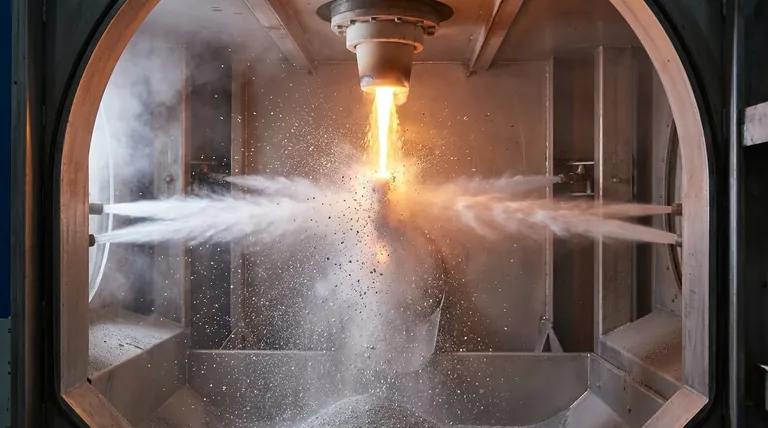
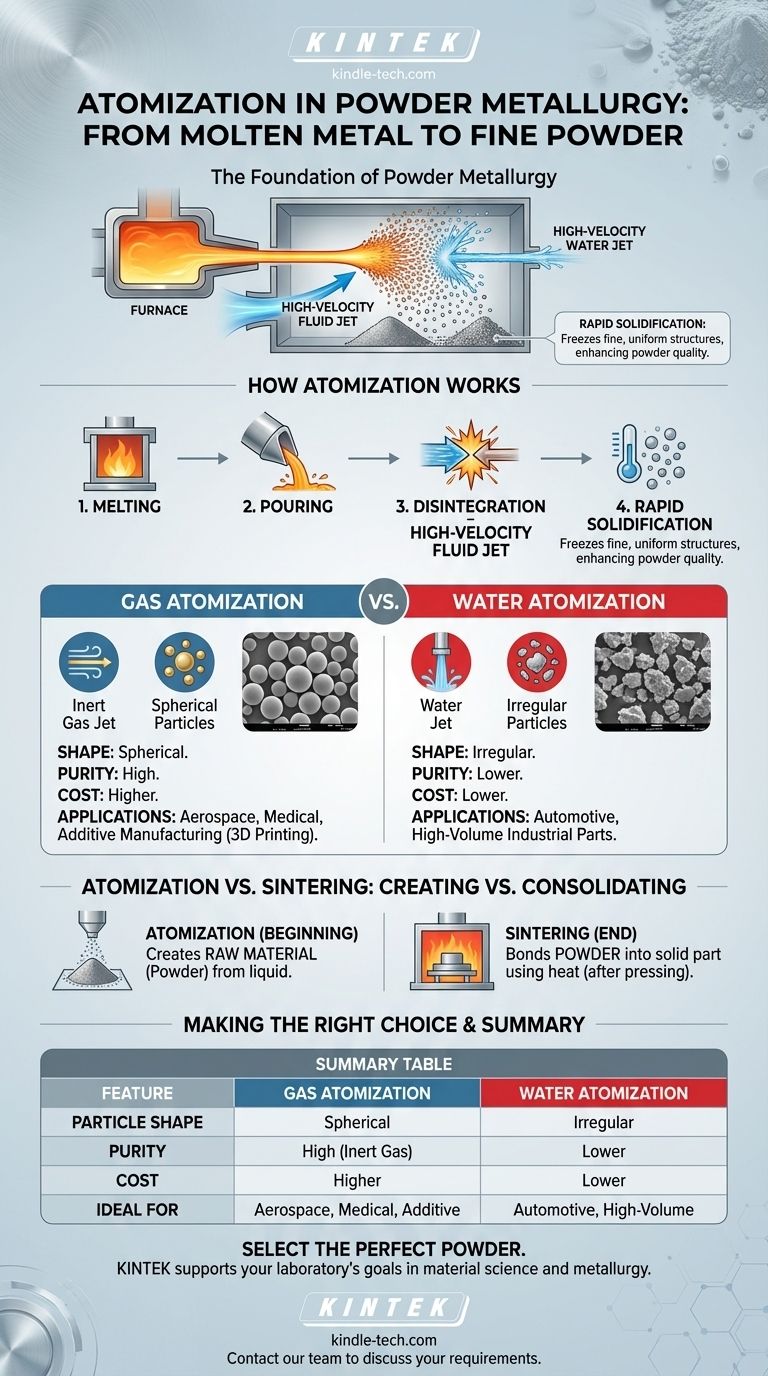
In powder metallurgy, atomization is the dominant process for converting molten metal into a fine powder. This is accomplished by striking a stream of liquid metal with a high-velocity jet of gas or liquid, which breaks the metal into millions of tiny droplets that cool and solidify into powder particles before they even hit the ground.
Atomization is the foundational step that dictates the final properties of a powder metallurgy part. The method used to create the powder—its shape, size, and purity—directly controls the strength, density, and performance of the finished component.

How Atomization Works: From Liquid to Powder
Atomization is a physical process of disintegration. A carefully controlled stream of molten metal is engineered to collide with a high-energy fluid.
The Core Mechanism
The process begins by melting the desired metal or alloy in a furnace. This molten metal is then poured through a specialized nozzle, forming a predictable stream.
A high-pressure jet of gas or liquid is directed at this molten stream. The immense kinetic energy of the jet shatters the liquid metal into a spray of fine droplets.
The Role of Rapid Solidification
These droplets, now dispersed in the atomizing chamber, cool and solidify almost instantly. This rapid solidification is critical, as it freezes a very fine and uniform chemical structure into each powder particle, which is a key advantage of powder metallurgy.
Gas Atomization vs. Water Atomization
The fluid used has a profound impact on the final powder.
- Gas Atomization: Uses a high-pressure jet of inert gas, such as argon or nitrogen. This produces highly spherical powder particles with excellent purity because the inert gas prevents oxidation during the process.
- Water Atomization: Uses a high-pressure jet of water. This is a more aggressive quenching process, resulting in irregular, non-spherical powder particles. It is faster and more cost-effective than gas atomization.
Atomization vs. Sintering: Creating vs. Consolidating
It is crucial to distinguish between atomization and sintering, as they represent the beginning and end of the powder metallurgy workflow.
Atomization: The Beginning of the Process
Atomization is the manufacturing process for the raw material. Its sole purpose is to produce the metal powder from a bulk liquid state.
Sintering: Nearing the Finish Line
Sintering is a heat treatment that happens much later. After the powder is made, it is pressed into a desired shape (a "green compact").
This compact is then heated in a furnace to a temperature below the metal's melting point. During sintering, the powder particles bond and fuse together, creating a solid, dense part with mechanical strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between atomization methods is not about which is "better," but which is right for the application. The decision creates a cascade of consequences for both cost and performance.
Gas Atomization: High Performance, High Cost
The spherical, pure powders created by gas atomization flow very well and pack predictably. This makes them essential for high-performance applications like aerospace components, medical implants, and advanced additive manufacturing where material integrity is paramount. This quality comes at a higher production cost.
Water Atomization: High Volume, Lower Cost
The irregular powders from water atomization are significantly cheaper to produce. While they don't flow as well as spherical powders, their jagged shape provides good "mechanical interlocking" when pressed, leading to strong green compacts. This makes them the workhorse of the automotive and industrial parts industries.
Control Dictates Quality
In any atomization method, process control is everything. Adjusting parameters like metal temperature, nozzle design, and fluid pressure allows manufacturers to precisely tailor the final particle size distribution to meet the requirements of the application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct powder type is the first and most important decision in designing a powder metallurgy component.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and material purity: Gas-atomized powders are the necessary choice for their sphericity and low oxygen content, despite the higher cost.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production: Water-atomized powders offer an excellent and economical balance of properties for industrial and automotive parts.
- If your primary focus is strength before sintering: The irregular shape of water-atomized powder can provide advantages in creating a robust component after pressing but before the final heating stage.
Ultimately, understanding the atomization process empowers you to select the right raw material, which is the most critical decision in powder metallurgy.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Gas Atomization | Water Atomization |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Shape | Spherical | Irregular |
| Purity | High (Inert Gas) | Lower |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Ideal For | Aerospace, Medical, Additive Manufacturing | Automotive, High-Volume Industrial Parts |
Ready to select the perfect metal powder for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for material science and metallurgy. Whether you're developing components for aerospace, medical implants, or high-volume automotive parts, understanding your raw material is the first step to success.
Our experts can help you navigate the complexities of powder metallurgy to ensure you get the performance and cost-efficiency you need.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- How is diamond coating made? A Guide to CVD and PVD Methods
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies



















