherent limitations. While the machine's operation presents straightforward hazards like noise and vibration, the most significant dangers often stem from the generation of hazardous dust and the potential for drawing incorrect conclusions from flawed data.
While a sieve shaker is a mechanically simple device, its true risks are not in its complexity but in its interaction with the material being analyzed. The greatest hazards are the inhalation of fine particles and the misinterpretation of inaccurate results, both of which can have serious consequences.

Understanding the Primary Physical Hazards
A sieve shaker is a robust piece of equipment, and its mechanical action creates a predictable set of physical hazards that require management in any laboratory environment.
Noise Exposure
The aggressive shaking motion, combined with the rattling of particles and sieves, generates significant noise. Prolonged exposure can exceed safe occupational limits, leading to hearing damage. This is a consistent and often underestimated hazard.
Vibration and Movement
Sieve shakers produce strong vibrations by design. If not placed on a solid, level, and sufficiently massive workbench, the machine can "walk" or move during operation, posing a risk of falling or creating instability for nearby equipment.
Mechanical Pinch Points
The clamping systems used to secure the stack of sieves are a potential pinch point. While not a high-speed mechanism, an operator's fingers can be caught and injured when securing or releasing the sieve stack.
The Critical Hazard: Material Exposure
The most serious health risk associated with sieve shakers is often not the machine itself, but the sample it aerosolizes. The primary function of the machine is to agitate particles, which inevitably makes them airborne.
Generation of Respirable Dust
The shaking action is highly effective at creating fine, airborne dust. When working with materials like aggregates, metal powders, soil, or certain chemicals, this dust can be respirable, meaning the particles are small enough (<10 µm) to bypass the body's natural defenses and lodge deep within the lungs.
Chemical and Biological Exposure
The hazard is defined by the material. Sieving fine chemical powders can lead to toxic exposure through inhalation. Similarly, analyzing soil samples could aerosolize harmful bacteria, fungi, or other microorganisms. The material's Safety Data Sheet (SDS) is a critical document for assessing this risk.
The Role of Wet Sieving
Some sieve shakers support wet sieving, which uses a liquid (usually water) to help separate particles. This method can dramatically reduce or eliminate dust generation, making it a key strategy for mitigating inhalation hazards when the sample material is compatible.
A Different Kind of Hazard: Data Integrity
Beyond physical safety, a sieve shaker presents a significant hazard to the quality and reliability of your results. Using the method outside its limitations can lead to incorrect conclusions, which can be a costly or dangerous error in a quality control or research setting.
Inaccurate Results from Particle Shape
Sieve analysis fundamentally assumes all particles are perfect spheres. This is rarely true. Elongated or flat particles can pass through a sieve mesh end-on, reporting a smaller size than their true volume, or lie flat and be retained, reporting a larger size. This can severely skew the particle size distribution.
Limitations with Fine Powders
Dry sieving is generally unreliable for particles finer than 50-100 µm. At this scale, electrostatic forces and particle cohesion cause powders to clump together (agglomerate), preventing them from passing through the sieve mesh. This leads to inaccurate results that overstate the average particle size.
Sample Degradation (Attrition)
The very action that makes the shaker work can also damage the sample. The vigorous motion can cause friable or brittle particles to break apart, a process called attrition. This creates more fine particles than were present in the original sample, biasing the results toward a smaller particle size.
Sieve Damage and Clogging
Improper use or poor maintenance can lead to sieve clogging or distortion. A clogged mesh prevents particles from passing through, while a stretched or damaged mesh allows oversized particles to pass. Both scenarios destroy the accuracy of the measurement.
How to Mitigate These Hazards
A proactive approach is essential to using a sieve shaker safely and effectively. Simply running the machine is not enough; the entire process must be managed.
Engineering and Administrative Controls
The most effective way to control dust is to contain it at the source. Using the sieve shaker inside a fume hood or a ventilated enclosure is the best practice. For noise, place the machine in a dedicated room or sound-dampening cabinet.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Operators must use appropriate PPE. Hearing protection is non-negotiable. For dusty materials, respiratory protection (e.g., an N95 mask or a higher-rated respirator) is critical. Safety glasses and lab coats should be standard.
Sieve Maintenance and Calibration
Sieves are precision instruments. They must be inspected for damage, cleaned thoroughly after each use to prevent clogging, and periodically checked against calibration standards to ensure the mesh apertures are accurate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to managing sieve shaker hazards depends directly on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Prioritize engineering controls like ventilation and enforce strict PPE usage, especially respiratory and hearing protection.
- If your primary focus is data accuracy for coarse materials (>100µm): Focus on regular sieve calibration, inspection for damage, and standardized shaking times and amplitudes to ensure reproducibility.
- If your primary focus is analyzing fine powders (<50µm): Recognize the inherent limitations of mechanical sieving and consider alternative methods like air jet sieving or laser diffraction for more reliable results.
By understanding and mitigating these operational, material, and data-related hazards, you can leverage the sieve shaker as a powerful and reliable analytical tool.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Category | Specific Risks | Key Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Hazards | Noise exposure, vibration, pinch points | Hearing protection, stable workbench, careful operation |
| Material Exposure | Respirable dust, chemical/biological aerosols | Fume hood, wet sieving, respiratory PPE (N95+) |
| Data Integrity | Particle shape bias, fine powder limitations, sample attrition | Sieve calibration, alternative methods for fines, standardized protocols |
Ensure accurate particle analysis and protect your team with the right equipment and expertise. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including sieve shakers and safety accessories tailored for laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the ideal sieving solution and implement best practices for hazard mitigation. Contact us today to discuss your specific application and safety requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What is the function of sieving equipment in CuAlMn alloys? Master Pore Size Precision
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis



















