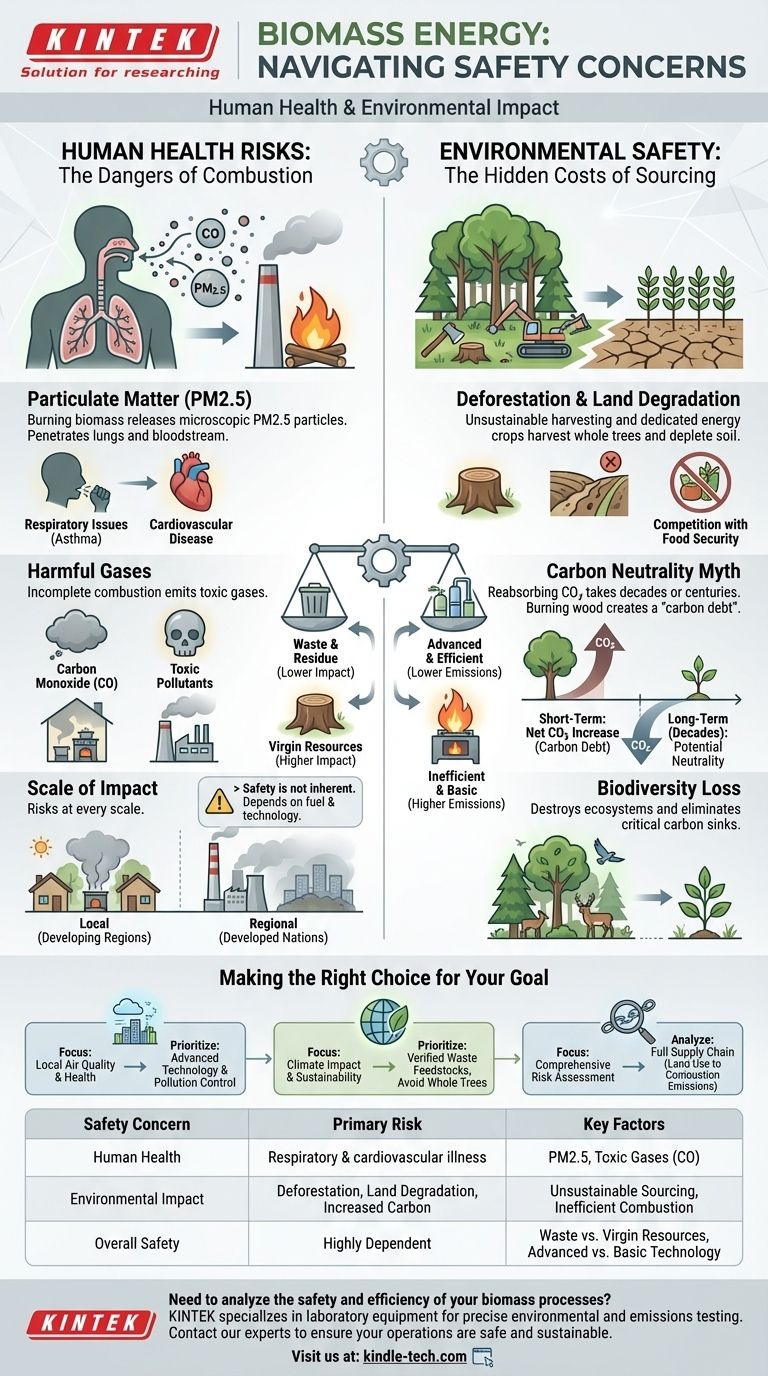
At its core, the primary safety concerns of biomass energy are twofold. First, the combustion process releases harmful air pollutants, including particulate matter and toxic gases, which pose direct risks to human health. Second, the sourcing of biomass fuel can lead to significant environmental degradation, including deforestation and land degradation, undermining the long-term ecological safety and sustainability of the practice.
While often promoted as a "clean" or "carbon-neutral" alternative, the safety of biomass energy is not inherent. It is critically dependent on the fuel source and the combustion technology, with poor practices posing health and environmental risks comparable to those of fossil fuels.

Human Health Risks: The Dangers of Combustion
The most immediate safety concern with biomass energy stems from the simple act of burning organic matter. This process is often incomplete and inefficient, releasing a cocktail of substances detrimental to human health.
The Problem with Particulate Matter
Burning biomass, especially wood, releases fine particulate matter (PM2.5). These microscopic particles can penetrate deep into the lungs and enter the bloodstream, causing or worsening respiratory conditions like asthma and contributing to cardiovascular disease.
The Release of Harmful Gases
In addition to visible smoke, biomass combustion emits a range of harmful gases. The smoke from burning biomass, particularly in inefficient open fires or when using moist wood, is a major source of indoor and outdoor air pollution that can cause serious health issues for nearby communities. Incomplete combustion also produces carbon monoxide (CO), a highly toxic gas.
The Scale of the Impact
These health risks exist at every scale. In developing regions, inefficient cookstoves using wood or dung are a leading cause of premature death. In developed nations, even large-scale biomass power plants can degrade regional air quality if they lack sufficient pollution control technology.
Environmental Safety: The Hidden Costs of Sourcing
Beyond the smokestack, the methods used to acquire biomass fuel present a separate and equally serious set of safety and sustainability concerns. The demand for fuel can easily outstrip the environment's ability to regenerate.
The Risk of Deforestation
When biomass demand leads to the harvesting of whole trees at an unsustainable rate, it results in deforestation. This not only destroys ecosystems and reduces biodiversity but also eliminates a critical natural carbon sink, paradoxically worsening climate change.
Land Degradation and Competition
Using large plots of land to grow dedicated "energy crops" for biomass can have severe consequences. It can lead to monoculture farming, which depletes soil nutrients, increases erosion, and makes the land unsuitable for other uses, including growing food. This creates a direct conflict between energy security and food security.
The Carbon Neutrality Myth
The claim that biomass is "carbon neutral" is a dangerous oversimplification. While a new tree can eventually reabsorb the CO2 released by burning one, this process can take decades or even centuries. In the short-to-medium term—the critical window for climate action—burning wood creates a "carbon debt" and contributes a net increase in atmospheric CO2.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Not All Biomass is Equal
The safety profile of biomass is not uniform. The level of risk is determined by two key factors: what you burn and how you burn it. Understanding this distinction is crucial for any honest evaluation.
Feedstock Matters: Waste vs. Virgin Resources
There is a vast difference between burning true waste materials—such as agricultural residue, sawdust from lumber mills, or municipal organic waste—and harvesting forests specifically for fuel. Using genuine waste streams has a much lower environmental impact and is far more sustainable.
Technology Matters: Inefficient vs. Advanced Combustion
The health impact is directly tied to the efficiency of the combustion technology. A modern power plant with advanced filters, scrubbers, and high-temperature boilers will release significantly fewer particulates and harmful gases than an open fire or a basic residential wood stove.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To properly assess the safety of a biomass project, you must look at the entire lifecycle and align the evaluation with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is local air quality and public health: Prioritize projects that use advanced, high-efficiency combustion technology with proven pollution control systems to capture particulate matter and other emissions.
- If your primary focus is climate impact and sustainability: Prioritize projects that use verified waste feedstocks and avoid those that rely on harvesting whole trees or using dedicated energy crops grown on valuable land.
- If your primary focus is a comprehensive risk assessment: You must analyze the entire supply chain, from the land-use impact of the fuel source to the emissions profile of the final combustion.
True energy safety requires looking beyond the fuel itself to understand its full impact on our health and our planet.
Summary Table:
| Safety Concern | Primary Risk | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Human Health | Respiratory & cardiovascular illness from air pollution. | Particulate matter (PM2.5), toxic gases (e.g., carbon monoxide). |
| Environmental Impact | Deforestation, land degradation, and increased carbon emissions. | Unsustainable sourcing, land-use change, inefficient combustion. |
| Overall Safety | Highly dependent on fuel source and combustion technology. | Use of waste streams vs. virgin resources; advanced vs. basic technology. |
Need to analyze the safety and efficiency of your biomass processes? KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables for precise environmental and emissions testing. Our solutions help you accurately measure particulate matter, analyze gas emissions, and assess fuel quality to ensure your biomass operations are safe and sustainable. Contact our experts today to find the right tools for your lab's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Super Negative Oxygen Ion Generator Machine for Air Purification
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the tolerances for laser sintering? A Guide to Achieving Accurate SLS Parts
- What technical challenges do integrated membrane technologies address? Overcome Mass Transfer in Wastewater Treatment
- What is the sputtering method of deposition? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Coating
- What are the two types of hot air ovens? Choose the Right Air Circulation for Your Lab
- How do you evaporate ethyl acetate? Master Safe & Efficient Solvent Removal with Rotary Evaporation
- What is the source of XRF radiation? Understanding X-ray Tubes vs. Radioisotopes for Analysis
- Does brazing require heat? Yes, it's the catalyst for creating strong, permanent bonds.
- What is the microwave heating technique? A Guide to Fast, Uniform Thermal Processing




