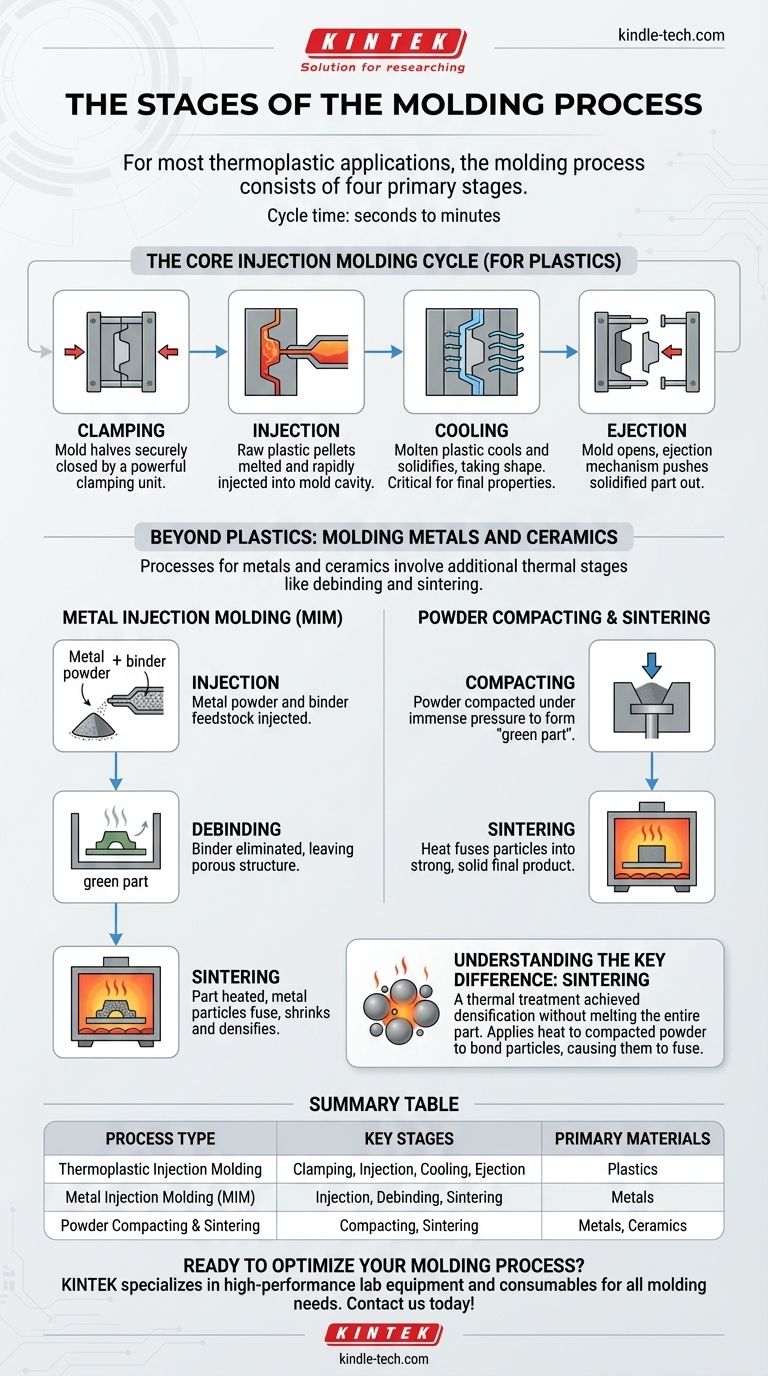
For most thermoplastic applications, the molding process consists of four primary stages: clamping, injection, cooling, and ejection. This entire cycle is highly automated and can be completed in a time frame ranging from a few seconds to a couple of minutes, depending on the complexity and size of the part.
The term "molding process" is context-dependent. While the classic four-stage cycle applies to plastics, processes for metals and ceramics involve additional, distinct stages like debinding and sintering to achieve their final solid form.
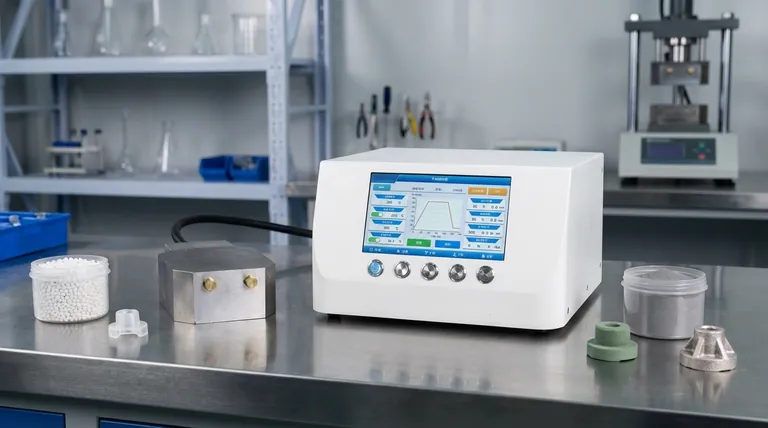

The Core Injection Molding Cycle (For Plastics)
The standard for high-volume plastic part production is a four-stage cycle that efficiently transforms raw polymer pellets into finished products. Each stage is critical for ensuring the final part meets its required specifications.
Stage 1: Clamping
Before the material is injected, the two halves of the mold must be securely closed. A powerful clamping unit pushes the mold halves together with enough force to keep them sealed against the pressure of the molten plastic injection.
Stage 2: Injection
Raw plastic pellets are melted and then injected rapidly into the closed mold cavity. The pressure and speed are precisely controlled to ensure the cavity is completely filled before the material begins to solidify.
Stage 3: Cooling
Once the mold cavity is filled, the molten plastic begins to cool and solidify, taking the shape of the mold. The cooling time is a critical part of the cycle, as it dictates the final properties and dimensional stability of the part.
Stage 4: Ejection
After the part has cooled sufficiently, the mold opens. An ejection mechanism, typically using pins or plates, pushes the solidified part out of the mold cavity, completing the cycle and preparing the mold for the next injection.
Beyond Plastics: Molding Metals and Ceramics
When working with metals or ceramics, the process fundamentally changes. While it may begin with an injection step, it requires subsequent thermal processes to create a dense, solid part from a powdered raw material.
The Process: Metal Injection Molding (MIM)
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) is a multi-step process for creating complex metal parts.
First, a fine metal powder is mixed with a polymer binder to create a feedstock. This mixture is then injected into a mold, much like plastic. The resulting "green part" is then moved to a furnace where the binder is eliminated (debinding), leaving a porous metal structure.
Finally, this porous part is heated to a high temperature in a process called sintering. The metal particles fuse together, causing the part to shrink and densify into its final, solid state.
The Process: Powder Compacting & Sintering
For many ceramic or metal parts, the process begins without a molten injection stage.
The initial raw material, usually a powder, is first prepared, sometimes mixed with a binder to form a slurry. This material is then compacted under immense pressure in a die or mold to form a "green part."
This compacted part is then heated in a controlled furnace or kiln during the sintering stage. The heat fuses the individual particles together, creating a strong, cohesive, and solid final product.
Understanding the Key Difference: Sintering
Sintering is the critical step that distinguishes metal and ceramic molding from plastic molding. It's a thermal treatment that achieves densification without melting the entire part.
What is Sintering?
Sintering is the process of applying heat to a compacted powder to bond its particles together. The temperature is kept below the material's full melting point.
During this process, atoms diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, causing them to fuse and creating a single solid piece. This causes the part to shrink as the voids between particles are eliminated.
Why is it Necessary?
Metals and ceramics have extremely high melting points, making them difficult and energy-intensive to process in a fully molten state like plastics.
Sintering allows for the creation of dense, strong parts from these materials at lower temperatures. It provides a practical and effective way to manufacture complex shapes that would be otherwise difficult to cast or machine.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
Your material choice dictates the specific stages your molding process will require.
- If your primary focus is working with thermoplastics: The process is the standard four-stage cycle: clamping, injection, cooling, and ejection.
- If your primary focus is creating complex metal parts: You will use Metal Injection Molding (MIM), which involves injection with a binder, followed by debinding and sintering.
- If your primary focus is starting with a metal or ceramic powder: Your process will involve compacting the powder into a shape and then sintering it to create the final solid part.
Understanding these distinct pathways is the key to successfully transforming raw material into a finished component.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Key Stages | Primary Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastic Injection Molding | Clamping, Injection, Cooling, Ejection | Plastics |
| Metal Injection Molding (MIM) | Injection, Debinding, Sintering | Metals |
| Powder Compacting & Sintering | Compacting, Sintering | Metals, Ceramics |
Ready to optimize your molding process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for all your molding needs. Whether you're working with plastics, metals, or ceramics, our solutions ensure precision, efficiency, and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific requirements and help you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Lab Infrared Press Mold
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
People Also Ask
- What role does a benchtop hot press play in densifying composite cathodes? Achieve <10% Porosity with Thermo-Mechanical Flow
- What is the temperature range for compression molding? Optimize Your Process for Perfect Parts
- What is the hot press molding method? A Guide to Shaping Materials with Heat & Pressure
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- How is conventional heating different from induction heating? Direct vs. Indirect Heat Explained



















