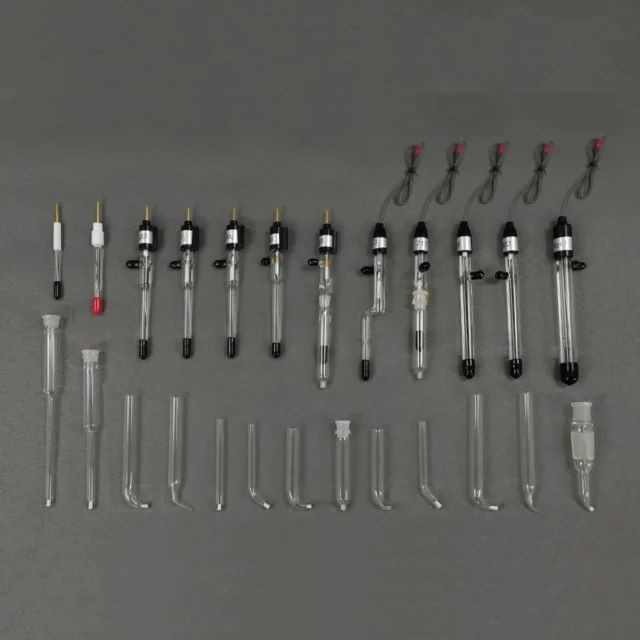

Electrochemical Consumables
Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
Item Number : ELERA
Price varies based on specs and customizations
$19.90 / set
- Applicable temperature range
- 0 ~ 60℃
- Types
- Complete and diverse models, customizable
Shipping:
Contact us to get shipping details Enjoy On-time Dispatch Guarantee.
Why Choose Us
Easy ordering process, quality products, and dedicated support for your business success.
Introduction
Calomel, Silver Chloride, and Mercury Sulfate are three important compounds used in laboratory equipment and consumables. Calomel, also known as mercurous chloride, is a white or yellowish powder that is insoluble in water. It is used as a reference electrode in electrochemistry and as a cathartic and diuretic in medicine. Silver Chloride is a white or grayish-white powder that is insoluble in water. It is used as a disinfectant, an antiseptic, and a photographic reagent. Mercury Sulfate is a white or yellowish-white powder that is soluble in water. It is used as a disinfectant, an antiseptic, and a fungicide.
We offer complete models of reference electrodes for electrochemical experiments that are resistant to acid and alkali, made with high-quality materials, and designed to be both safe and durable. Additionally, we provide customization options to meet your specific needs.
Technical specifications
Saturated calomel electrode



| Features | Good reproducibility, accurate potential application |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 25℃ |
| Dimensions | The overall length is 140mm, with the upper tube measuring 9.5mm by 35mm and the lower tube measuring 6mm by 65mm. |
| Types | Amalgam-mercury type. It offers a neutral charge and is available in three variations: single salt bridge, double salt bridge, and bent tube. |
Silver chloride electrode 1

| Features | suitable for small volumes |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 40℃ |
| Dimensions | 90mm overall length, 4*45mm in the down tube |
| The electrode properties are Ag/AgCI | |
Silver chloride electrode 2

| Features | suitable for any situation |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 60℃ |
| Dimensions | 105mm overall length, 6*45mm in the down tube |
| The nature of the electrode is Ag/AgCI, and the curved tube can be customized for silver chloride | |
Saturated silver chloride electrode

| Features | Potential stability |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 60℃ |
| Dimensions | The overall size of the unit is 140mm, with the upper tube measuring φ9.5*35mm and the lower tube measuring φ6*65mm. |
| Types | Ag/AgCI type, neutral electrode; there are two kinds of single salt bridge and double salt bridge |
Mercurous sulfate electrode

| Features | use acidic electrolyte |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 60℃ |
| Dimensions | The overall size of the unit is 140mm, with the upper tube measuring φ9.5*35mm and the lower tube measuring φ6*65mm. |
| Types | Mercury type, acid electrode; there are two kinds of single salt bridge and double salt bridge |
Mercury Oxide Electrode


| Features | Suitable for alkaline electrolytes |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 60℃ |
| Dimensions | The overall size of the unit is 140mm, with the upper tube measuring φ9.5*35mm and the lower tube measuring φ6*65mm. |
| Types | Mercury type, alkaline electrode; there are two kinds of single salt bridge and double salt bridge |
Silver Chloride Type 218

| Features | Suitable for long-term reactions |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 60℃ |
| Dimensions | The overall size of the unit is 145mm, the lower tube measuring φ9.2*120mm. Wiring is U-shaped blade |
| Types | The nature of the electrode is Ag/AgCI type, which can react unattended for a long time |
Silver Chloride Type 219

| Features | Suitable for long-term reactions |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 60℃ |
| Dimensions | The overall size of the unit is 145mm, the lower tube measuring φ9.2*120mm. Wiring is U-shaped blade |
| Types | The nature of the electrode is Ag/AgCI type, and the second liquid junction of the double junction type can be added on demand |
Sand core salt bridge

| Features | Protective electrode, easy to use |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 80℃ |
| Dimensions | Standard φ10*70mm, extended φ10*100mm |
| Types | The built-in sand core liquid junction is used to protect the electrode and reduce the liquid junction potential |
Lukin Capillary

| Features | Protective electrode, easy to use |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 80℃ |
| Dimensions | Standard φ10*70mm, extended φ10*100mm |
| Used to protect the electrode and reduce the liquid junction potential | |
Variable diameter sand core salt bridge

| Features | Protective electrode, easy to use |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 80℃ |
| Dimensions | φ12*70mm / φ6*70mm / φ6*100 |
| Used to protect the electrode and reduce the liquid junction potential | |
Straight Sand Core Salt Bridge

| Features | Protective electrode, easy to use |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 50℃ |
| Dimensions | φ6*80mm / φ10*80mm |
| The guard electrode reduces the liquid junction potential | |
Detail & Parts
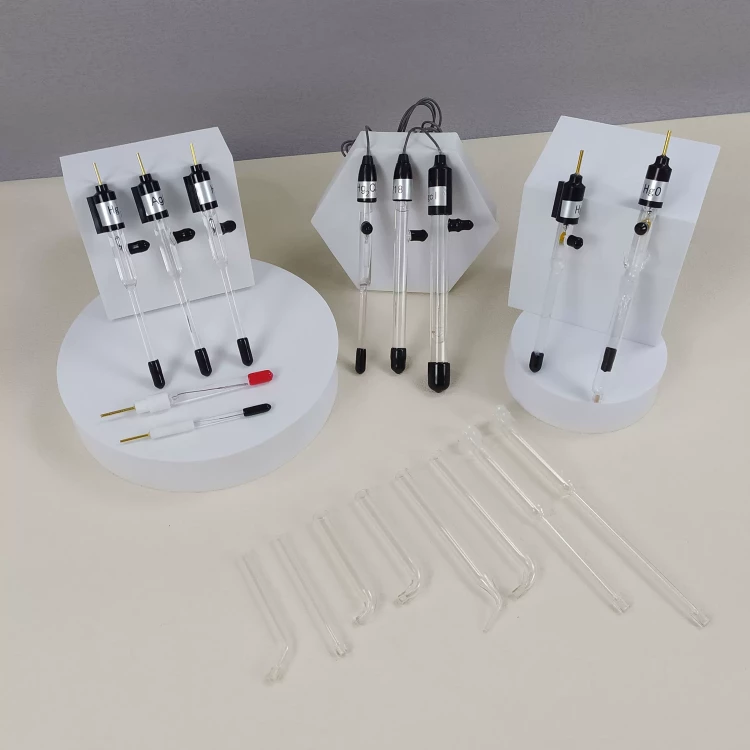
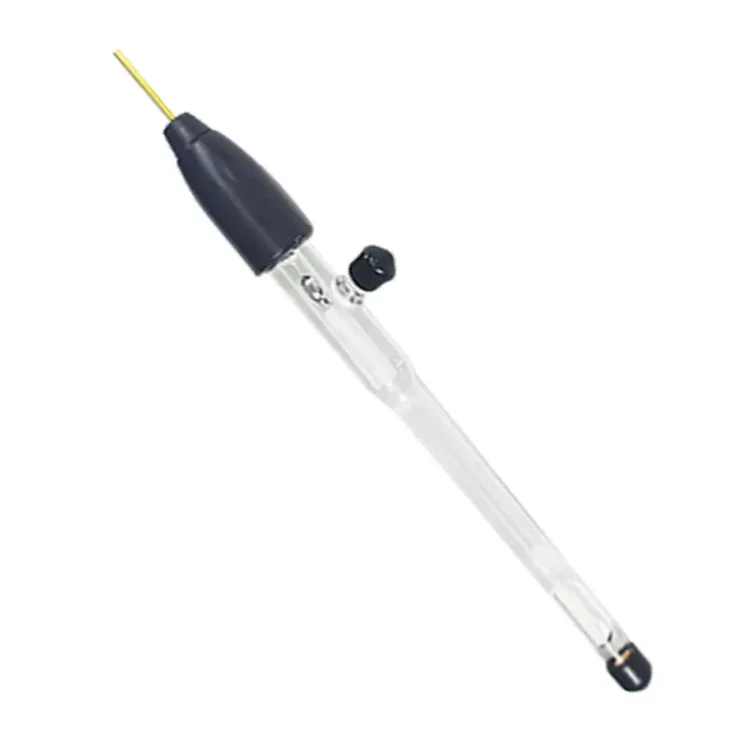
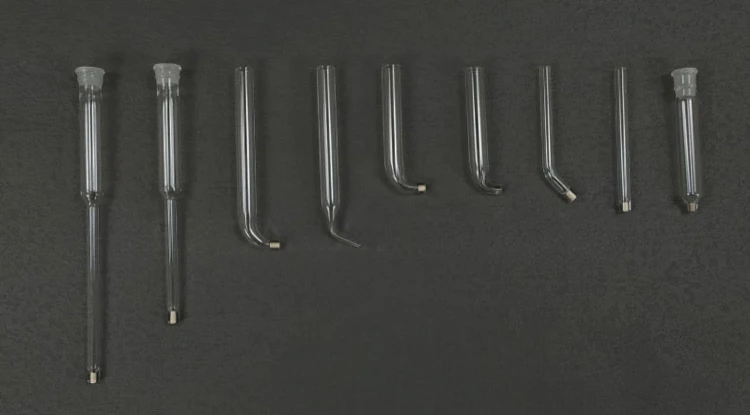
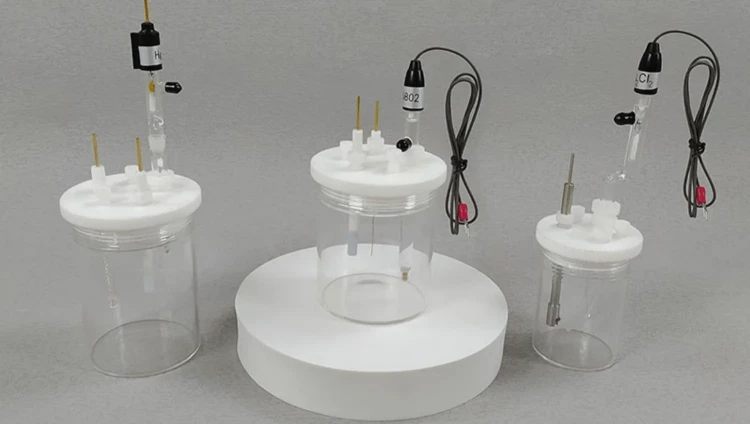
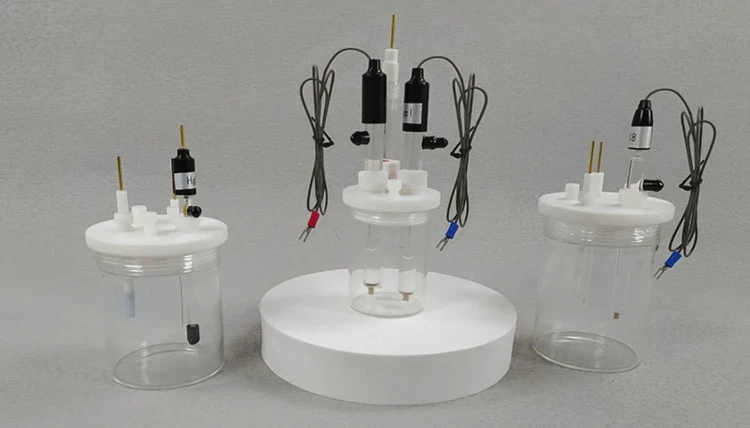
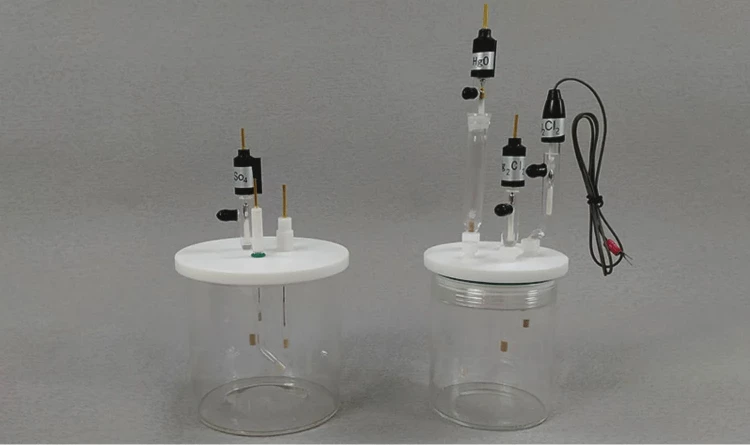
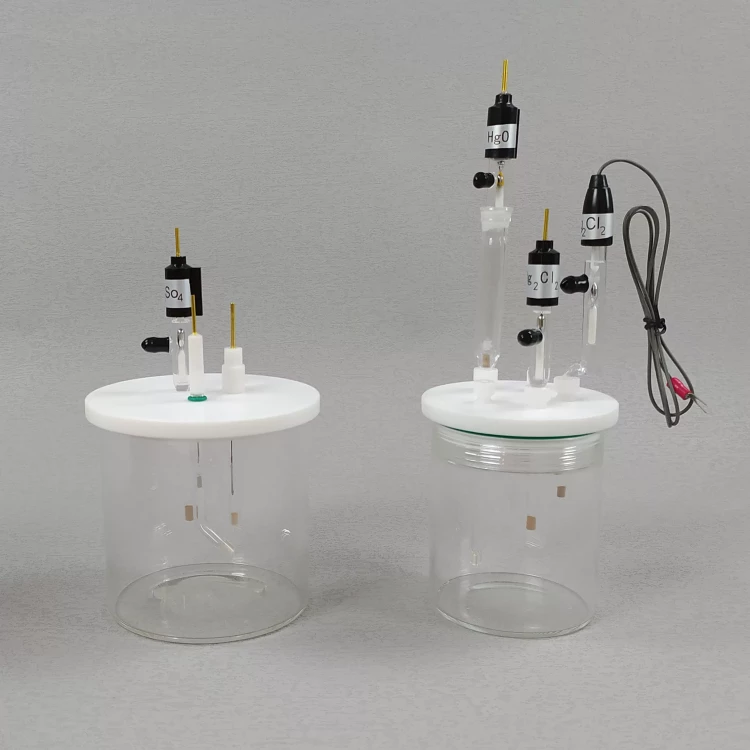


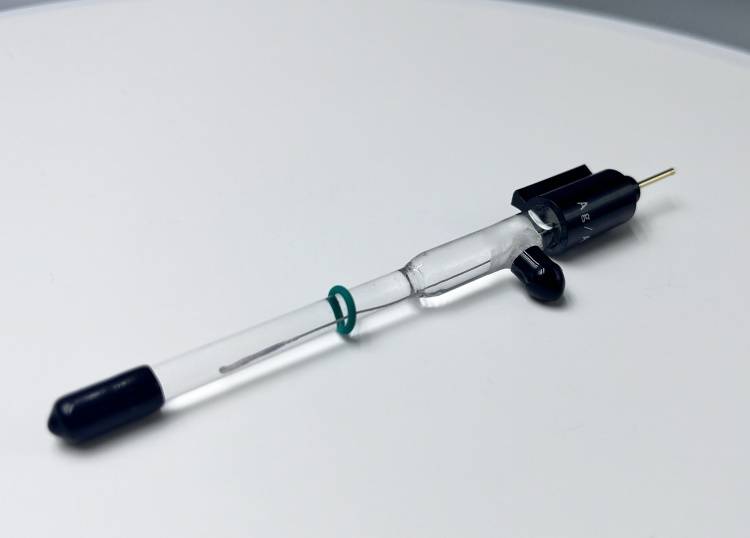
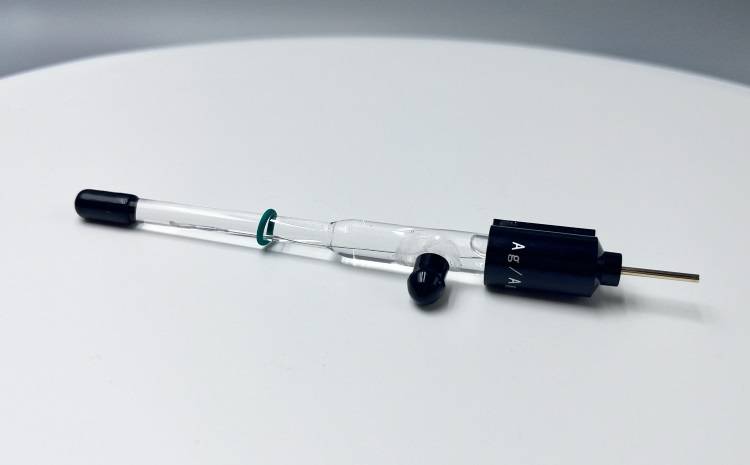
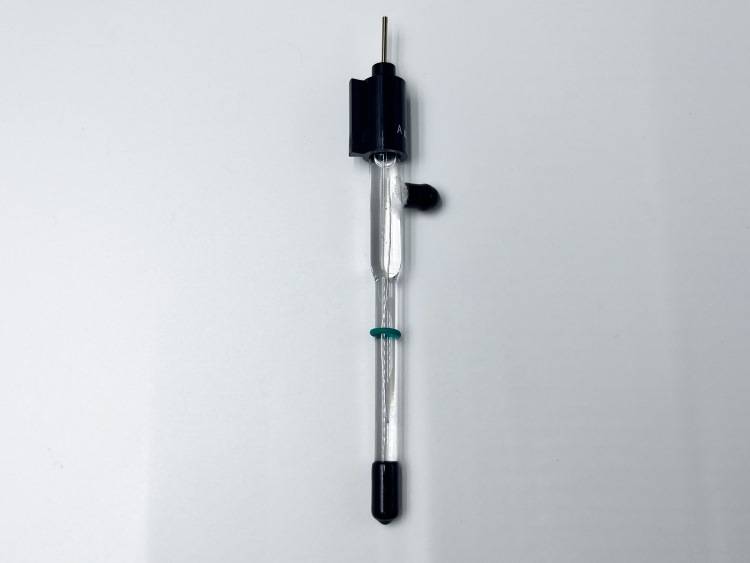





Principle
The Calomel / Silver Chloride / Mercury Sulfate principle is based on the electrochemical reaction between calomel (Hg2Cl2) and silver chloride (AgCl) in the presence of mercury sulfate (HgSO4). When the calomel electrode is immersed in a solution containing chloride ions, the following reaction occurs:
Hg2Cl2(s) + 2e- → 2Hg(l) + 2Cl-(aq)
This reaction generates an electrical potential that is proportional to the concentration of chloride ions in the solution. The silver chloride electrode serves as a reference electrode with a stable and well-defined potential, providing a stable reference point for measuring the potential of the calomel electrode.
Applications
Calomel / Silver Chloride / Mercury Sulfate electrodes are widely used in electrochemistry, particularly in applications such as:
- Reference electrodes in electrochemical cells and potentiometric measurements
- Determination of redox potentials and electrochemical reactions
- Corrosion studies and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
- Electroplating and electrorefining processes
- Monitoring and control of chemical processes in various industries
Designed for You
KinTek provide deep custom made service and equipment to worldwide customers, our specialized teamwork and rich experienced engineers are capable to undertake the custom tailoring hardware and software equipment requirements, and help our customer to build up the exclusive and personalized equipment and solution!
Would you please drop your ideas to us, our engineers are ready for you now!
Trusted by Industry Leaders

FAQ
What Are The Advantages Of Using A Calomel Electrode?
What Are The Different Types Of Reference Electrodes Available?
When Should I Use A Calomel Electrode Instead Of An Ag/AgCl Electrode?
What Is An Electrode In Electrochemistry?
What Is Reference Electrode With An Example?
What Is The Function Of Auxiliary Electrode?
What Are The 3 Electrodes In Electrochemistry?
What Is The Role Of Reference Electrode?
What Is The Difference Between Auxiliary And Reference Electrode?
What Are The Different Types Of Electrochemical Electrodes?
What Is Reference Electrode Used For?
What Materials Are Commonly Used For Auxiliary Electrodes?
What Materials Are Commonly Used For Electrochemical Electrodes?
What Is A Reference Electrode Vs Counter Electrode?
What Is The Difference Between Standard And Reference Electrode?
How Do Auxiliary Electrodes Affect The Performance Of An Electrochemical Cell?
What Factors Should Be Considered When Selecting An Electrochemical Electrode?
Why Are Auxiliary Electrodes Necessary In Electrochemical Systems?
How Can Electrochemical Electrodes Be Used In Various Applications?
Are There Any Limitations Or Considerations When Using Auxiliary Electrodes?
4.7 / 5
The reference electrode is performing as promised and has met my expectations.
4.8 / 5
The reference electrode arrived quickly and in perfect condition. I am very satisfied with the purchase.
4.9 / 5
The quality of the reference electrode is excellent. It is well-made and durable.
4.6 / 5
I have been using the reference electrode for a few weeks now and I am very happy with it. It is easy to use and gives accurate results.
4.7 / 5
The reference electrode is a great value for the price. It is affordable and works just as well as more expensive models.
4.8 / 5
I would definitely recommend the reference electrode to other researchers. It is a reliable and affordable option.
4.9 / 5
The reference electrode has been a great addition to my lab. It has helped me to improve the accuracy of my experiments.
4.7 / 5
I am very satisfied with the reference electrode. It is a high-quality product that has met all of my needs.
4.8 / 5
The reference electrode is a valuable tool for my research. It has helped me to obtain more accurate data.
REQUEST A QUOTE
Our professional team will reply to you within one business day. Please feel free to contact us!
Related Products

Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
Elevate your experiments with our Metal Disk Electrode. High-quality, acid and alkali resistant, and customizable to fit your specific needs. Discover our complete models today.

Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
Explore the benefits of Non-Consumable Vacuum Arc Furnace with high melting point electrodes. Small, easy to operate & eco-friendly. Ideal for laboratory research on refractory metals & carbides.

Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
Get your exclusive CVD furnace with KT-CTF16 Customer Made Versatile Furnace. Customizable sliding, rotating, and tilting functions for precise reactions. Order now!

Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
KT-PE12 Slide PECVD System: Wide power range, programmable temp control, fast heating/cooling with sliding system, MFC mass flow control & vacuum pump.

1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
Discover our KT-12A Pro Controlled atmosphere furnace - high precision, heavy duty vacuum chamber, versatile smart touch screen controller, and excellent temperature uniformity up to 1200C. Ideal for both laboratory and industrial application.

Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
Create uniform samples easily with Square Lab Press Mold - available in various sizes. Ideal for battery, cement, ceramics, and more. Custom sizes available.

Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
Discover our Glassy Carbon Sheet - RVC. Perfect for your experiments, this high-quality material will elevate your research to the next level.

Side Window Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
Experience reliable and efficient electrochemical experiments with a side window optical electrolytic cell. Boasting corrosion resistance and complete specifications, this cell is customizable and built to last.

Thin-Layer Spectral Electrolysis Electrochemical Cell
Discover the benefits of our thin-layer spectral electrolysis cell. Corrosion-resistant, complete specifications, and customizable for your needs.

Conductive Carbon Cloth Carbon Paper Carbon Felt for Electrodes and Batteries
Conductive carbon cloth, paper, and felt for electrochemical experiments. High-quality materials for reliable and accurate results. Order now for customization options.

Square Bidirectional Pressure Mold for Lab Use
Discover precision in molding with our Square Bidirectional Pressure Mold. Ideal for creating diverse shapes and sizes, from squares to hexagons, under high pressure and uniform heating. Perfect for advanced material processing.

50L Chiller Water Bath Cooling Circulator Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
KinTek KCP 50L chilling circulator is a reliable and efficient equipment for supplying constant chilling power with circulating fluids in various working circumstances.

Lab Sterile Slapping Type Homogenizer for Tissue Mashing and Dispersing
The slapping sterile homogenizer can effectively separate the particles contained in and on the surface of solid samples, ensuring that the mixed samples in the sterile bag are fully representative.
Related Articles

Reference Electrodes: Calomel, Silver Chloride, and Mercury Sulfate - A Comprehensive Guide
Explore the world of reference electrodes, including calomel, silver chloride, and mercury sulfate. Understand their construction, principles, and applications in electrochemical measurements.

Understanding Saturated Calomel Reference Electrodes: Composition, Uses, and Considerations
Explore the detailed guide on saturated calomel reference electrodes, including their composition, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. Ideal for researchers and lab technicians.

Comprehensive Guide to Reference Electrodes: Types, Applications, and Selection Criteria
Explore the world of reference electrodes with our detailed guide. Learn about different types, their applications, and how to select the right one for your needs. Ideal for researchers and lab technicians.

AgAgCl Reference Electrode Working Principle and Applications
Ag/AgCl reference electrode is a widely used reference electrode due to its stable potential and long-term stability.

How to Make Your Own Ag/AgCl Reference Electrode for Electrochemical Experiments
A reference electrode is an electrode with a stable and well-defined potential that is used as a reference point to measure the potential of other electrodes. Reference electrodes are commonly used in electrochemical experiments to determine the potential difference between two electrodes.

Electrochemical Electrodes in Chemical Analysis
Electrochemical electrodes are essential tools used in many chemical analysis techniques and experiments. These electrodes are devices that allow us to measure the electrical potential difference in a chemical reaction.

Electrolytes and Electrochemical Electrodes
Electrolytes and electrodes play an essential role in electrochemistry. Electrolytes are substances that conduct electricity when dissolved in water or melted.

A Comprehensive Guide to Reference Electrodes
Reference electrodes are used in electrochemical measurements to establish a stable potential against which the potential of the working electrode can be measured.

A Beginner's Guide to Understanding Reference Electrodes in Electrochemistry
Reference electrodes provide a stable and known potential that other electrodes can be compared to, allowing for accurate measurements of electrochemical reactions.

How to Choose the Right Reference Electrode for Your Application
When it comes to measuring the electrical potential of a solution accurately, a reference electrode is an essential tool in the laboratory. It provides a stable and consistent reference point for other electrodes to measure against, ensuring accurate and reliable results.

A Guide to Choosing the Right Reference Electrode for Your ISE Analysis
Reference electrodes are an essential component of any electrochemical measurement.

How to Choose the Right Electrochemical Electrode
The choice of electrode material can have a significant impact on the performance of the electrochemical system.