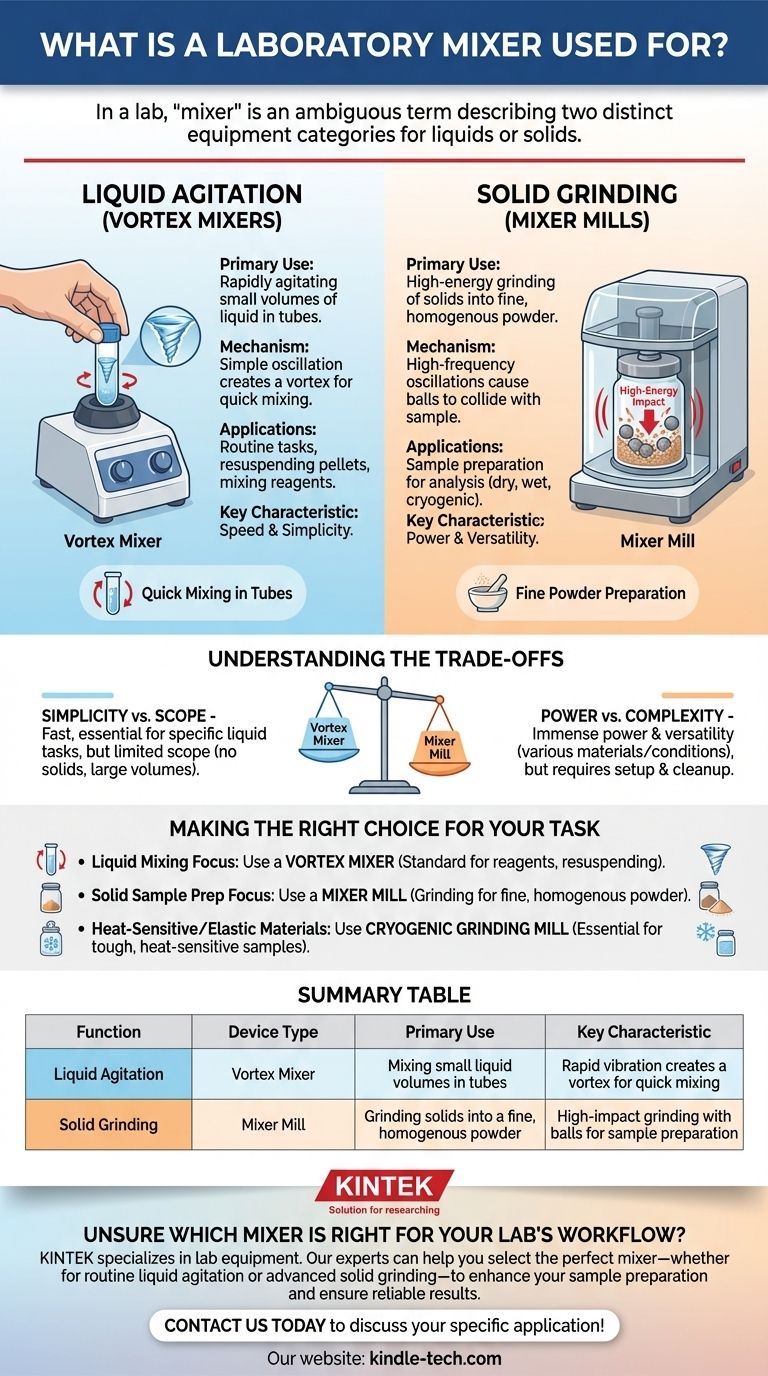
In a laboratory setting, a "mixer" is not one specific device but a term that primarily describes two distinct categories of equipment. Depending on the context, a lab mixer is used for either rapidly agitating liquids in small vials or for high-energy grinding of solid materials into a fine powder for analysis.
The term "laboratory mixer" is ambiguous. It's critical to distinguish between devices for simple liquid agitation (like vortex mixers) and those for powerful solid sample grinding (like mixer mills), as they perform fundamentally different tasks.

The Two Core Functions of Laboratory Mixers
The right mixer for your task depends entirely on whether you are working with liquids or solids. Each type operates on a completely different principle to achieve its goal.
Function 1: Liquid Agitation (Vortex Mixers)
A vortex mixer is the most common device people think of for quick mixing in a lab. Its purpose is to agitate small volumes of liquid contained in a test tube or other small vessel.
The mechanism is simple: an electric motor oscillates a small rubber cup. When you press a tube into the cup, the rapid vibration is transferred to the liquid, creating a vortex that quickly and thoroughly mixes the contents.
These are true "lab workhorses," ideal for routine tasks like resuspending cell pellets or mixing reagents.
Function 2: Solid Grinding (Mixer Mills)
A mixer mill is a much more powerful and specialized device used for sample preparation. Its function is to grind small quantities of solid material into a very fine, homogenous powder.
This is essential when preparing samples for analytical techniques that require uniformity. These mills are particularly effective for materials that are difficult to grind using other methods.
How a High-Energy Mixer Mill Works
Unlike the simple vibration of a vortex mixer, a mixer mill uses a high-impact process to pulverize samples.
The Principle of High-Energy Impact
A mixer mill operates by placing the sample into a sealed grinding jar along with one or more grinding balls.
The jar is then subjected to intense, high-frequency oscillations. This causes the balls inside to repeatedly collide with the sample material at high speed, crushing and grinding it down to a micro-scale powder.
This high-energy impact results in much faster and finer grinding than is possible with other types of laboratory mills.
Key Applications and Capabilities
Mixer mills are versatile. They can be used for dry grinding, wet grinding (with a solvent), and even cryogenic grinding.
Cryogenic grinding involves using a medium like liquid nitrogen to chill the sample and grinding jar. This makes it possible to pulverize tough, elastic materials and is essential for preserving samples that are sensitive to heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these devices involves recognizing their specific strengths and limitations.
Vortex Mixer: Simplicity vs. Scope
The primary advantage of a vortex mixer is its speed and simplicity for a very specific task: mixing liquids in small tubes. It is an essential, everyday tool.
Its limitation is its scope. It cannot handle solids, larger volumes, or sealed containers, and it imparts relatively low energy into the sample.
Mixer Mill: Power vs. Complexity
The strength of a mixer mill is its immense power and versatility for sample preparation. It can handle a wide range of materials (hard, soft, brittle, fibrous) and conditions (dry, wet, cryogenic).
The trade-off is complexity. It requires careful setup with specific jars and balls, and significant cleanup is often needed between samples to prevent cross-contamination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Task
Your application will dictate which "mixer" you need.
- If your primary focus is quick liquid mixing: A vortex mixer is the standard tool for agitating reagents or resuspending samples in test tubes.
- If your primary focus is preparing solid samples for analysis: A mixer mill is necessary for grinding materials into a fine, homogenous powder.
- If you are working with heat-sensitive or elastic materials: The cryogenic grinding capability of a specialized mixer mill is the critical feature you need.
Understanding the distinction between simple liquid agitation and high-energy solid grinding is the key to selecting the correct tool and ensuring reliable results in your lab.
Summary Table:
| Function | Device Type | Primary Use | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid Agitation | Vortex Mixer | Mixing small liquid volumes in tubes | Rapid vibration creates a vortex for quick mixing |
| Solid Grinding | Mixer Mill | Grinding solids into a fine, homogenous powder | High-impact grinding with balls for sample preparation |
Unsure which mixer is right for your lab's workflow?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect mixer—whether for routine liquid agitation or advanced solid grinding—to enhance your sample preparation and ensure reliable results.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and find the ideal solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Open Type Two Roll Mixing Mill Machine for Rubber Crusher
- Laboratory Jar Mill with Agate Grinding Jar and Balls
People Also Ask
- What is the twin screw extrusion process? A Guide to Advanced Mixing & Compounding
- What fillers for rubber compounds? Choose the Right Filler for Performance vs. Cost
- What are natural rubber sheets used for? Unlock Durability, Elasticity, and Vibration Damping
- What is the mixing process of rubber? Master the Stages for Superior Compound Quality
- What does vulcanizing a tire do? Achieve a Permanent, Structural Tire Repair
- What is multilayer blown film? Engineered Packaging for Superior Performance
- What are the three 3 basic types of mixers? Find Your Perfect Match for Baking & Production
- What are the different types of rubber mixing? Choose the Right Method for Your Production Scale



















