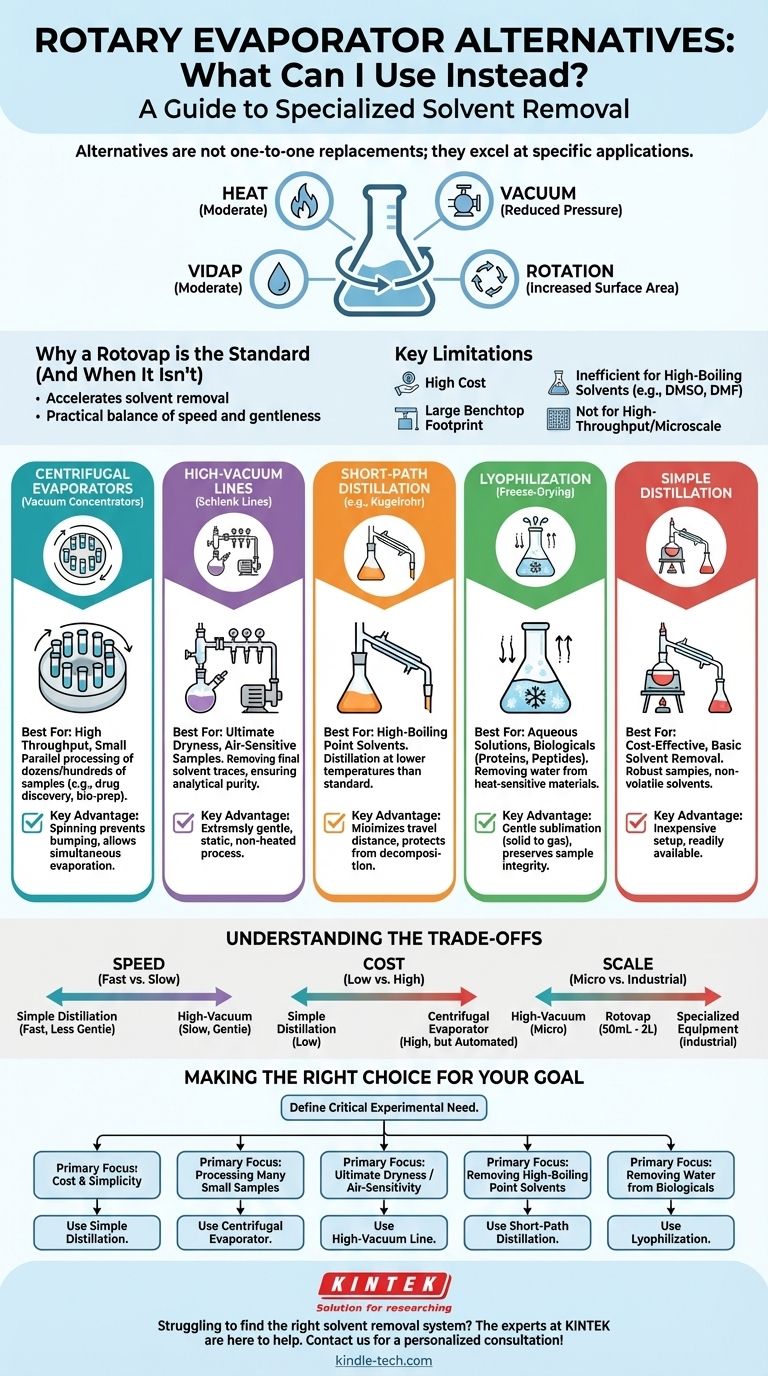
The best alternative to a rotary evaporator depends entirely on your specific goal. Common replacements include centrifugal evaporators for high throughput, high-vacuum lines for achieving ultimate dryness, simple distillation for basic solvent removal, and lyophilization for removing water from sensitive samples. The right choice is determined by your sample's volume, its sensitivity to heat, and the boiling point of the solvent you need to remove.
A rotary evaporator is a tool for accelerating solvent removal by applying moderate heat, reducing pressure, and increasing surface area through rotation. Alternatives are not one-to-one replacements; instead, they are specialized tools that excel at one or two of these principles, making them better suited for specific applications where a rotovap is inefficient or impractical.

Why a Rotovap is the Standard (and When It Isn't)
To understand the alternatives, we must first appreciate what makes the rotary evaporator (rotovap) the default choice in many organic chemistry labs.
The Core Principle of Operation
A rotovap combines three key factors to efficiently remove solvent. It gently heats the sample in a water bath, uses a vacuum pump to reduce the pressure (lowering the solvent's boiling point), and rotates the flask to constantly expose a thin film of the sample, dramatically increasing the surface area for evaporation.
Key Limitations of the Rotovap
Despite its utility, a rotovap is not always the optimal tool. Its primary limitations include high cost, a significant benchtop footprint, and difficulty removing very high-boiling point solvents like DMSO or DMF. It is also inefficient for processing dozens of very small samples simultaneously or for removing trace amounts of solvent to achieve an ultra-dry final product.
Common Alternatives for Different Laboratory Goals
Choosing an alternative means matching the tool to the specific constraints of your experiment, whether that is sample volume, sensitivity, or the desired level of dryness.
For Small Volumes or High Throughput: Centrifugal Evaporators
Also known as vacuum concentrators (with brand names like Genevac or SpeedVac), these devices hold multiple sample tubes or vials in a rotor inside a vacuum chamber. The rotor spins to prevent the solvent from bumping or boiling over as the vacuum is applied.
This method is ideal for parallel synthesis or applications where you need to evaporate solvent from dozens or even hundreds of small samples at once, such as in drug discovery or biological sample preparation.
For Ultimate Dryness or Air-Sensitive Samples: High-Vacuum Lines
When a compound must be completely free of residual solvent, a high-vacuum (or "Schlenk") line is the superior tool. After initial bulk solvent removal, the sample flask is attached to the line, which uses a more powerful pump to achieve a much lower pressure than a standard rotovap setup.
This is a static, non-heated process, making it extremely gentle. It is the gold standard for preparing sensitive reagents or ensuring a sample is analytically pure and free from volatile impurities before characterization.
For High-Boiling Point Solvents: Short-Path Distillation
When dealing with solvents that have very high boiling points, a rotovap struggles because its vacuum and heating capabilities are often insufficient. A short-path distillation apparatus (including specialized versions like a Kugelrohr) minimizes the distance the vapor has to travel from the heated flask to the condenser.
This setup, often combined with a high-performance vacuum pump, allows for the distillation of compounds and removal of solvents at lower temperatures than a standard distillation, protecting the sample from decomposition.
For Aqueous Solutions: Lyophilization (Freeze-Drying)
If your goal is to remove water, especially from heat-sensitive biological materials like proteins or peptides, lyophilization is the ideal method. The sample is first frozen, and then a deep vacuum is applied.
Under these conditions, the frozen water sublimes—turning directly from a solid to a gas—bypassing the liquid phase entirely. This process is exceptionally gentle and results in a fluffy, easily re-dissolvable solid.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single method is perfect for all situations. The primary trade-offs you will encounter are between speed, gentleness, cost, and scale.
Speed vs. Gentleness
Applying direct heat via simple distillation is fast but can degrade sensitive compounds. A high-vacuum line is extremely gentle but can take hours or even days to remove the final traces of solvent. A rotovap offers a practical balance between these two extremes.
Cost vs. Capability
A simple distillation apparatus is inexpensive but labor-intensive and lacks precise control. In contrast, a centrifugal evaporator can cost as much or more than a rotovap but offers automation and high-throughput capabilities that justify the expense in a busy lab.
Scale vs. Efficiency
A rotovap is most efficient for volumes between 50 mL and 2 L. For the microgram scale, drying under a stream of nitrogen or using a high-vacuum line is more practical. For industrial scales involving tens or hundreds of liters, specialized equipment like falling film evaporators are used.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct instrument, start by defining your most critical experimental need.
- If your primary focus is cost and simplicity: Use simple distillation for robust samples and non-volatile solvents.
- If your primary focus is processing many small samples: A centrifugal evaporator is the most efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is ultimate dryness or air-sensitivity: A high-vacuum line is the required standard.
- If your primary focus is removing high-boiling point solvents: A short-path distillation setup offers the necessary performance.
- If your primary focus is removing water from biologicals: Lyophilization is the only method that guarantees sample integrity.
By understanding the fundamental principles of evaporation, you can select the precise tool that best serves your chemistry.
Summary Table:
| Alternative Method | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal Evaporator | High-throughput, small samples | Parallel processing of dozens of samples |
| High-Vacuum Line | Ultimate dryness, air-sensitive samples | Gentle, static process for pure products |
| Short-Path Distillation | High-boiling point solvents | Efficient removal at lower temperatures |
| Lyophilization | Aqueous solutions, biologicals | Gentle freeze-drying preserves sample integrity |
| Simple Distillation | Cost-effective, basic removal | Inexpensive setup for robust samples |
Struggling to find the right solvent removal system for your laboratory workflow? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the ideal lab equipment and consumables for your specific application, whether you need a high-throughput centrifugal evaporator, a gentle lyophilizer for sensitive biologicals, or a robust distillation setup. Our team will work with you to understand your sample volume, sensitivity, and solvent requirements to recommend the perfect solution that maximizes your lab's efficiency and protects your valuable samples. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and let us help you optimize your solvent removal process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What role do freeze dryers play in biotechnology and research? Ensure Sample Integrity and Reproducibility
- How does freeze-drying contribute to long-term sample storage? Achieve Maximum Preservation Without Refrigeration
- What are the applications of lab freeze dryers? Preserve Your Most Sensitive Materials
- What are some other applications of freeze dryers? Preserving Delicate Materials in Tech and Research
- Where are evaporators used in food industry? Concentrate Products & Reduce Costs



















