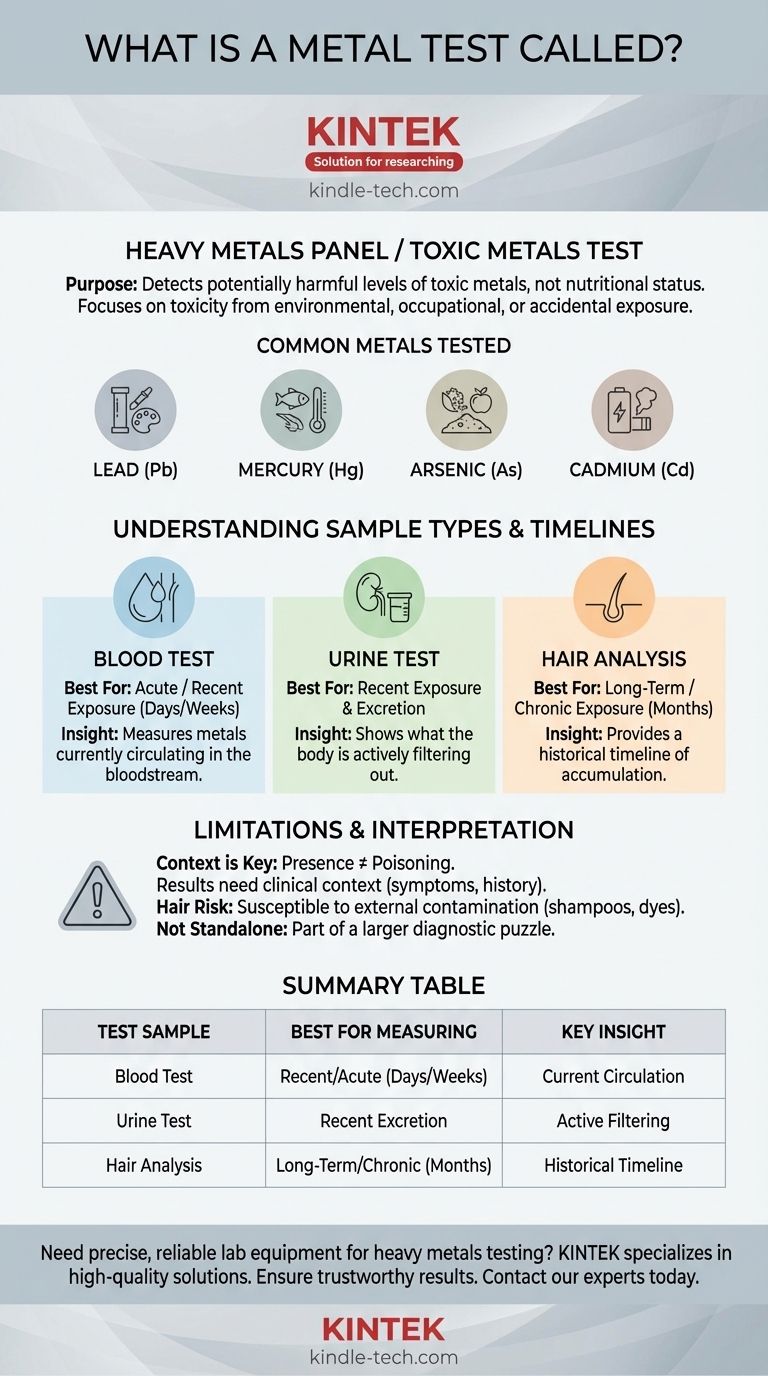
A test that measures metals in the body is most commonly referred to as a Heavy Metals Panel or a Toxic Metals Test. These terms are often used interchangeably to describe a test designed to detect and quantify the levels of specific, potentially harmful metals within a biological sample.
While several names exist for a metal test, the core purpose is to identify potentially harmful levels of specific heavy metals. The choice of which test to use—blood, urine, or hair—depends entirely on whether the goal is to investigate recent or long-term exposure.
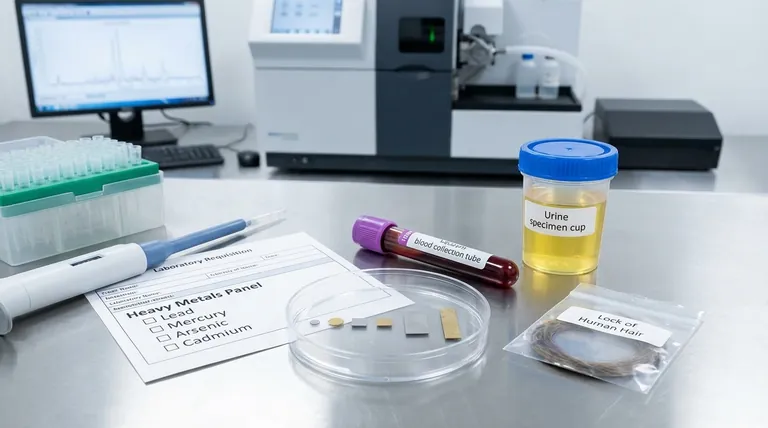

What is a Heavy Metals Panel?
A heavy metals panel is not a single, standardized test but a category of tests. Its primary function is to screen for toxicity, not to assess nutritional status.
The Core Purpose: Detecting Toxicity
The human body requires trace amounts of certain metals, like zinc and iron, to function. A heavy metals panel, however, focuses on metals that offer no biological benefit and can be toxic even at low concentrations.
The test is ordered when there is a suspected exposure to a toxic metal, either through environmental, occupational, or accidental means, or if a person presents with symptoms consistent with heavy metal poisoning.
Common Metals Tested
While the exact metals included can vary by lab, a typical panel will screen for the most common and dangerous culprits. These often include:
- Lead: Found in old paint, contaminated water, and some industrial settings.
- Mercury: Found in certain types of fish, dental amalgams, and industrial waste.
- Arsenic: Can contaminate water, soil, and food.
- Cadmium: Found in cigarette smoke, batteries, and some industrial processes.
Understanding Different Sample Types
The term "metal test" is broad because the type of sample used provides different information. The choice of sample is critical for getting a useful result.
Blood Testing: The Short-Term View
A blood test measures the amount of a metal currently circulating in your bloodstream. This makes it the ideal choice for diagnosing acute or very recent exposure.
Because the body actively works to move metals out of the blood and into tissues or organs for storage, blood levels can drop relatively quickly after an exposure ends.
Urine Testing: The Excretion Pathway
A urine test measures the amount of metals the body is currently excreting. This is also effective for identifying recent exposure, as it shows what your kidneys are actively filtering out.
For some metals, a "provoked" or "chelation" urine test is used, where a chemical agent is given to pull metals from tissues into the urine, though this practice is controversial and must be managed by an expert.
Hair Analysis: The Long-Term Record
A hair analysis provides a longer-term historical record of exposure. As hair grows, metals from the bloodstream are incorporated into the hair shaft.
By testing segments of hair, it is possible to create a timeline of exposure over the past several months. This is useful for investigating chronic, low-level exposure rather than an acute poisoning event.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While these tests are powerful, their results require careful interpretation. A positive result does not automatically equal a diagnosis of poisoning.
The Risk of Misinterpretation
The mere presence of a heavy metal does not always indicate a health problem. Labs provide reference ranges, but "normal" can vary based on geography, diet, and occupation. Results must be placed in the context of an individual's symptoms and exposure history.
The Controversy of Hair Testing
Hair analysis is particularly susceptible to external contamination. Environmental dust, shampoos, or hair dyes can deposit metals onto the hair, leading to a false positive. For this reason, many conventional medical doctors rely more heavily on blood and urine tests for diagnosis.
Not a Standalone Diagnostic Tool
No metal test should be interpreted in a vacuum. It is one piece of a larger diagnostic puzzle that includes a physical exam, a review of symptoms, and a detailed patient history focused on potential sources of exposure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To have an effective conversation with a healthcare provider, it is essential to understand which test aligns with your concern.
- If you suspect recent, acute exposure (within days or weeks): A blood or urine test is the most appropriate first step to measure what is currently in your system.
- If you want to understand long-term or past exposure (over months): Hair analysis can provide a historical record, but results should be interpreted with caution by a professional aware of its limitations.
- If you are experiencing unexplained symptoms: The test should be ordered and interpreted by a qualified medical professional who can connect the results to your clinical picture.
Ultimately, knowing the correct test for your situation is the key to getting a meaningful answer and taking the right next steps for your health.
Summary Table:
| Test Sample Type | Best For Measuring | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Test | Recent or acute exposure (days/weeks) | Shows what's currently circulating in your system. |
| Urine Test | Recent exposure and excretion levels | Indicates what your body is actively filtering out. |
| Hair Analysis | Long-term, chronic exposure (months) | Provides a historical timeline of metal accumulation. |
Need precise, reliable lab equipment for your own heavy metals testing? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables essential for accurate analysis. Ensure your results are trustworthy—contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Gold Platinum Copper Iron Metal Sheets
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Nature Agate Mortar and Pestle for Grinding and Mixing
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
People Also Ask
- Where is soldering commonly used? From Everyday Electronics to Industrial Applications
- What is the difference between metallic and non-metallic coating? A Guide to Sacrificial vs. Barrier Protection
- Why is platinum unreactive? The Atomic Secrets Behind Its Remarkable Stability
- What are the disadvantages of using metal? Understanding Corrosion, Weight, and Cost Challenges
- What are the guidelines for using gold or platinum sheets during an experiment? Ensure Precise and Reliable Results














