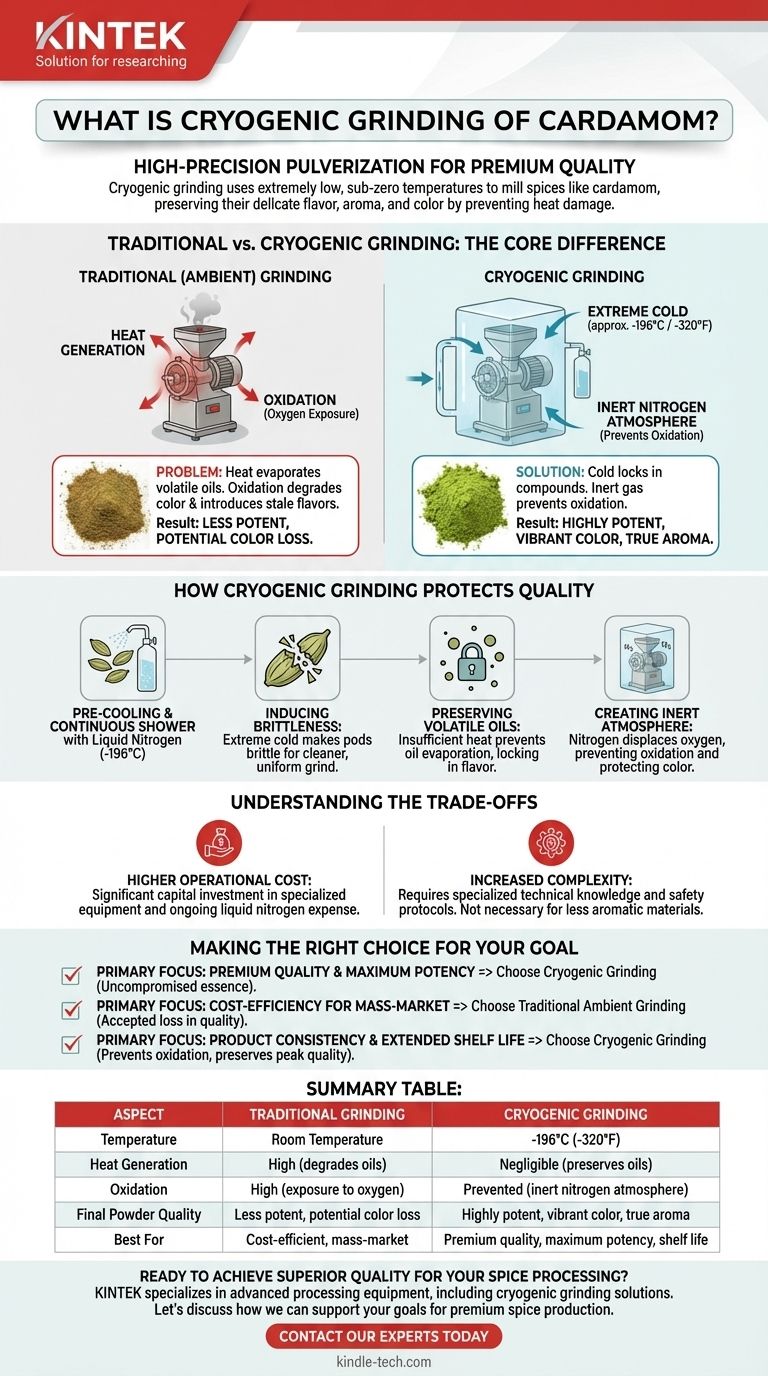
In essence, cryogenic grinding is a high-precision method of pulverizing spices like cardamom at extremely low, sub-zero temperatures. The process uses liquid nitrogen to chill the cardamom to a brittle, glass-like state before and during grinding. This prevents the heat generated by friction from destroying the spice's delicate flavor, aroma, and color.
Traditional grinding methods generate heat, which causes the volatile essential oils in cardamom to evaporate, permanently degrading its quality. Cryogenic grinding solves this problem by using extreme cold to lock in these compounds, resulting in a final powder that is significantly more potent and true to its original state.

The Core Problem with Traditional Grinding
Traditional, or ambient, grinding methods operate at room temperature. While effective for reducing size, this process introduces two primary enemies to high-quality spices: heat and oxygen.
The Enemy: Heat
The friction created by mechanical grinders generates significant heat. This heat causes the delicate and volatile oils responsible for cardamom's unique aroma and flavor to vaporize and escape.
The Impact: Oxidation
As the spice is broken down, its internal structures are exposed to oxygen in the air. This exposure, accelerated by the grinding heat, leads to oxidation, which degrades the spice's natural color and can introduce stale flavors.
How Cryogenic Grinding Protects Quality
Cryogenic grinding is a systematic approach designed to counteract the destructive forces of heat and oxidation. It relies on the properties of liquid nitrogen to create the ideal grinding environment.
The Role of Liquid Nitrogen
Cardamom is pre-cooled and continuously showered with liquid nitrogen, which maintains a temperature of around -196°C (-320°F) throughout the grinding process.
Inducing Brittleness for a Cleaner Grind
The extreme cold makes the fibrous cardamom pods intensely brittle. This allows the grinding machinery to cleanly shatter the material rather than tearing or smearing it. The result is a much finer and more uniform particle size.
Preserving Volatile Oils
Because the entire process occurs at sub-zero temperatures, there is insufficient thermal energy for the volatile oils to evaporate. They remain locked within the spice particles, preserving the full aromatic profile.
Creating an Inert Atmosphere
As the liquid nitrogen turns from a liquid to a gas, it displaces all the oxygen in the grinding chamber. This creates a dry, inert nitrogen atmosphere, completely preventing oxidation and protecting the cardamom's vibrant green color and complex flavor.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the quality benefits are clear, cryogenic grinding is a more complex and resource-intensive process than traditional methods.
Higher Operational Cost
The specialized equipment—including insulated grinders, pressure valves, and storage for liquid nitrogen—represents a significant capital investment. The ongoing cost of the liquid nitrogen itself is also a major operational expense.
Increased Complexity
Operating a cryogenic grinding system requires specialized technical knowledge and stringent safety protocols for handling super-cooled liquid gases. It is not as straightforward as a conventional ambient grinder.
Not a Universal Necessity
The profound benefits of cryogenic grinding are most apparent in high-oil, delicate spices like cardamom, cloves, nutmeg, and vanilla. For tougher, less aromatic materials, the additional cost may not provide a proportional return in quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use cryogenic grinding depends entirely on the desired quality and positioning of the final product.
- If your primary focus is premium quality and maximum potency: Cryogenic grinding is the definitive choice for capturing the full, uncompromised essence of the cardamom.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for mass-market applications: Traditional ambient grinding is often sufficient, though it comes with an accepted loss in quality.
- If your primary focus is product consistency and extended shelf life: The investment in cryogenic technology provides a clear return by preventing oxidation and preserving the spice at its peak.
Ultimately, understanding the impact of temperature in the grinding process is the key to protecting the integrity of a spice from its raw form to the final powder.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Traditional Grinding | Cryogenic Grinding |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Room Temperature | -196°C (-320°F) |
| Heat Generation | High (degrades oils) | Negligible (preserves oils) |
| Oxidation | High (exposure to oxygen) | Prevented (inert nitrogen atmosphere) |
| Final Powder Quality | Less potent, potential color loss | Highly potent, vibrant color, true aroma |
| Best For | Cost-efficient, mass-market applications | Premium quality, maximum potency, shelf life |
Ready to achieve superior quality for your spice processing?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory and processing equipment, including solutions for cryogenic grinding. Our expertise helps you preserve the delicate flavors and aromas of high-value materials like cardamom, ensuring your final product stands out for its potency and quality.
Let's discuss how we can support your goals for premium spice production.
Contact our experts today to explore the right equipment for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Research and Development
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
- Laboratory Jaw Crusher
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- How does the use of a vacuum freeze dryer benefit cys-CDs powder preparation? Preserve Nanoparticle Integrity
- Why is a laboratory vacuum freeze dryer essential for plant extracts? Preserve Bioactivity & Structure
- Why is vacuum freeze-drying equipment superior to conventional oven drying? Protect Hydrogel Precursors Structure
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum freeze dryer? Optimize Yttrium Oxide Nanopowder Precursors
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred over thermal drying for Fe-ZTA cermets? Ensure Pure, Homogeneous Slurry Processing


















