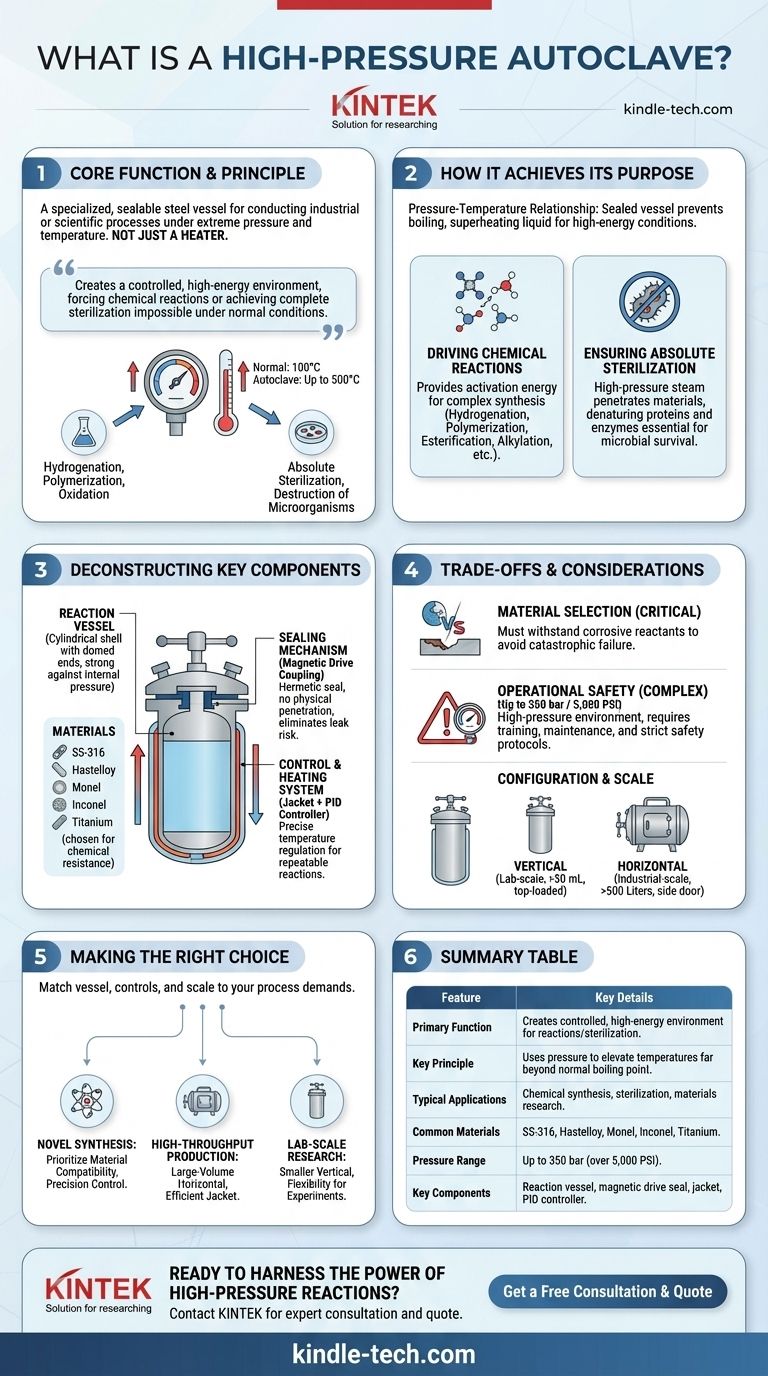
At its core, a high-pressure autoclave is a specialized, sealable steel vessel engineered to conduct industrial or scientific processes under extreme pressure and temperature. It is not simply a heater but a highly controlled environment designed to force chemical reactions or achieve a level of sterilization that is impossible under normal atmospheric conditions.
A high-pressure autoclave's true function is to create a controlled, high-energy environment. By using immense pressure to elevate temperatures far beyond the normal boiling point of liquids, it provides the necessary conditions to drive complex chemical synthesis or ensure the complete destruction of all microorganisms.
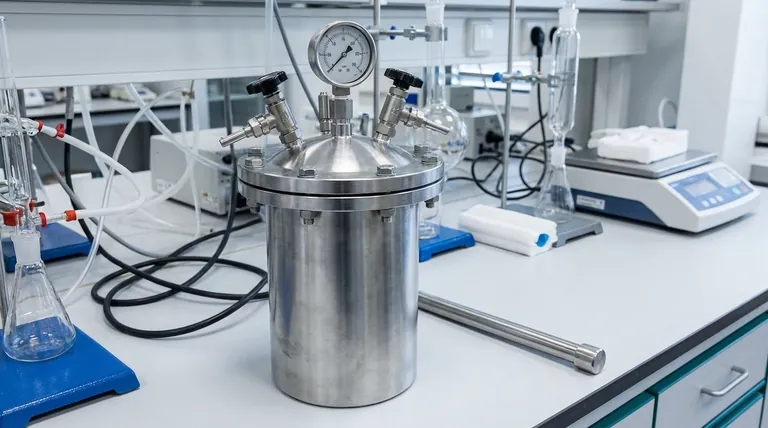

How a High-Pressure Autoclave Achieves Its Purpose
The operation of a high-pressure autoclave is governed by the fundamental relationship between pressure and temperature. By containing a substance within a sealed vessel, the pressure builds as heat is applied, unlocking unique process capabilities.
The Fundamental Principle: Pressure and Temperature
Under normal atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). Inside a sealed autoclave, the increasing pressure prevents boiling, allowing the liquid water or solvent to reach much higher temperatures—often up to 500°C.
This superheated, high-pressure state creates a high-energy environment that is the key to the autoclave's function.
Driving Chemical Reactions
Many chemical reactions require a significant amount of energy to begin, known as activation energy. The extreme conditions inside a high-pressure autoclave provide this energy efficiently and uniformly.
This makes it an indispensable tool for processes like hydrogenation, polymerization, oxidation, esterification, and alkylation, among many others.
Ensuring Absolute Sterilization
For sterilization, the combination of high pressure and intense heat is lethal to all forms of life, including resilient bacterial spores and viruses.
The high-pressure steam penetrates materials completely, denaturing the proteins and enzymes essential for microbial survival, thus ensuring absolute sterility.
Deconstructing the Key Components
The ability to safely contain and control extreme conditions depends on a robust and precise design. Several core components are critical to the autoclave's function.
The Reaction Vessel
The vessel itself is typically a cylindrical shell with domed ends, a shape inherently strong against internal pressure. It is constructed from specialized materials chosen for their strength and chemical resistance.
Common materials include SS-316 (Stainless Steel), Hastelloy, Monel, Inconel, and Titanium, selected based on the specific chemicals being used.
The Sealing Mechanism
A perfect seal is non-negotiable for safety and process integrity. High-pressure autoclaves often use a magnetic drive coupling to stir the contents.
This mechanism uses magnets to connect the motor outside the vessel to the agitator inside, creating a hermetic seal with no physical penetration, which eliminates the risk of leaks at high pressures.
The Control and Heating System
Precision is paramount. An external jacket surrounds the vessel, allowing heating or cooling media to circulate and manage the internal temperature.
This system is governed by a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller, which provides highly accurate and stable temperature regulation essential for repeatable and successful reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, high-pressure autoclaves are complex systems that demand careful consideration. Their operation involves inherent risks and requires specific expertise.
Material Selection is Critical
The choice of vessel material is one of the most important decisions. Using an autoclave made of a material that cannot withstand the corrosive nature of the reactants can lead to catastrophic failure. The process chemicals dictate the required alloy.
Operational Complexity and Safety
Operating at pressures up to 350 bar (over 5,000 PSI) creates a high-risk environment. These are not simple devices. Proper operator training, rigorous maintenance schedules, and adherence to strict safety protocols are absolutely essential.
Configuration and Scale
Autoclaves come in two primary configurations. Vertical autoclaves are loaded from the top and are typically used for smaller, lab-scale volumes (from 50 mL).
Horizontal autoclaves feature a side door and are used for larger, industrial-scale production, with volumes reaching up to 500 liters or more.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting an autoclave is not about finding the "best" one, but the right one for a specific application. Your primary goal should guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is novel chemical synthesis: Prioritize material compatibility with your specific reactants and a precise PID control system for process repeatability.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production: A large-volume, horizontal autoclave with an efficient heating and cooling jacket is necessary to minimize cycle times.
- If your primary focus is lab-scale research: A smaller, vertical autoclave provides greater flexibility for experimenting with different reactions and volumes.
Ultimately, selecting the correct high-pressure autoclave is about matching the vessel's material, controls, and scale to the unique demands of your process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Creates a controlled, high-energy environment for chemical reactions or sterilization. |
| Key Principle | Uses pressure to elevate temperatures far beyond the normal boiling point of liquids. |
| Typical Applications | Chemical synthesis (hydrogenation, polymerization), sterilization, materials research. |
| Common Materials | SS-316, Hastelloy, Monel, Inconel, Titanium (selected for chemical resistance). |
| Pressure Range | Can operate at pressures up to 350 bar (over 5,000 PSI). |
| Key Components | Reaction vessel, magnetic drive seal, heating/cooling jacket, PID controller. |
Ready to harness the power of high-pressure reactions for your lab?
Choosing the right autoclave is critical for the safety, efficiency, and success of your processes. The experts at KINTEK specialize in matching the perfect lab equipment to your specific needs, whether you're in research, chemical synthesis, or production.
We provide autoclaves with the precise material compatibility, control systems, and scale required for your application. Contact us today to discuss your process requirements and find the ideal high-pressure solution.
Get a Free Consultation & Quote
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the contribution of a hydrothermal reactor to graded pore construction? Precision Templates for TAS
- How does a high-pressure reactor demonstrate its value in accelerated aging? Predict Catalyst Durability Fast
- Why are high-pressure autoclaves essential for preparing bio-based polyamide curing agents from dimeric acid?
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature hydrothermal reactor? Enhance Iodine@Activated Carbon Cathode Synthesis
- What roles do autoclaves play in MFI zeolite synthesis? Master Hydrothermal Crystalline Growth



















