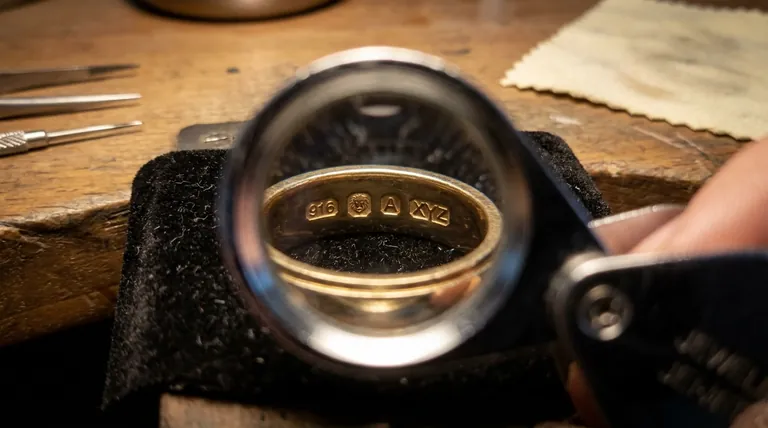
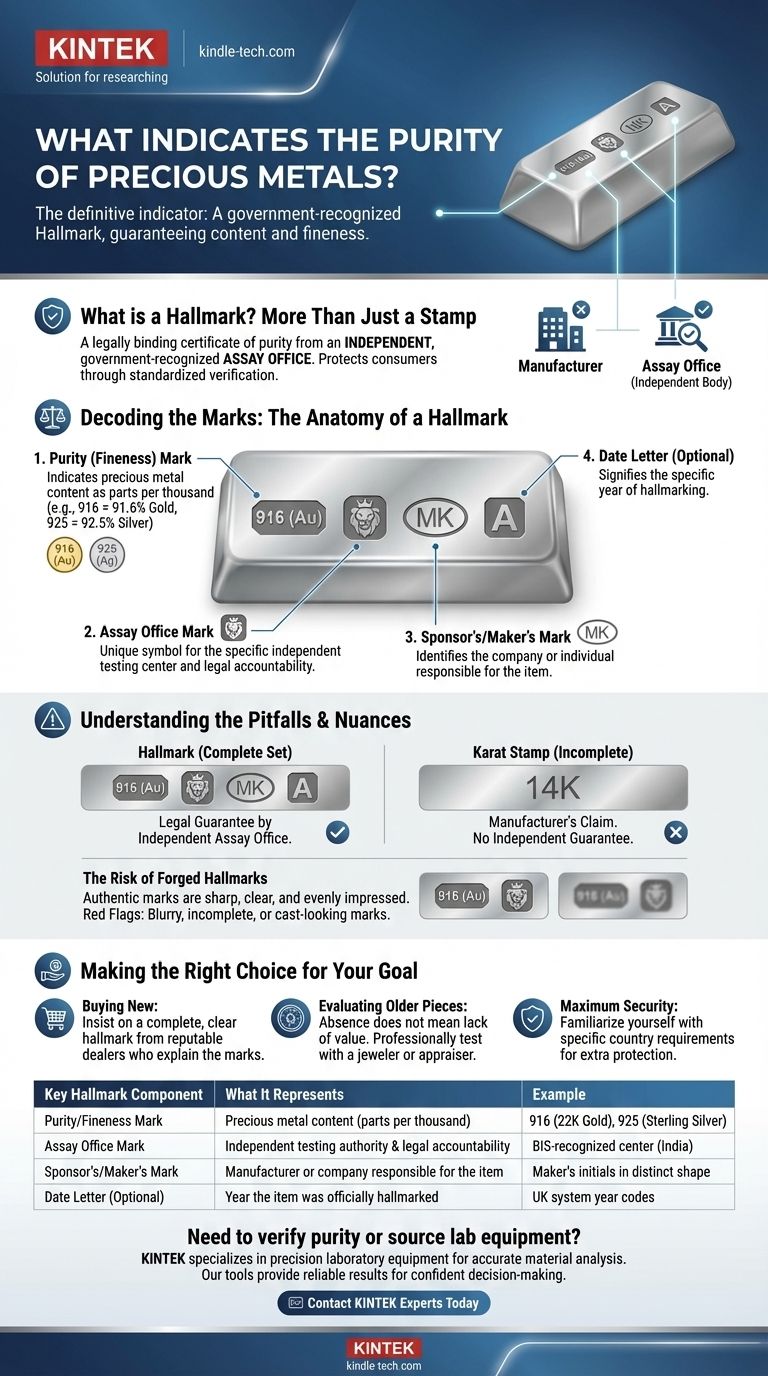
The definitive indicator of a precious metal's purity is a set of official marks known as a hallmark. These marks are not applied by the manufacturer but by an independent, government-recognized assay office after the item has been scientifically tested. A complete hallmark legally guarantees the metal content and fineness.
A hallmark is more than just a stamp; it is a legally binding certificate of purity applied by a neutral third party. Its primary purpose is to protect the consumer by providing a trustworthy, standardized system for verifying the true value of a precious metal item.

What is a Hallmark? More Than Just a Stamp
A common misconception is that any stamp on a piece of metal is a hallmark. The key difference lies in who applies the mark and the legal guarantee it represents.
A Legal Guarantee of Purity
A true hallmark is a legal mark. It certifies that an independent body has assayed (tested) the metal and verified that its purity, or fineness, meets a recognized legal standard.
This system removes the conflict of interest that would exist if manufacturers were solely responsible for marking the purity of their own goods.
The Role of Independent Assay Offices
The hallmarking process is managed by government-authorized or state-appointed assay offices. In India, for example, these are BIS-recognized centers.
These offices are the only entities permitted to strike the official hallmark onto an item after it passes a rigorous testing process. This third-party verification is the foundation of the system's integrity.
Decoding the Marks: The Anatomy of a Hallmark
A complete hallmark is typically composed of several distinct, compulsory marks. While the exact symbols vary by country, the information they convey is consistent.
The Purity (Fineness) Mark
This is the most critical mark for the consumer. It indicates the precious metal content as parts per thousand.
For example, "916" on a gold item means it is 91.6% pure gold (22 karat). Similarly, "925" on a silver item means it is 92.5% pure silver, commonly known as Sterling Silver.
The Assay Office Mark
Each assay office has its own unique symbol. This mark shows exactly where the item was tested and hallmarked, creating a chain of accountability.
If an item is ever found to be of a lower purity than marked, the assay office that applied the mark can be held responsible.
The Sponsor's or Maker's Mark
This mark identifies the company or individual who manufactured the item or sent it for hallmarking. It usually consists of the maker's initials within a distinct shape.
Additional Marks
Some hallmarking systems, like the one in the UK, also include a date letter. This optional mark signifies the specific year the item was hallmarked.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Nuances
Relying on markings requires you to distinguish between a legal hallmark and a simple manufacturer's stamp.
Hallmark vs. 'Karat' Stamp
A simple stamp, such as "14K" or "925" by itself, is not a hallmark. It is merely the manufacturer's claim of purity.
Without the accompanying assay office mark and sponsor's mark, there is no independent guarantee that the claim is accurate. A true hallmark is the complete set of marks.
The Risk of Forged Hallmarks
As with any sign of value, hallmarks can be forged. Authentic hallmarks are struck with high-quality steel punches, resulting in marks that are sharp, clear, and evenly impressed.
Be wary of marks that are blurry, incomplete, or look cast into the piece rather than stamped. These are significant red flags.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to verifying purity depends on your situation.
- If your primary focus is buying new precious metal items: Always insist on seeing a complete and clear hallmark and buy only from reputable dealers who can explain each mark to you.
- If your primary focus is evaluating an older or un-marked piece: The absence of a hallmark does not mean it isn't valuable, but it does mean its purity is unverified. The only certain method is to have it professionally tested by a jeweler or appraiser.
- If your primary focus is maximum security: Familiarize yourself with the specific hallmark symbols required in your country, as this provides an extra layer of protection against counterfeits.
Understanding these marks transforms you from a passive buyer into an informed investor, capable of verifying an item's fundamental value.
Summary Table:
| Key Hallmark Component | What It Represents | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Purity/Fineness Mark | Precious metal content (parts per thousand) | 916 (22K Gold), 925 (Sterling Silver) |
| Assay Office Mark | Independent testing authority & legal accountability | BIS-recognized center (India) |
| Sponsor's/Maker's Mark | Manufacturer or company responsible for the item | Maker's initials in distinct shape |
| Date Letter (Optional) | Year the item was officially hallmarked | UK system year codes |
Need to verify the purity of your precious metals or source reliable lab equipment for material testing?
KINTEK specializes in precision laboratory equipment and consumables for accurate material analysis. Whether you're a jeweler, appraiser, or precious metals investor, our tools provide the reliable results you need for confident decision-making.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific testing requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your verification processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the general procedure and what precautions should be taken during the polishing process? Achieve a Flawless Electrode Finish
- What is the process of mounting in metallurgy? A Guide to Perfect Specimen Preparation
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press contribute to MIC testing? Ensure Precision in Stainless Steel Specimens
- What are the advantages of an electrolytic polishing device for EK-181 steel TEM samples? Ensure Peak Sample Integrity
- What is a hot mounting press machine? Precision Control for Metallurgy & Electronics Assembly



















