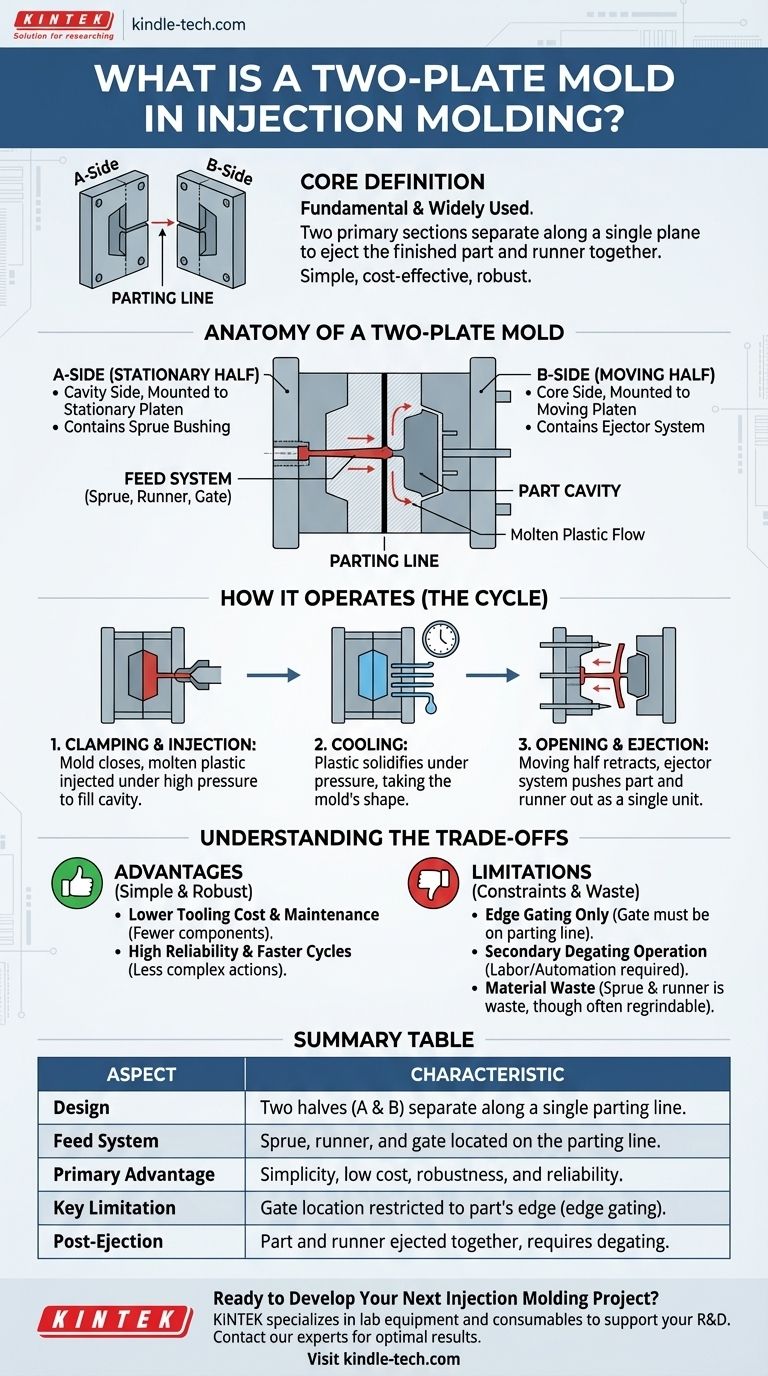
A two-plate mold is the most fundamental and widely used design in injection molding. It consists of two primary sections, often called the A-side and B-side, which come together to form the part cavity and then separate along a single plane, known as the parting line, to eject the finished part.
At its core, the two-plate mold is defined by its simplicity. Because the part and its plastic feed system (the runner) are on the same side of the parting line, they are ejected together, making this design cost-effective and robust but limiting where the plastic can be injected into the part.

The Anatomy of a Two-Plate Mold
To understand its function, you must first understand its core components. The design is a study in efficient, direct mechanics.
The Stationary Half (A-Side)
This half, also known as the cavity side, is mounted to the stationary platen of the injection molding machine. It contains the sprue bushing, which receives the molten plastic directly from the machine's nozzle.
The Moving Half (B-Side)
This half, also known as the core side, is mounted to the moving platen of the machine. It contains the ejector system (pins, sleeves, etc.) responsible for pushing the solidified part out of the mold after it opens.
The Parting Line
This is the single surface where the A-side and B-side meet when the mold is closed. The separation of the mold happens exclusively along this plane. This is the defining feature that distinguishes it from more complex mold types.
The Feed System (Sprue, Runner, and Gate)
In a two-plate mold, the entire feed system is machined into the parting line. The sprue connects the nozzle to the runners, which are channels that guide plastic to the gates—the small openings where plastic enters the actual part cavity.
How a Two-Plate Mold Operates
The molding cycle is a direct reflection of the mold's simple structure. Each step is clear and sequential.
1. Clamping and Injection
The molding machine closes the mold, clamping the two halves together with immense force. Molten plastic is then injected under high pressure, traveling through the sprue and runner system to fill the part cavity.
2. Cooling
Once the cavity is filled, the plastic is held under pressure and begins to cool and solidify, taking the shape of the mold. This cooling phase is a critical part of the overall cycle time.
3. Opening and Ejection
The moving platen retracts, separating the mold at the parting line. As it opens, the ejector system on the B-side activates, pushing the part, the attached runner, and the sprue out of the mold as a single unit.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The simplicity of the two-plate design brings a clear set of advantages and limitations that are critical for any technical professional to understand.
Key Advantage: Simplicity and Cost
Fewer components and no complex mechanical actions make two-plate molds the most cost-effective to design, manufacture, and maintain. This is their primary business advantage.
Key Advantage: Robustness and Speed
The simple design is inherently robust, with fewer parts that can wear out or fail. This leads to high reliability in production and can support faster cycle times when compared to more complex actions required by other mold types.
Limitation: Gating Location
This is the most significant technical constraint. Because the runner system is on the parting line, the gate must also be on the edge of the part. This is known as edge gating. It is not suitable for parts that require a gate in the cosmetic center or away from the parting line for structural or flow reasons.
Limitation: Secondary Operations
The solidified runner system remains attached to the part after ejection. This requires a secondary operation—either manual or robotic—to separate the runner from the finished parts. This "degating" step adds labor cost and time to the overall production process.
Limitation: Material Waste
The sprue and runner system is waste material. While this plastic can often be reground and reused (regrind), it represents a processing inefficiency, especially in multi-cavity molds with large, complex runners.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Choosing a two-plate mold is a strategic decision driven by part design, budget, and production requirements.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness: The two-plate mold is the default choice for its low tooling investment and simple maintenance.
- If your part design allows for edge gating: This design is ideal for parts where a gate mark on the parting line is aesthetically and functionally acceptable.
- If you are producing simple, high-volume parts: The robustness and reliability of a two-plate mold make it a workhorse for producing items that don't have complex geometric or cosmetic requirements.
- If automated degating is not a priority: For smaller runs or situations where a manual secondary operation is feasible, the benefits of the simple mold often outweigh the cost of degating.
By understanding these fundamental trade-offs, you can confidently specify the right tooling, ensuring an efficient balance between cost, quality, and production speed.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Two-Plate Mold Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Design | Two halves (A-side & B-side) that separate along a single parting line. |
| Feed System | Sprue, runner, and gate are all located on the parting line. |
| Primary Advantage | Simplicity, low cost, robustness, and reliability. |
| Key Limitation | Gate location is restricted to the part's edge (edge gating). |
| Post-Ejection | Part and runner are ejected together, requiring a secondary degating operation. |
Ready to Develop Your Next Injection Molding Project?
Choosing the right mold design is critical for balancing cost, quality, and production efficiency. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables needed to support your R&D and production processes, ensuring you have the right tools for success.
Let us help you achieve optimal results. Our expertise can guide you in selecting the perfect solution for your specific application.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Carbon Graphite Plate Manufactured by Isostatic Pressing Method
- Lab Internal Rubber Mixer Rubber Kneader Machine for Mixing and Kneading
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Stirring Bar Recovery Rod
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the properties of the graphite? Unlock High-Temperature Strength & Conductivity
- What role does convection play in heat transfer? Understanding Heat Movement in Fluids
- Does graphite lead electricity? Unlocking the Secrets of Its Atomic Structure
- What are the advantages disadvantages and uses of sheet metal? The Ultimate Guide to Material Selection
- How can different materials have different heat capacity? Unlocking the Microscopic Secrets of Energy Storage











