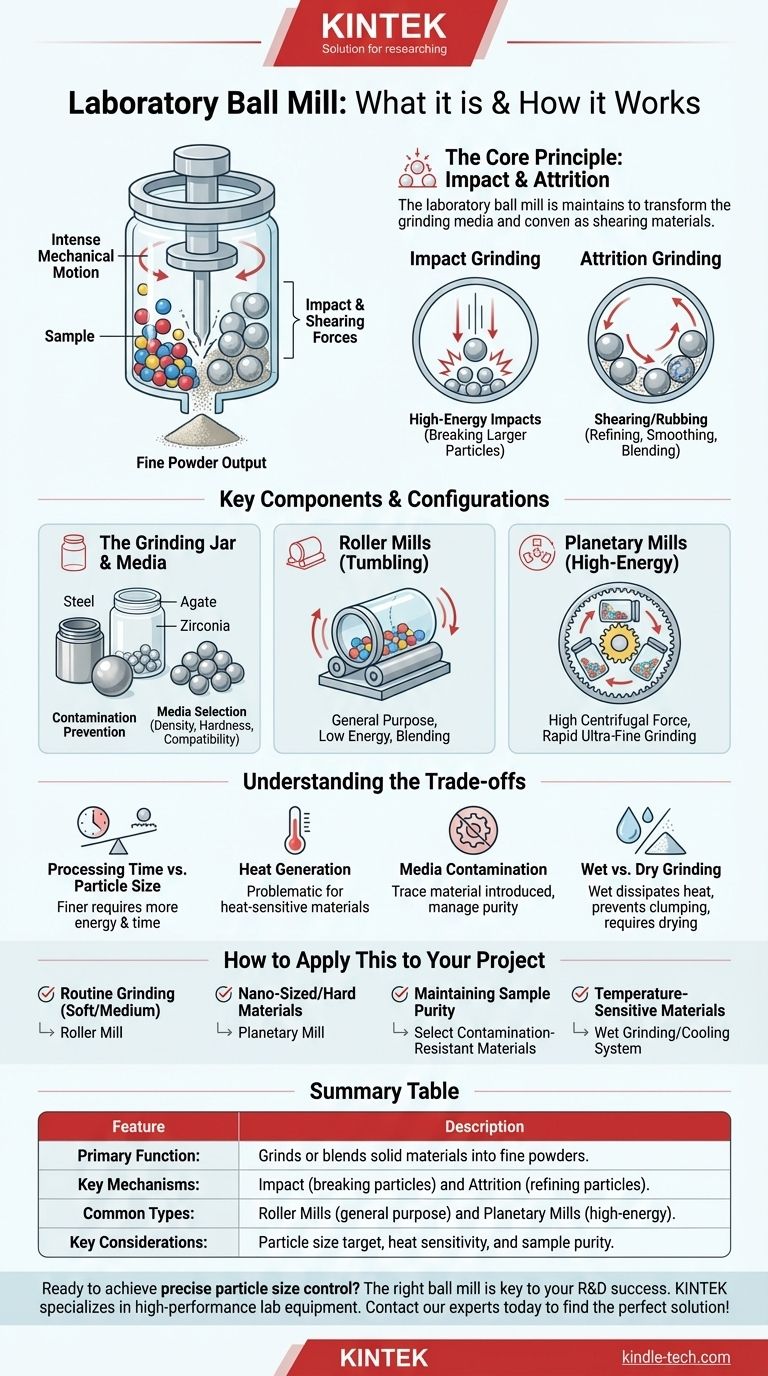
At its core, a laboratory ball mill is a high-performance grinder designed to reduce small-scale samples of solid material into extremely fine powders or to blend different materials together intimately. It operates by placing the sample material into a sealed jar along with hardened grinding media (balls) and subjecting the jar to intense mechanical motion. This motion causes the balls to repeatedly collide with the sample, breaking it apart through powerful impact and shearing forces.
The true purpose of a laboratory ball mill is not just to grind, but to achieve precise control over final particle size and distribution. This control is fundamental for research and development, as the physical properties of a material are often dictated by the size of its constituent particles.

The Core Principle: Impact and Attrition
A ball mill's effectiveness comes from two distinct but simultaneous grinding mechanisms. The balance between these forces is controlled by the mill's speed, the size of the balls, and the type of mill used.
Impact Grinding
As the grinding jar rotates, the balls inside are carried up the inner wall. At a certain point, gravity overcomes the centrifugal force, and the balls cascade or fall from near the top of the jar. This action creates high-energy impacts, striking the material and causing brittle fractures, which is highly effective for breaking down larger particles.
Attrition Grinding
Simultaneously, the balls are in constant motion against each other and the jar wall, creating a shearing or rubbing action. This attrition is more effective at reducing already small particles into even finer powders, smoothing their surfaces, and blending materials on a microscopic level.
Key Components and Configurations
While the principle is simple, the configuration of the mill dramatically affects its performance and applications.
The Grinding Jar and Media
The sample is sealed inside a grinding jar, which can be made from various materials like hardened steel, stainless steel, agate, or zirconia to prevent sample contamination.
Inside the jar are the grinding media (the balls), which do the actual work. They are chosen based on their density, hardness, and chemical compatibility with the sample. Common materials include steel, tungsten carbide, and various ceramics.
Roller Mills (Tumbling Mills)
The simplest configuration involves placing the grinding jar on a set of motorized rollers. The rollers spin the jar around its long axis, creating a tumbling motion inside. This setup is excellent for general-purpose grinding and blending but operates at relatively low energy.
Planetary Mills
For high-energy applications, a planetary ball mill is used. Grinding jars are mounted on a large "sun wheel" that rotates in one direction, while the jars themselves rotate on their own axes in the opposite direction. This complex motion results in extremely high centrifugal forces, creating significantly more powerful and frequent impacts for rapid, ultra-fine grinding.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Using a ball mill is an exercise in balancing competing factors. Understanding these trade-offs is key to achieving reliable and repeatable results.
Processing Time vs. Final Particle Size
Achieving finer particles requires more energy and time. Grinding a sample down to a few microns may take minutes, while milling it into the nanometer range can take many hours.
Heat Generation
The immense energy involved, especially in planetary mills, generates significant heat. This can be problematic for heat-sensitive or organic materials, potentially causing them to melt, decompose, or undergo a phase change.
Media Contamination
The grinding process is inherently abrasive. The grinding balls and jar will inevitably wear down over time, introducing trace amounts of their own material into your sample. For high-purity applications, this cross-contamination is a critical factor that must be managed by carefully selecting the jar and media materials.
Wet vs. Dry Grinding
Grinding can be done dry or wet by adding a liquid (like water or a solvent). Wet grinding helps to dissipate heat, prevent particles from clumping together, and can often result in a finer, more uniform final powder. However, it adds the complexity of a post-processing drying step.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of mill, media, and parameters depends entirely on your material and your final goal.
- If your primary focus is routine grinding of soft-to-medium materials: A simple roller mill is often a cost-effective and sufficient solution.
- If your primary focus is producing nano-sized particles or grinding very hard materials: A planetary ball mill is necessary to provide the required energy input.
- If your primary focus is maintaining sample purity: Select grinding jars and balls made of a material that will not contaminate your sample, or one whose trace elemental contamination is acceptable for your analysis.
- If your primary focus is processing temperature-sensitive materials: Use wet grinding, run the mill in shorter cycles with cooling periods, or use a mill with a built-in cooling system.
By mastering these variables, you transform the ball mill from a simple grinder into a precise instrument for engineering material properties.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Grinds or blends solid materials into fine powders. |
| Key Mechanisms | Impact (breaking particles) and Attrition (refining particles). |
| Common Types | Roller Mills (general purpose) and Planetary Mills (high-energy). |
| Key Considerations | Particle size target, heat sensitivity, and sample purity. |
Ready to achieve precise particle size control in your lab? The right ball mill is key to your R&D success. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including a range of ball mills and grinding media tailored to your specific material and purity requirements. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your grinding and blending challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Cabinet Planetary Ball Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the ball mill based on the principle of? Impact and Attrition for Efficient Grinding
- Why are zirconia (ZrO2) milling jars recommended for sulfide electrolytes? Ensure Purity in Li6PS5Cl Synthesis
- Why are silicon nitride or zirconia preferred for milling iodo-vanadate-lead precursors? Ensure High Purity Results
- What is the benefit of using tungsten carbide (WC) milling jars and balls? Achieve High-Energy Milling Efficiency
- Why are tungsten carbide grinding jars and balls preferred for high-purity lithium ceramic powders? Ensure Peak Purity.



















