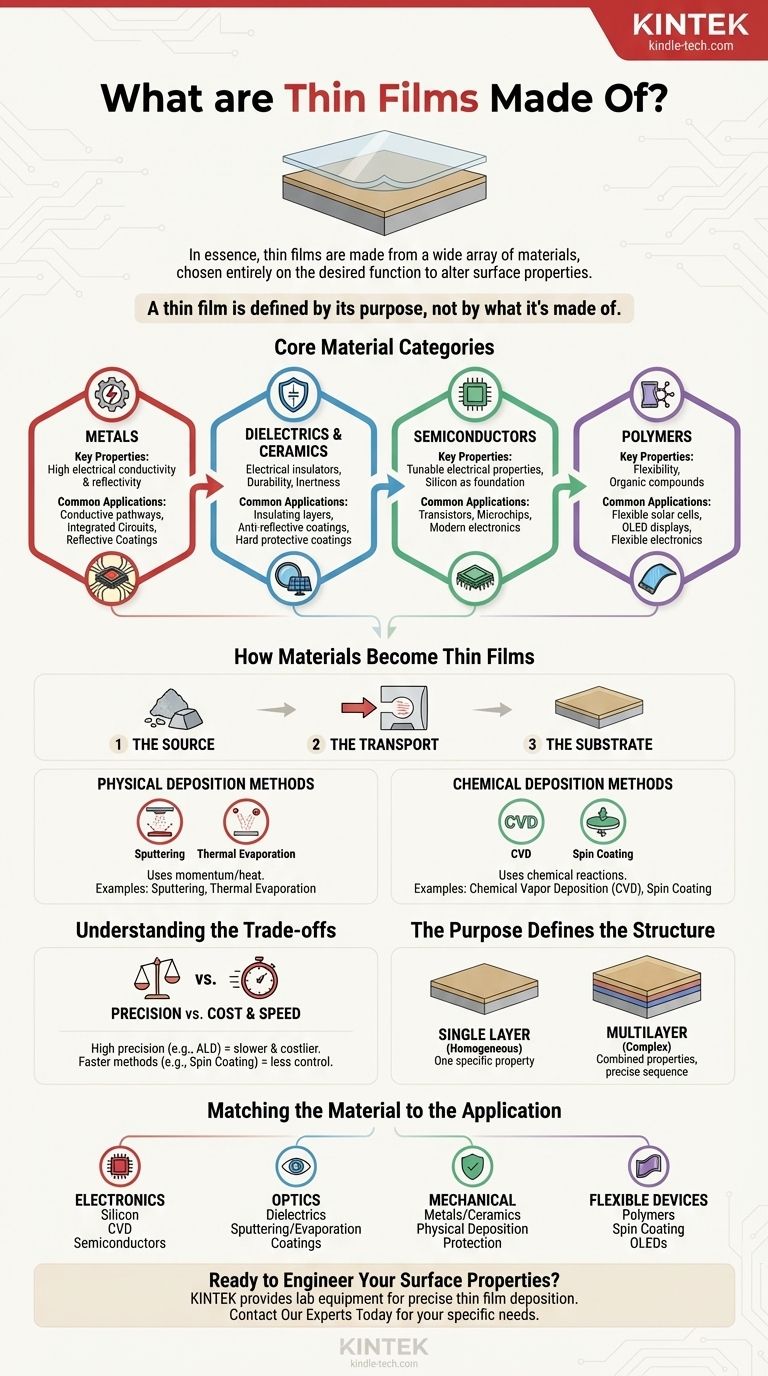
In essence, thin films are made from a wide array of materials, most commonly metals, dielectrics (ceramics), semiconductors, and polymers. The specific material is not inherent to the concept of a "thin film" itself; rather, it is chosen based entirely on the desired function, such as altering the electrical, optical, or physical properties of a surface.
A thin film is defined not by what it's made of, but by its purpose. The material is simply the medium chosen to impart specific new properties to the surface of a bulk material without altering its core nature.

The Core Material Categories
The material selected for a thin film is a direct reflection of the problem it is meant to solve. Materials are generally chosen from one of four major categories.
Metals
Metallic films are often used for their excellent electrical conductivity and reflectivity. They are fundamental in creating conductive pathways in integrated circuits, reflective coatings for mirrors, and connections in electronic devices.
Dielectrics and Ceramics
Dielectric materials are electrical insulators. They are used to create insulating layers in capacitors, anti-reflective coatings on lenses and solar panels, and hard, protective coatings on tools due to their durability and inertness.
Semiconductors
Semiconductors, with silicon being the most famous example, are the foundation of modern electronics. Thin films of semiconductor materials are meticulously layered to build transistors and other essential components of microchips.
Polymers
Newer applications, especially in flexible electronics, rely on thin films made from polymer compounds. These organic materials are crucial for creating flexible solar cells and Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLEDs) used in modern displays.
How Materials Become Thin Films
The process of applying these materials is as critical as the material itself. This is accomplished through highly controlled deposition techniques that build the film, sometimes one atomic layer at a time.
The Three Key Elements
Every deposition process involves three components:
- The Source: The raw material that will form the film.
- The Transport: The method for moving the material from the source to the target.
- The Substrate: The bulk material or surface onto which the film is deposited.
Physical Deposition Methods
These methods use physical means, like momentum or heat, to move material from the source to the substrate. Common techniques include sputtering, where ions bombard a target to eject atoms, and thermal evaporation, where a material is heated in a vacuum until it vaporizes and condenses on the substrate.
Chemical Deposition Methods
These methods use chemical reactions to form the film on the substrate's surface. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), for instance, introduces precursor gases into a chamber that react and deposit a solid film. For polymers, techniques like spin coating use centrifugal force to spread a liquid solution evenly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of material and deposition method is a complex decision involving multiple competing factors. There is no single "best" approach; the optimal choice depends entirely on the application's requirements.
Precision vs. Cost and Speed
Methods like Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) offer incredible precision, allowing for the creation of films with single-atom thickness control. However, this precision comes at the cost of being a very slow and expensive process.
In contrast, methods like spin coating or electroplating can be much faster and more cost-effective but offer less control over the final film's structure and thickness.
Material and Substrate Compatibility
Not every material can be deposited using every method. The melting point, chemical reactivity, and other physical properties of the source material dictate which deposition techniques are viable. Similarly, the substrate must be able to withstand the conditions of the process, such as high temperatures or vacuum.
The Purpose Defines the Structure
Ultimately, the goal is to engineer a specific surface property. This can be achieved with structures ranging from the simple to the incredibly complex.
Single vs. Multilayer Films
A thin film can be a single, uniform layer of one material (a homogeneous structure) designed to provide one specific property, like wear resistance.
Alternatively, films can be complex multilayer structures, where different materials are stacked in a precise sequence to achieve combined properties that a single material cannot provide, such as in advanced optical filters.
Modifying Surface Properties
The core function of a thin film is to change the characteristics of a surface. This allows engineers to use a cost-effective or strong bulk material (like glass or steel) and add a thin, functional layer that provides a property—like conductivity, scratch resistance, or anti-reflection—that the bulk material lacks.
Matching the Material to the Application
To select the right approach, you must start with your end goal.
- If your primary focus is electronics and semiconductors: You will primarily work with materials like silicon compounds, deposited with high-precision methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
- If your primary focus is optics: You will use dielectric materials to create anti-reflective or reflective coatings, often applied via physical methods like sputtering or evaporation.
- If your primary focus is mechanical protection: Hard metals and ceramics are applied to create wear-resistant coatings on tools and components, often using physical deposition.
- If your primary focus is flexible devices: You will explore polymer compounds applied through methods like spin coating to create next-generation technologies like OLEDs.
Ultimately, the material of a thin film is a strategic choice driven by the specific surface property you need to achieve.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Metals | High electrical conductivity, reflectivity | Conductive pathways, reflective coatings |
| Dielectrics/Ceramics | Electrical insulation, durability, inertness | Insulating layers, anti-reflective coatings |
| Semiconductors | Tunable electrical properties | Transistors, microchips |
| Polymers | Flexibility | Flexible solar cells, OLED displays |
Ready to Engineer Your Surface Properties?
Choosing the right thin film material and deposition process is critical to your project's success. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables needed for precise thin film deposition, from research to production.
Whether you are working with metals, ceramics, semiconductors, or polymers, our expertise can help you achieve the perfect surface properties for your application.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's thin film innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials



















