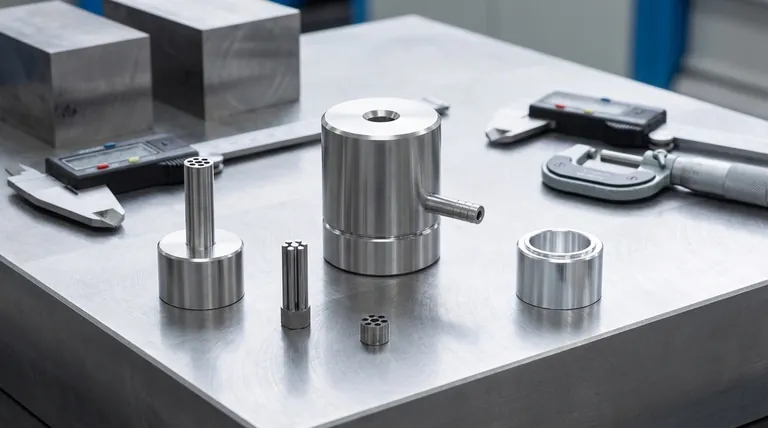
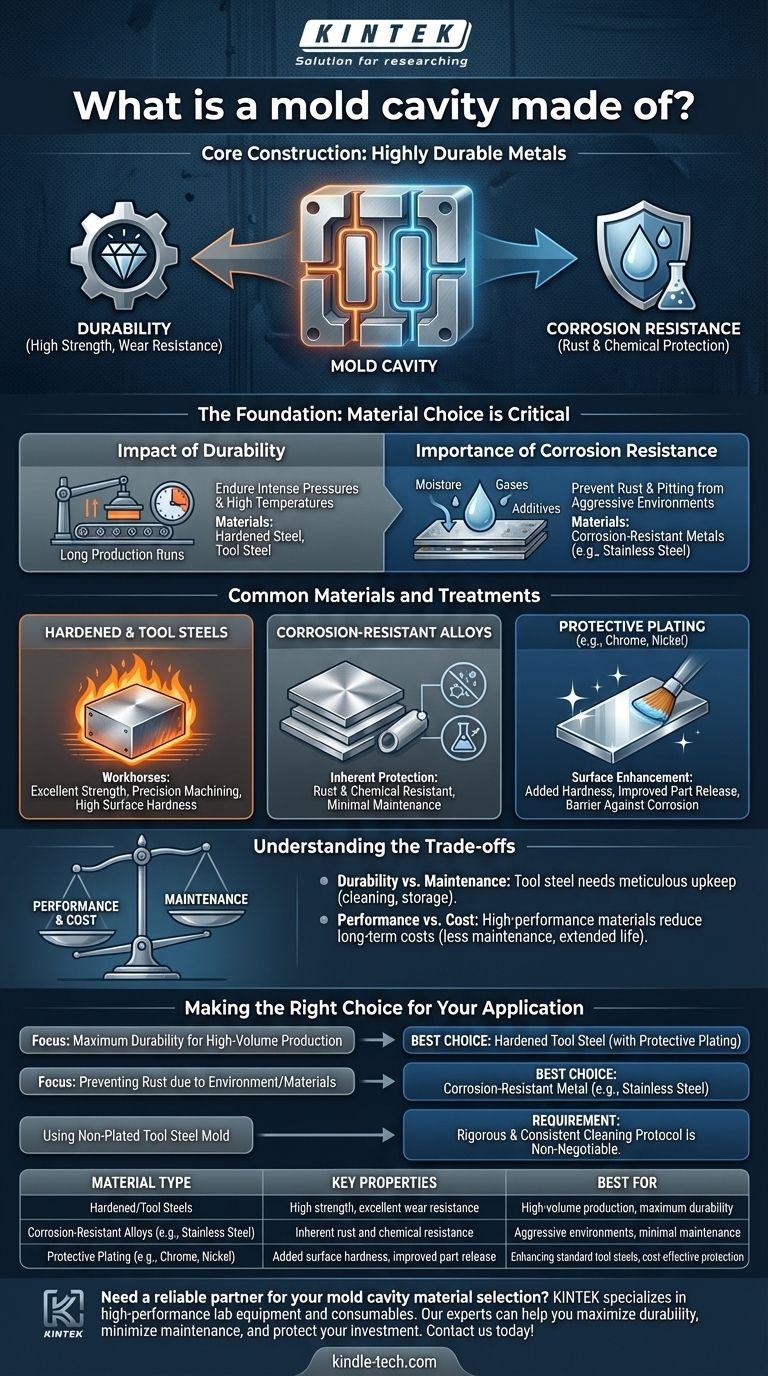
At its core, a mold cavity is constructed from highly durable metals. The most common choices are hardened tool steels and other corrosion-resistant alloys, selected specifically to withstand the intense pressures and temperatures of the molding process while ensuring a long operational life.
The selection of a mold cavity material is a foundational engineering decision that balances durability against the need for corrosion resistance, directly impacting the mold's maintenance requirements and longevity.

The Foundation: Why Material Choice is Critical
The material used for a mold cavity is not arbitrary. It dictates the mold's ability to produce consistent parts over millions of cycles and its vulnerability to environmental or chemical degradation.
The Impact of Durability
A mold cavity must endure immense clamping and injection pressures. Hardened steel and tool steel provide the necessary strength and hardness to resist wear, deformation, and damage over long production runs.
The Importance of Corrosion Resistance
Molding processes can involve moisture, outgassing from plastics, or fire-retardant additives that create a corrosive environment. Using corrosion-resistant metals or protective coatings prevents rust and pitting that would ruin the surface finish and compromise the final parts.
Common Materials and Treatments
While "metal" is the simple answer, the specific type and treatment are chosen based on the application's demands.
Hardened and Tool Steels
These are the workhorses of the molding industry. They offer excellent strength, can be machined to precise tolerances, and can be heat-treated to achieve very high surface hardness.
Corrosion-Resistant Alloys
Metals like stainless steel are inherently resistant to rust and chemical attack. They are chosen when the molding material or operating environment is particularly aggressive, reducing the need for constant maintenance.
The Role of Protective Plating
When a mold is made of a standard tool steel that isn't naturally corrosion-resistant, a layer of protective plating is often applied. Coatings like chrome or nickel add hardness, improve the release of the part, and provide a critical barrier against corrosion.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right material involves balancing performance, cost, and maintenance. Ignoring these factors leads to premature mold failure and production downtime.
Durability vs. Maintenance
A mold made from tool steel without protective plating offers high durability but requires meticulous upkeep. It must be thoroughly cleaned, often with a mild alkaline solution as recommended, and properly stored to prevent rust.
Performance vs. Cost
High-performance materials like stainless steel or molds with advanced plating are more expensive upfront. However, they reduce long-term costs by minimizing maintenance, preventing downtime, and extending the operational life of the tool.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The optimal material depends entirely on the project's specific goals and challenges.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability for high-volume production: A hardened tool steel, ideally with protective plating for wear and corrosion resistance, is the most effective choice.
- If your primary focus is preventing rust due to environment or materials: A mold cavity made from a corrosion-resistant metal like stainless steel is the most reliable path.
- If you are using a non-plated tool steel mold: A rigorous and consistent cleaning and maintenance protocol is non-negotiable to protect your investment.
Ultimately, selecting the correct material is the first step in guaranteeing the quality of your parts and the longevity of your mold.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Properties | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Hardened/Tool Steels | High strength, excellent wear resistance | High-volume production, maximum durability |
| Corrosion-Resistant Alloys (e.g., Stainless Steel) | Inherent rust and chemical resistance | Aggressive environments, minimal maintenance |
| Protective Plating (e.g., Chrome, Nickel) | Added surface hardness, improved part release | Enhancing standard tool steels, cost-effective protection |
Need a reliable partner for your mold cavity material selection? The right material is critical for your mold's performance and longevity. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including materials suited for demanding molding applications. Our experts can help you choose the right solution to maximize durability, minimize maintenance, and protect your investment. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and ensure your production runs smoothly!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Ball Press Mold for Lab
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What technical characteristics are required for specialty pressure molds used in the compaction of Li10GeP2S12? Expert Tips
- Why are custom pressure molds used during the hot pressing process for solid polymer electrolytes?
- What functions do High-Purity Graphite Molds perform? Enhance Your Aluminum Matrix Composite Hot-Press Sintering
- How do custom graphite molds contribute to Al-20% Si/graphite flake composites? Optimize Microstructure & Conductivity
- How does a stainless steel pressure die ensure the quality of the electrolyte layer? Unlock Precision Battery Assembly



















