In essence, a thin film evaporator is a specialized piece of equipment designed to separate mixtures by rapidly heating a very thin layer, or film, of liquid. Its unique design allows for extremely fast and gentle evaporation, making it ideal for processing materials that are sensitive to heat, highly viscous, or have high boiling points.
The core advantage of thin film evaporation is its ability to minimize thermal degradation. By drastically reducing the time a product is exposed to high temperatures, it preserves the quality of sensitive materials that would be destroyed in conventional distillation equipment.

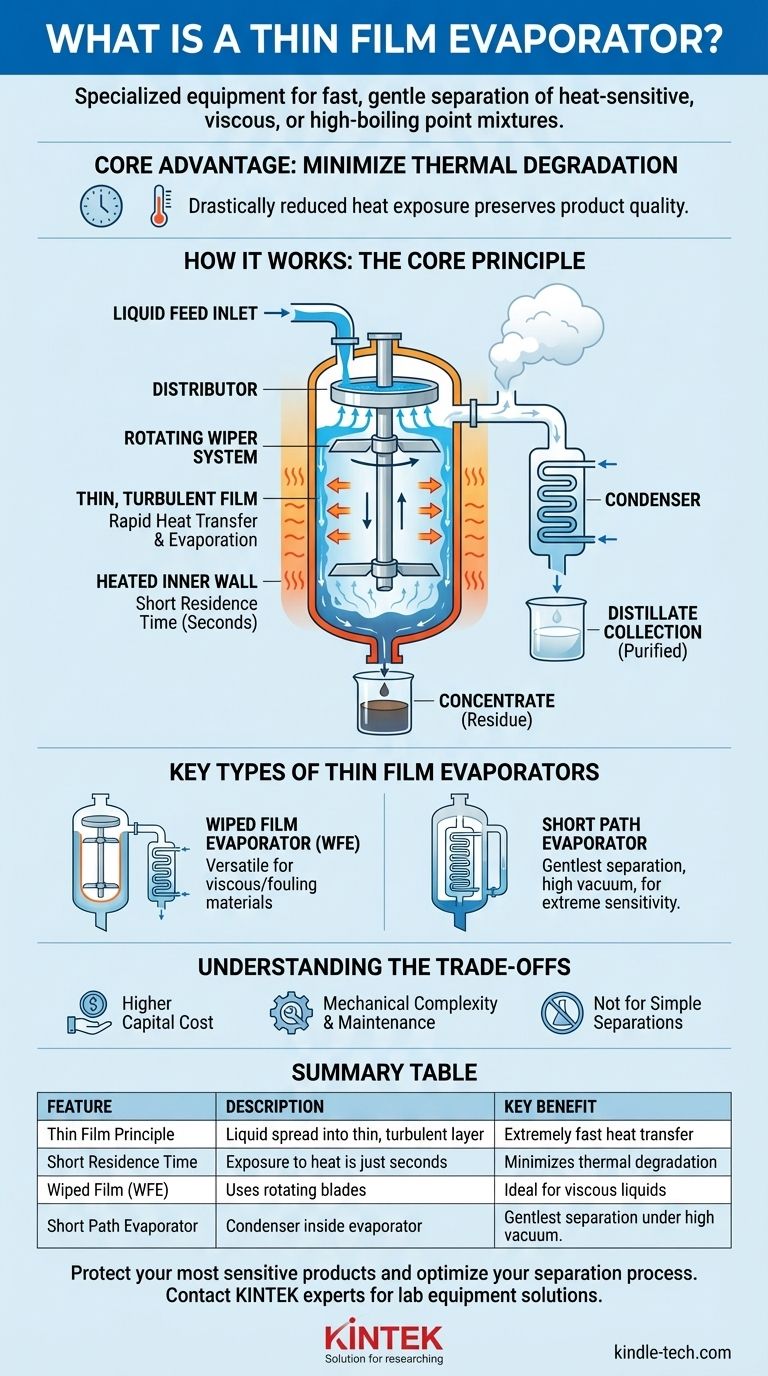
The Core Principle: How Thin Film Evaporation Works
A thin film evaporator operates on a simple but powerful principle: maximizing surface area and minimizing heating time. This is achieved through a precise mechanical process inside a heated vessel.
The Feed System
Liquid feed is introduced at the top of a vertical, heated cylinder. The goal is to distribute this liquid evenly around the inner circumference of the cylinder wall.
The Rotating Wiper System
This is the heart of the machine. A central rotating assembly, equipped with blades or rollers, spins at high speed. These wipers make close contact with the heated inner wall of the cylinder.
As the liquid feed flows down the wall, the rotating wipers continuously spread it into a very thin, turbulent film. This action ensures the entire volume of liquid is constantly renewed and exposed to the heated surface.
Rapid Heat Transfer and Evaporation
Because the liquid film is incredibly thin (often less than a millimeter), heat transfers from the cylinder wall almost instantaneously. This causes the more volatile components of the mixture to evaporate rapidly.
This entire process, from feed inlet to exit, can take just a few seconds. This extremely short residence time is what protects heat-sensitive products.
Separate Collection of Products
The generated vapor flows to a condenser, where it is cooled and collected as the distillate (the purified, volatile component). The less volatile, concentrated liquid continues to flow down the cylinder wall and is collected at the bottom as the concentrate or residue.
Key Types of Thin Film Evaporators
While the principle is the same, different designs are optimized for specific applications.
Wiped Film Evaporator (WFE)
This is the most common configuration. It uses rotating blades that maintain a small clearance from the heated wall to create the thin film. WFEs are versatile and effective for a wide range of viscous and fouling materials.
Short Path Evaporator
A short path evaporator is a specialized type of WFE that integrates the condenser inside the evaporator body. The condenser is placed centrally, directly opposite the heated wall where the film is generated.
This design creates the shortest possible travel distance—or "short path"—for the vapor. It is critical for operating under a deep vacuum, which lowers the mixture's boiling point and provides the gentlest possible separation for extremely sensitive materials like vitamins, oils, and pharmaceuticals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, thin film evaporators are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Capital Cost
The mechanical precision required for the rotating internals and vacuum systems makes this technology significantly more expensive than simpler alternatives like falling film or rising film evaporators.
Mechanical Complexity and Maintenance
The internal rotor, bearings, and vacuum seals are moving parts that require regular maintenance and can be points of failure. This adds to the operational cost and complexity compared to static equipment.
Not Ideal for Simple Separations
For low-viscosity, non-heat-sensitive materials (like separating salt from water), the benefits of a thin film evaporator do not justify its cost and complexity. Simpler, more energy-efficient methods are better suited for these tasks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct evaporation technology depends entirely on the properties of your material and your final goal.
- If your primary focus is processing highly heat-sensitive or high-molecular-weight materials: A short path evaporator is the superior choice due to its low-temperature, high-vacuum capabilities.
- If your primary focus is handling viscous liquids or feeds with suspended solids: A standard wiped film evaporator provides the necessary mechanical agitation to ensure efficient heat transfer and prevent fouling.
- If your primary focus is a simple, cost-effective solvent recovery from a non-sensitive product: A simpler technology like a falling film evaporator is likely a more practical and economical solution.
Ultimately, choosing a thin film evaporator is a strategic decision to protect product integrity in applications where conventional methods would fail.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Thin Film Principle | Liquid is spread into a thin, turbulent layer on a heated wall. | Extremely fast heat transfer and evaporation. |
| Short Residence Time | Product exposure to heat is just seconds. | Minimizes thermal degradation of sensitive materials. |
| Wiped Film (WFE) | Uses rotating blades to create the film. | Ideal for viscous liquids and materials prone to fouling. |
| Short Path Evaporator | Condenser is inside the evaporator body. | Gentlest separation for extremely sensitive products under high vacuum. |
Protect your most sensitive products and optimize your separation process.
Choosing the right evaporation technology is critical for product quality and process efficiency. The experts at KINTEK specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing tailored solutions for your laboratory's unique challenges. Whether you're working with high-value pharmaceuticals, delicate oils, or complex chemical mixtures, we can help you select the ideal thin film evaporator to preserve your product's integrity.
Contact us today to discuss your application and discover how our expertise can enhance your lab's capabilities.
Get in touch with our specialists now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Lab Sterile Slapping Type Homogenizer for Tissue Mashing and Dispersing
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















