At its core, a ball mill is a highly versatile tool for grinding and blending materials. It is used across industries to reduce the particle size of substances like mining ores, pigments, and ceramics. In scientific research, it is an essential instrument for creating novel materials, producing uniform powders, and even changing a material's fundamental properties through mechanical force.
A ball mill is more than just a grinder. It is a powerful instrument for manipulating the physical state of solid materials, enabling everything from large-scale industrial processing to the laboratory creation of advanced nanomaterials.

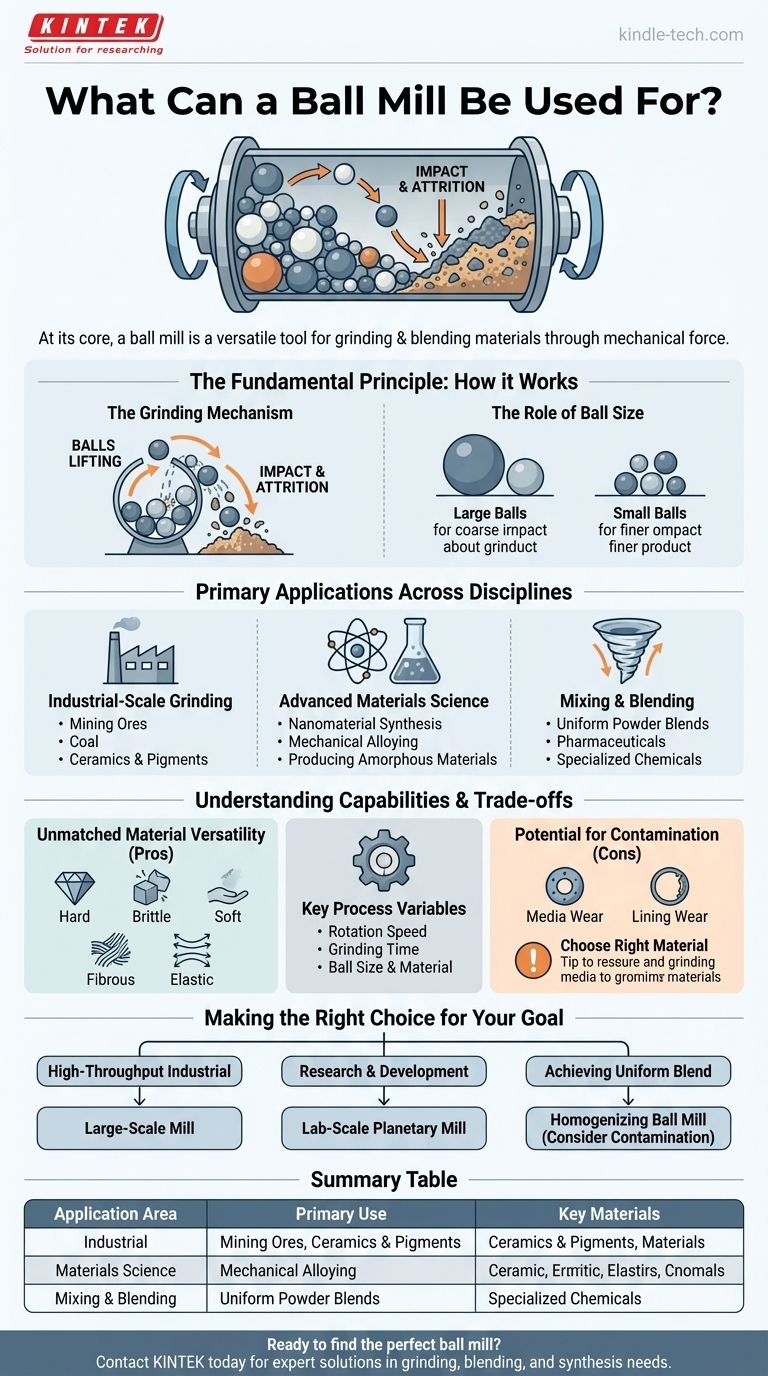
The Fundamental Principle: How a Ball Mill Works
A ball mill is a type of grinder used to turn coarse materials into fine powder. Its effectiveness comes from a simple but powerful mechanical principle.
The Grinding Mechanism
The equipment consists of a hollow cylinder that rotates on its axis. This cylinder is partially filled with the material to be ground, along with a grinding medium—most commonly, hardened steel or ceramic balls.
As the cylinder rotates, the balls are lifted up the side of the chamber. At a certain point, they cascade back down, crushing and grinding the material through a combination of impact and attrition (friction).
The Role of Ball Size
The size of the grinding media is critical. Large balls are used to break down coarse feed materials through forceful impact. Smaller balls create a finer final product by filling the gaps and increasing the surface area for grinding.
Primary Applications Across Disciplines
The versatility of the ball mill makes it a staple in vastly different fields, from heavy industry to advanced research and development.
Industrial-Scale Grinding
In industrial settings, ball mills are workhorses for processing bulk materials. This includes grinding mining ores to liberate valuable minerals, pulverizing coal for power generation, and processing raw materials like feldspar and pigments for the ceramics and paint industries.
Advanced Materials Science
In a laboratory, a ball mill is used for far more than simple size reduction. It is a key tool for:
- Nanomaterial Synthesis: Preparing particles on the nanoscale.
- Mechanical Alloying: Creating novel alloys by repeatedly fracturing and cold-welding powder particles together.
- Producing Amorphous Materials: Destroying the crystalline structure of a material to create a glass-like, non-crystalline solid.
Mixing and Blending
The constant tumbling action makes the ball mill an excellent mixer. It can be used to create highly uniform blends of different powders. This is critical in applications ranging from pharmaceuticals to the careful and controlled blending of specialized chemical mixtures, including explosives.
Understanding the Capabilities and Trade-offs
While powerful, a ball mill is not the right tool for every job. Understanding its strengths and limitations is key to using it effectively.
Unmatched Material Versatility
One of the ball mill's greatest strengths is its ability to process a vast range of materials. Depending on the setup, it can effectively grind samples that are hard, brittle, soft, fibrous, or elastic.
Process Control vs. Simplicity
The operational concept is simple: load, run, and unload. However, achieving a specific, repeatable particle size requires precise control over variables like rotation speed, grinding time, and the size and material of the balls.
Potential for Contamination
A critical consideration, especially in high-purity research, is contamination. The grinding media and the mill's inner lining can wear down over time, introducing small amounts of unwanted material into the sample. Choosing the right ball material (e.g., ceramic instead of steel) can mitigate this risk.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting and using a ball mill effectively depends entirely on your final objective.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput industrial production: You need a large-scale, robust mill designed for continuous processing of coarse raw materials.
- If your primary focus is research and development: A laboratory-scale planetary ball mill offers precise control over parameters and is ideal for small, high-value samples.
- If your primary focus is achieving a uniform powder blend: A ball mill provides excellent homogenization, but you must carefully consider the potential for contamination from the grinding media.
Ultimately, the ball mill's value lies in its simple, powerful ability to transform solid materials through mechanical energy, making it an indispensable tool in both industry and science.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Primary Use | Key Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Processing | Grinding & Crushing | Mining Ores, Coal, Ceramics |
| Materials Science | Synthesis & Alloying | Nanomaterials, Metal Powders |
| Mixing & Blending | Homogenization | Pharmaceuticals, Chemicals |
Ready to find the perfect ball mill for your application?
Whether you are processing industrial materials or conducting advanced R&D, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment ensures you get the right solution. Our range of ball mills is designed for precision, durability, and minimal contamination.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific grinding, blending, or synthesis needs and let our experts help you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the function of an agate mortar and pestle in mixing LATP powders? Ensure Pure, Homogeneous Synthesis
- Why is it important to grind the sample finely and pack it tightly before performing a melting point determination? Ensure Accurate and Sharp Melting Points
- What is the feed size of a ball mill? Optimize Your Grinding Process for Maximum Efficiency
- How does the use of grinding equipment benefit iron-substituted manganese oxide? Optimize Energy Storage Performance
- What is a colloidal mill also known as? Discover the Power of Rotor-Stator Mixers
- What is the maximum feed size for a hammer mill? It's a System-Dependent Variable, Not a Fixed Number
- What is the grinding mechanism of ball mill? Master Impact & Attrition for Perfect Particle Size
- What is the primary function of a ball mill in magnesium production? Optimize Pretreatment for Efficiency



















