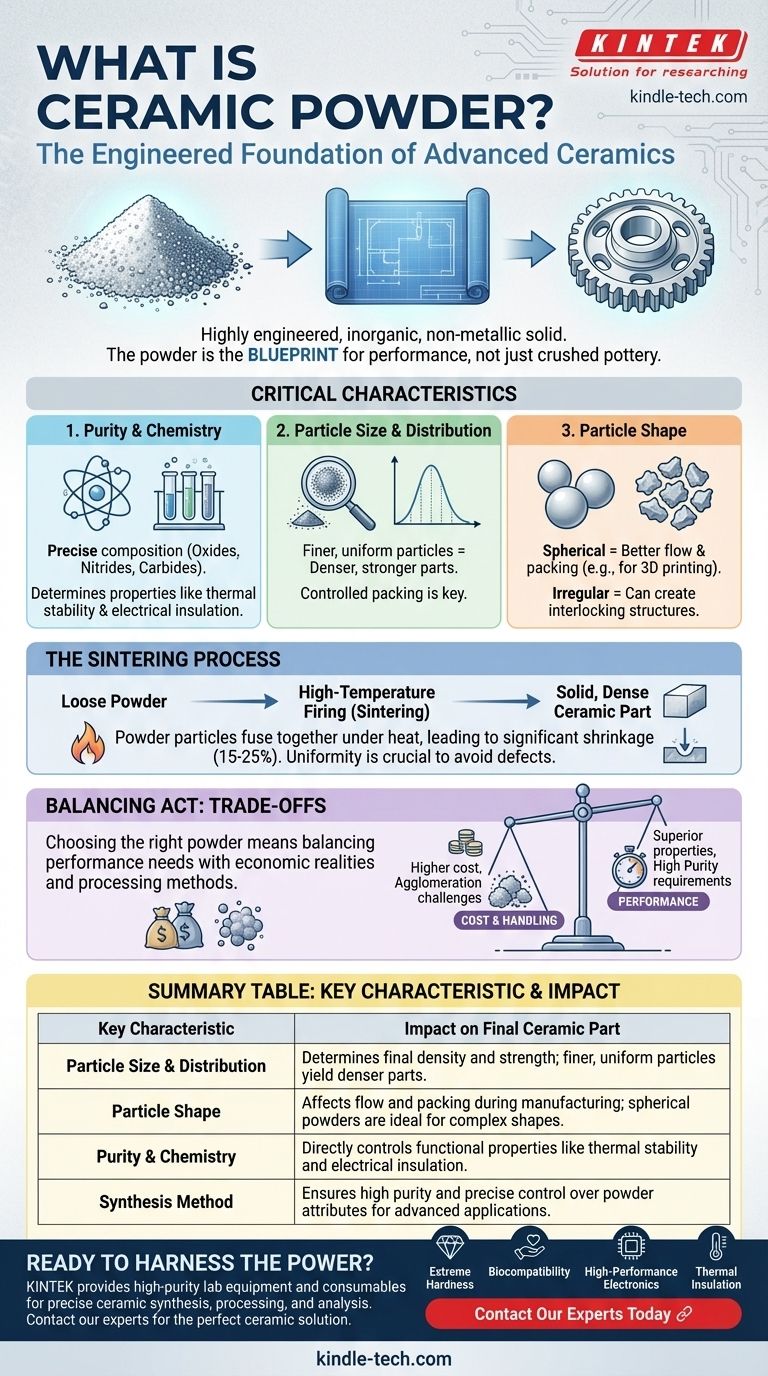
At its core, ceramic powder is the foundational raw material for creating advanced ceramic components. It is not simply crushed pottery, but a highly engineered, inorganic, non-metallic solid, synthesized and processed to have precise chemical and physical characteristics. These characteristics, established at the powder stage, directly determine the performance of the final, solid ceramic part.
The central concept to grasp is that control over the ceramic powder—its purity, particle size, and shape—is the most critical factor in manufacturing. The powder acts as the blueprint, dictating the strength, density, and functional properties of the finished component.

What Defines a Powder as "Ceramic"?
To understand ceramic powder, you must first understand the material itself. It is a class of materials defined by what it is not: it is neither metallic nor organic.
The Material Composition
Ceramic powders consist of inorganic, non-metallic compounds. This broad category includes oxides (like alumina and zirconia), nitrides (like silicon nitride), and carbides (like silicon carbide).
These materials are chosen for their exceptional properties, such as high-temperature stability, extreme hardness, chemical inertness, and unique electrical characteristics.
The Importance of Synthesis
Unlike raw materials that are simply mined and crushed, advanced ceramic powders are typically created through complex chemical synthesis processes.
Methods like sol-gel, co-precipitation, or gas-phase synthesis are used to achieve extremely high purity and control over the powder's attributes. This engineering is what separates advanced ceramics from traditional ceramics like clay.
Why Powder Characteristics Are So Critical
The transition from a loose powder to a dense, solid part is a process of consolidation and high-temperature firing (sintering). The initial state of the powder dictates the success of this entire process.
Particle Size and Distribution
The size of the individual powder grains, often measured in micrometers or even nanometers, is paramount. Finer particles generally lead to a denser and stronger final part because they pack together more efficiently, leaving smaller voids.
A narrow particle size distribution, where all particles are a similar size, is also desirable for uniform packing and predictable shrinkage during firing.
Particle Shape
Powder particles can be spherical, irregular, or even platelet-shaped. Spherical powders tend to flow більш smoothly and pack more predictably, which is crucial for manufacturing methods like injection molding and 3D printing.
Irregular shapes may create interlocking structures that can be beneficial for الأخرى processes like dry pressing, but they are often harder to work with.
Purity and Chemistry
The chemical purity of a ceramic powder is non-negotiable for high-performance applications. Even minuscule impurities, measured in parts per million (ppm), can drastically alter a ceramic's thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, or color.
The precise chemical composition is engineered to deliver specific properties, such as the stabilizing agents added to zirconia to prevent cracking.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing and working with ceramic powders involves balancing performance requirements with practical and economic realities. The ideal powder on paper is not always the right choice for a given project.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between powder quality and cost. Highly pure, nano-sized, perfectly spherical powders are significantly more expensive to produce.
The key is to select a powder that meets the performance requirements of the application without over-engineering and incurring unnecessary costs. A powder for a simple refractory brick does not need the same purity as one for a medical implant.
Handling and Agglomeration
Fine powders,尤其是纳米级粉末, present significant handling challenges. They have a strong tendency to clump together, a phenomenon known as agglomeration.
These clumps act like large particles, creating defects and voids in the final ceramic part, which compromises its strength and density. Special processing steps are often required to break these agglomerates apart before forming.
Sintering and Shrinkage
During firing, the ceramic part shrinks as the powder particles fuse together. This shrinkage can be significant, often 15-25% by volume.
If the powder is not uniform in its packing density, this shrinkage will be non-uniform, leading to warping, internal stress, and cracking. Controlling shrinkage begins with controlling the initial powder characteristics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The "best" ceramic powder is entirely dependent on your end goal. The material choice and its specifications must be driven by the demands of the application.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance: You will need powders like silicon carbide or boron carbide, where fine particle size is critical for achieving maximum density.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility and aesthetics: You require exceptionally pure and stable powders like zirconia or alumina, often with specific additives for color and fracture toughness in dental or medical implants.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics: Your choice will be driven by electrical properties, requiring high-purity powders like aluminum nitride for thermal management or barium titanate for its dielectric properties.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective thermal insulation: You can use less-pure, larger-grained powders like mullite or cordierite, as extreme mechanical strength is not the primary requirement.
Ultimately, mastering the use of ceramic powder is the key to unlocking the extraordinary potential of advanced ceramic materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Impact on Final Ceramic Part |
|---|---|
| Particle Size & Distribution | Determines final density and strength; finer, uniform particles yield denser parts. |
| Particle Shape | Affects flow and packing during manufacturing; spherical powders are ideal for complex shapes. |
| Purity & Chemistry | Directly controls functional properties like thermal stability and electrical insulation. |
| Synthesis Method | Ensures high purity and precise control over powder attributes for advanced applications. |
Ready to harness the power of advanced ceramic powders for your project?
The right ceramic powder is the foundation of a high-performance component. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-purity lab equipment and consumables needed for precise ceramic synthesis, processing, and analysis. Whether you are developing medical implants, electronic components, or cutting-edge industrial parts, our expertise ensures you have the materials and support to succeed.
Let's discuss your specific application requirements. Contact our experts today to find the perfect ceramic solution for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Alumina Granulated Powder for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Ceramic Ring
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina (Al₂O₃) Ceramic Positioning Pin Straight Bevel for Precision Applications
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
People Also Ask
- What should be done if scratches on an electrode cannot be removed with 1.0um alumina powder? Expert Repair Tips
- How high temperature can ceramic withstand? A Guide to Extreme Heat Performance
- What are the high temperature properties of alumina? Discover Its Stability, Strength, and Limits
- What is the maximum temperature for alumina tube? Unlock Its Full Potential with High Purity
- What measures should be taken to prevent cross-contamination when using different sizes of alumina powder?









