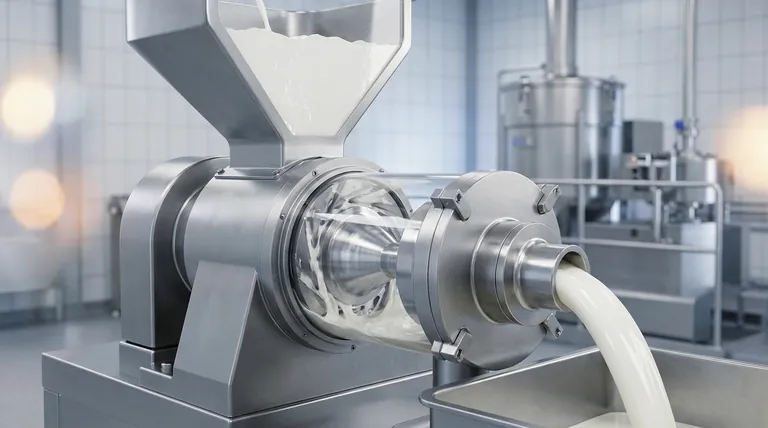
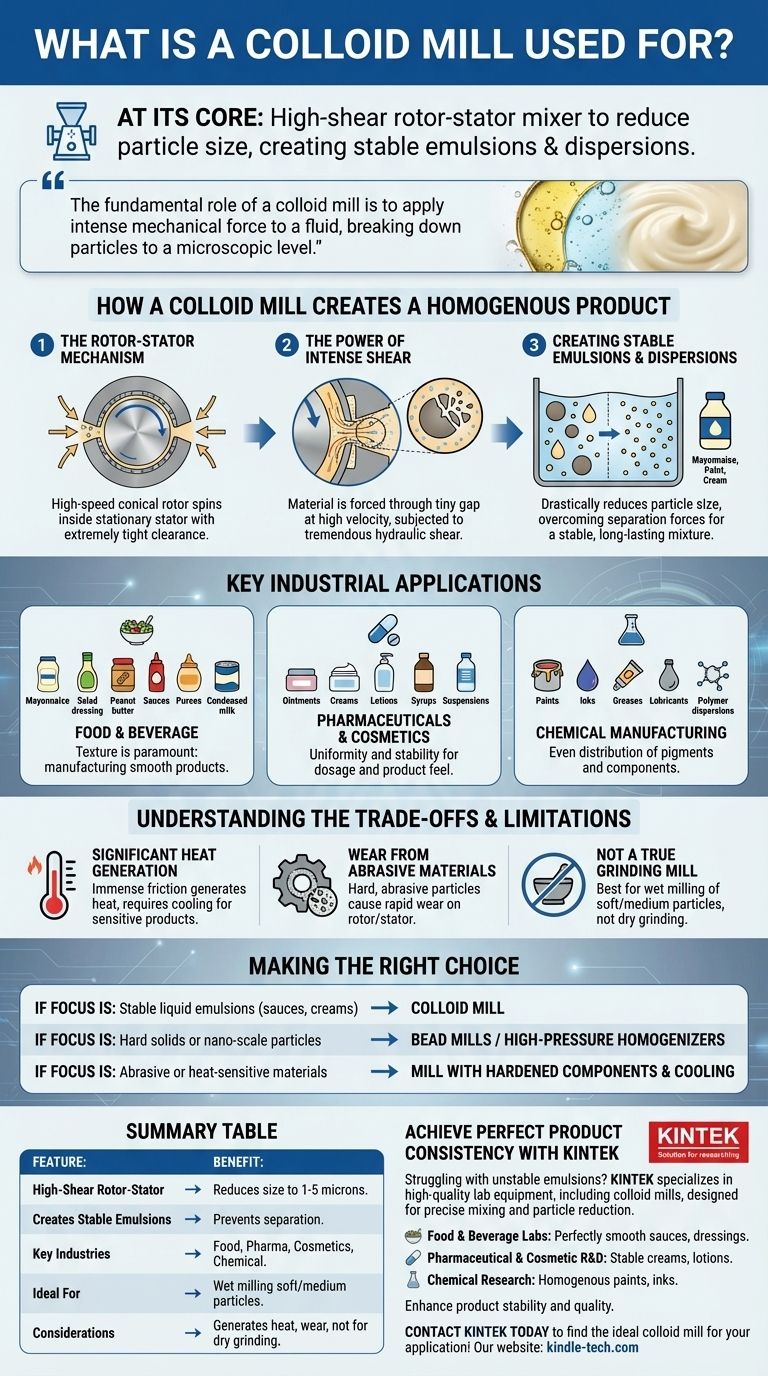
At its core, a colloid mill is a high-shear rotor-stator mixer designed to reduce the particle size of solids or droplets within a liquid. Its primary purpose is to create extremely stable emulsions and dispersions, turning otherwise separate ingredients into a smooth, uniform, and homogenous final product.
The fundamental role of a colloid mill is to apply intense mechanical force to a fluid, breaking down particles to a microscopic level. This process ensures that products like mayonnaise, paint, and pharmaceutical creams remain perfectly mixed and do not separate over time.

How a Colloid Mill Creates a Homogenous Product
A colloid mill's effectiveness comes from its simple yet powerful mechanical design. It forces a product through a narrow, controlled gap where it is subjected to immense physical stress.
The Rotor-Stator Mechanism
The heart of the machine is a high-speed conical rotor that spins with extremely tight clearance (often measured in thousandths of an inch) inside a stationary housing called the stator.
As the liquid or slurry is fed into the mill, centrifugal force pushes it into the gap between the rotor and stator.
The Power of Intense Shear
The material is subjected to tremendous hydraulic shear as it's forced through this tiny gap at high velocity.
This intense tearing action physically rips apart solid particles and liquid droplets, reducing them to a much smaller and more uniform size, typically in the range of 1-5 microns.
Creating Stable Emulsions and Dispersions
By drastically reducing particle size, the mill creates a colloidal suspension or emulsion.
The particles become so small that their kinetic energy and surface chemistry can overcome the forces of gravity or immiscibility that would normally cause them to separate, resulting in a stable, long-lasting mixture.
Key Industrial Applications
The ability to create stable, smooth mixtures makes colloid mills essential in a wide range of industries. They are workhorses for products that depend on a specific texture and consistency.
Food and Beverage Production
This is a primary application, where texture is paramount. Colloid mills are used for manufacturing mayonnaise, salad dressings, peanut butter, sauces, fruit purees, and condensed milk.
Pharmaceuticals and Cosmetics
In these industries, uniformity and stability are critical for dosage and product feel. Mills are used to produce ointments, creams, lotions, syrups, and injectable suspensions.
Chemical Manufacturing
Colloid mills are vital for producing paints, inks, greases, lubricants, and various polymer dispersions where pigment and other components must be evenly and permanently distributed.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, a colloid mill is not the universal solution for all mixing needs. Understanding its operational constraints is key to using it correctly.
Significant Heat Generation
The immense friction and shear generate considerable heat. For heat-sensitive products like some dairy or pharmaceutical compounds, this can be a significant issue requiring a cooling jacket or a different processing method.
Wear from Abrasive Materials
Processing materials with hard, abrasive particles (like certain pigments or minerals) can cause rapid wear on the rotor and stator. This increases maintenance costs and can introduce contaminants into the product.
Not a True Grinding Mill
A colloid mill is for "wet milling" and is best suited for reducing the size of soft to medium-hard particles already suspended in a liquid. It is not designed for grinding hard, dry powders.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct equipment depends entirely on your final product's required characteristics.
- If your primary focus is creating stable liquid emulsions like sauces, creams, or dressings: A colloid mill is an excellent and highly efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is processing hard solids or achieving nano-scale particles: You should investigate bead mills or high-pressure homogenizers.
- If your primary focus is processing highly abrasive or heat-sensitive materials: Ensure you select a mill with hardened components and a robust cooling system.
Ultimately, understanding the principle of high-shear mixing allows you to select the colloid mill as the precise tool for achieving superior product stability and texture.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit/Application |
|---|---|
| High-Shear Rotor-Stator | Reduces particle/droplet size to 1-5 microns for uniformity. |
| Creates Stable Emulsions | Prevents separation in products like mayonnaise, sauces, and creams. |
| Key Industries | Food & Beverage, Pharmaceuticals, Cosmetics, Chemical Manufacturing. |
| Ideal For | Wet milling of soft to medium-hard particles in a liquid suspension. |
| Considerations | Generates heat; wear from abrasive materials; not for dry grinding. |
Achieve Perfect Product Consistency with KINTEK
Struggling with unstable emulsions or inconsistent textures in your formulations? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including colloid mills, designed to meet the precise mixing and particle size reduction needs of laboratories and production facilities.
We provide reliable solutions for:
- Food & Beverage Labs: Create perfectly smooth sauces, dressings, and purees.
- Pharmaceutical & Cosmetic R&D: Develop stable creams, ointments, and lotions with uniform consistency.
- Chemical Research: Produce homogenous paints, inks, and dispersions.
Let our expertise help you enhance product stability and quality. Contact KINTEK today to find the ideal colloid mill for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Micro Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
- Laboratory Grinding Mill Mortar Grinder for Sample Preparation
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between a ball mill and a sag mill? A Guide to Primary vs. Secondary Grinding
- What is the feed size of a ball mill? Optimize Your Grinding Process for Maximum Efficiency
- How does a grinding mill work? A Guide to Crushing, Grinding, and Pulverizing
- What is the role of a laboratory-scale ball mill in the pretreatment of microalgae biomass? Boost Cell Wall Disruption
- What is the theory of ball milling? Mastering Particle Size Reduction Through Impact and Attrition



















