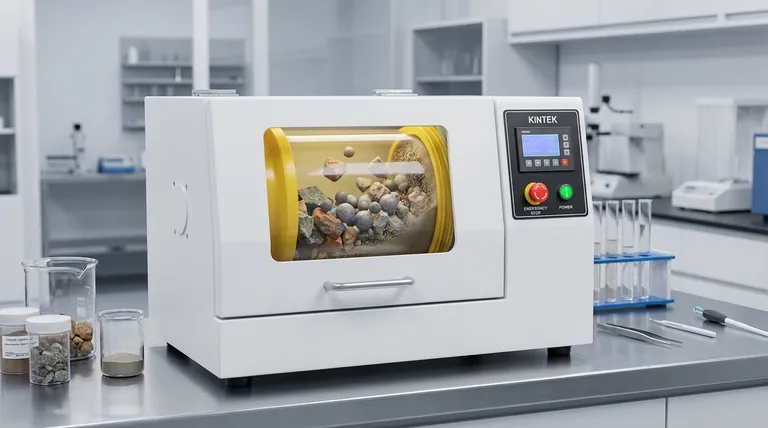
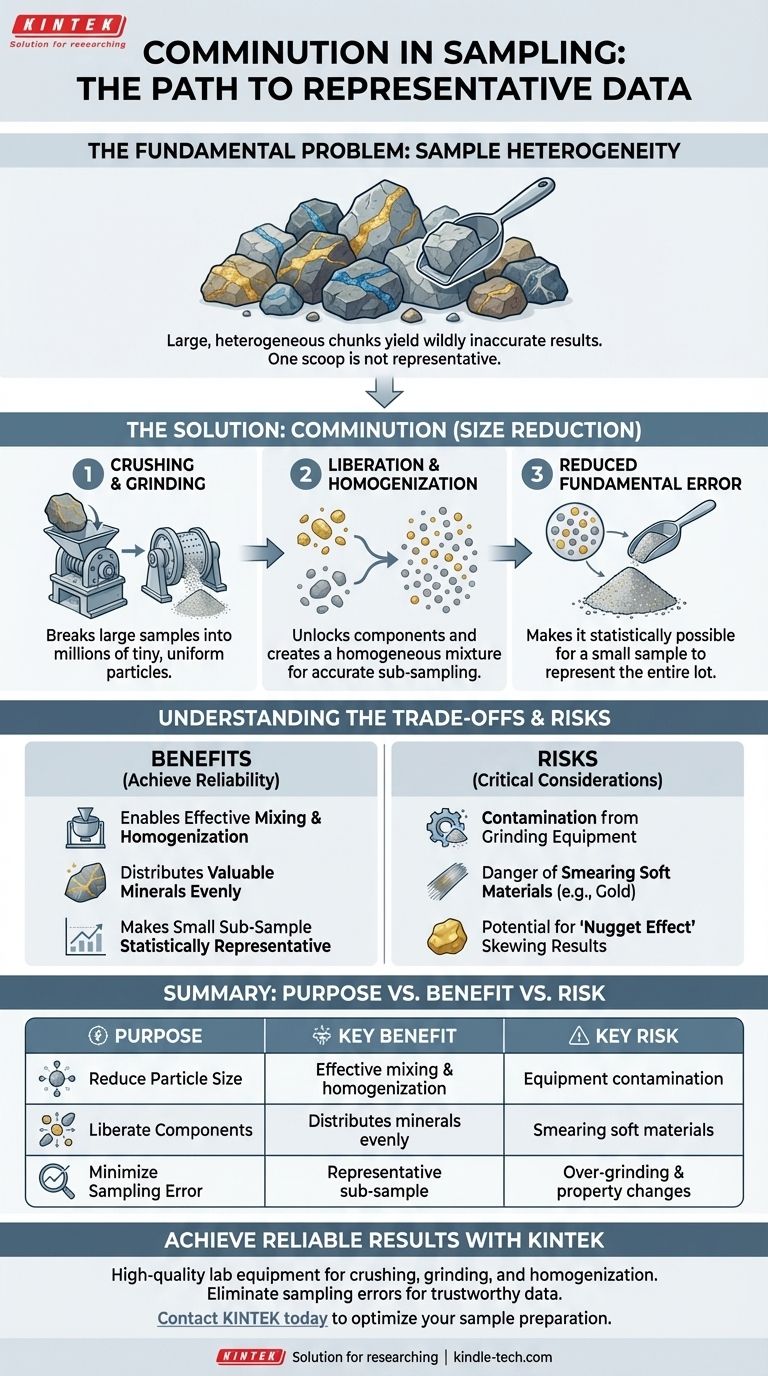
In the context of sampling, comminution is the process of reducing particle size. It involves the systematic breaking, crushing, or grinding of a large, coarse sample into a collection of much finer particles. This is not an arbitrary step; it is a foundational requirement for ensuring that a small sub-sample taken for laboratory analysis is truly representative of the much larger original batch of material.
The core challenge in sampling is that valuable components are often unevenly distributed within a large volume of material. Comminution solves this by breaking down large, heterogeneous chunks into millions of tiny, uniform particles, making it statistically possible for a small scoop to accurately reflect the composition of the whole.

The Fundamental Problem: Sample Heterogeneity
Why You Can't Analyze a Single Large Chunk
Raw materials like ore, rock, or industrial products are rarely uniform. The components you wish to measure—be it a precious metal, a contaminant, or a key ingredient—are often locked within larger particles in a non-uniform way.
Analyzing one large chunk would be like judging an entire batch of chocolate chip cookie dough by examining a single scoop that might contain ten chips or no chips at all. The result would be wildly inaccurate and misleading.
The Goal of Representativeness
The ultimate goal of sampling is to obtain a representative sample. This means the small portion sent to the lab for analysis must possess the same average physical and chemical properties as the entire batch, or "lot," from which it was taken.
Without this guarantee of representativeness, the subsequent, often expensive, chemical analysis is worthless. The entire process hinges on the quality of the initial sample preparation.
How Comminution Creates a Representative Sample
Reducing Fundamental Error
The primary purpose of comminution is to reduce what is known as the "Fundamental Sampling Error." This error is directly related to the size and distribution of particles in the sample.
By crushing a sample, you dramatically increase the number of individual particles. A single 1-kilogram rock becomes millions of tiny grains.
Liberating and Distributing Components
As the reference material notes, comminution serves to liberate valuable minerals from the waste rock, or "gangue," that surrounds them.
In sampling, this liberation allows the now-separate particles of interest to be distributed more evenly throughout the entire sample volume during mixing. It unlocks the components so they can be properly randomized.
Enabling Homogenization
You cannot effectively mix a pile of large, irregular rocks to achieve a uniform blend. However, a fine powder can be easily blended, rolled, or spun to create a homogeneous state.
Comminution is the essential precursor to homogenization. By reducing the material to a fine powder, you make it possible to mix it thoroughly, ensuring that every scoop has a near-identical composition.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
The Risk of Contamination
The equipment used for comminution—crushers and grinders made of steel, ceramic, or tungsten carbide—can wear down during use. This can introduce small amounts of foreign material into your sample.
For general bulk analysis, this may be negligible. But for high-precision trace element analysis, this contamination can be a significant source of error.
The Danger of Smearing or Over-Grinding
Excessive or improper grinding can be detrimental. For soft, malleable materials like native gold or lead, aggressive grinding can "smear" the metal across the grinding surfaces instead of breaking it into particles.
Over-grinding can also alter the chemical properties of a material or cause the loss of fine, dusty components, skewing the final analysis.
The "Nugget Effect"
Even after comminution, a sample can suffer from the nugget effect. This occurs when a few, small-but-exceptionally-rich particles exist within the sample powder.
If a sub-sample happens to include one of these "nuggets" (or happens to miss it), the result will be skewed high or low. Proper comminution aims to crush the material fine enough to minimize this effect, but it remains a critical consideration in high-variability materials like gold ore.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Properly applied comminution is a non-negotiable step in achieving reliable analytical data. The specific approach, however, depends on your objective.
- If your primary focus is an accurate grade of a bulk material: Your goal is to crush the sample fine enough so the sub-sample taken for analysis overcomes heterogeneity and truly represents the average composition.
- If your primary focus is analyzing for trace contaminants: You must balance the need for fine particles with the significant risk of introducing contamination from the crushing equipment itself.
- If your primary focus is preserving physical properties: You must use the minimum amount of comminution necessary, as excessive grinding can fundamentally alter particle shape, surface area, and chemical reactivity.
Ultimately, understanding and controlling comminution is the foundation upon which all accurate sample analysis is built.
Summary Table:
| Purpose of Comminution | Key Benefit | Key Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Reduce Particle Size | Enables effective mixing and homogenization | Risk of contamination from grinding equipment |
| Liberate Components | Distributes valuable minerals evenly | Danger of smearing soft materials (e.g., gold) |
| Minimize Sampling Error | Makes a small sub-sample statistically representative | Potential for over-grinding and altering properties |
Achieve Reliable Analytical Results with KINTEK
Accurate analysis starts with proper sample preparation. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for crushing, grinding, and homogenization, serving the precise needs of laboratories.
Let us help you eliminate sampling errors and ensure your data is trustworthy. Our experts can guide you to the right equipment for your specific material and analysis goals.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your sample preparation challenges and optimize your process for reliable results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon nitride or zirconia preferred for milling iodo-vanadate-lead precursors? Ensure High Purity Results
- Why use zirconia ball milling jars for SiC/ZTA composite powders? Ensure High Purity & Efficient Particle Refinement
- What is the ball mill based on the principle of? Impact and Attrition for Efficient Grinding
- What is the benefit of using tungsten carbide (WC) milling jars and balls? Achieve High-Energy Milling Efficiency
- Why are tungsten carbide grinding jars and balls preferred for high-purity lithium ceramic powders? Ensure Peak Purity.



















