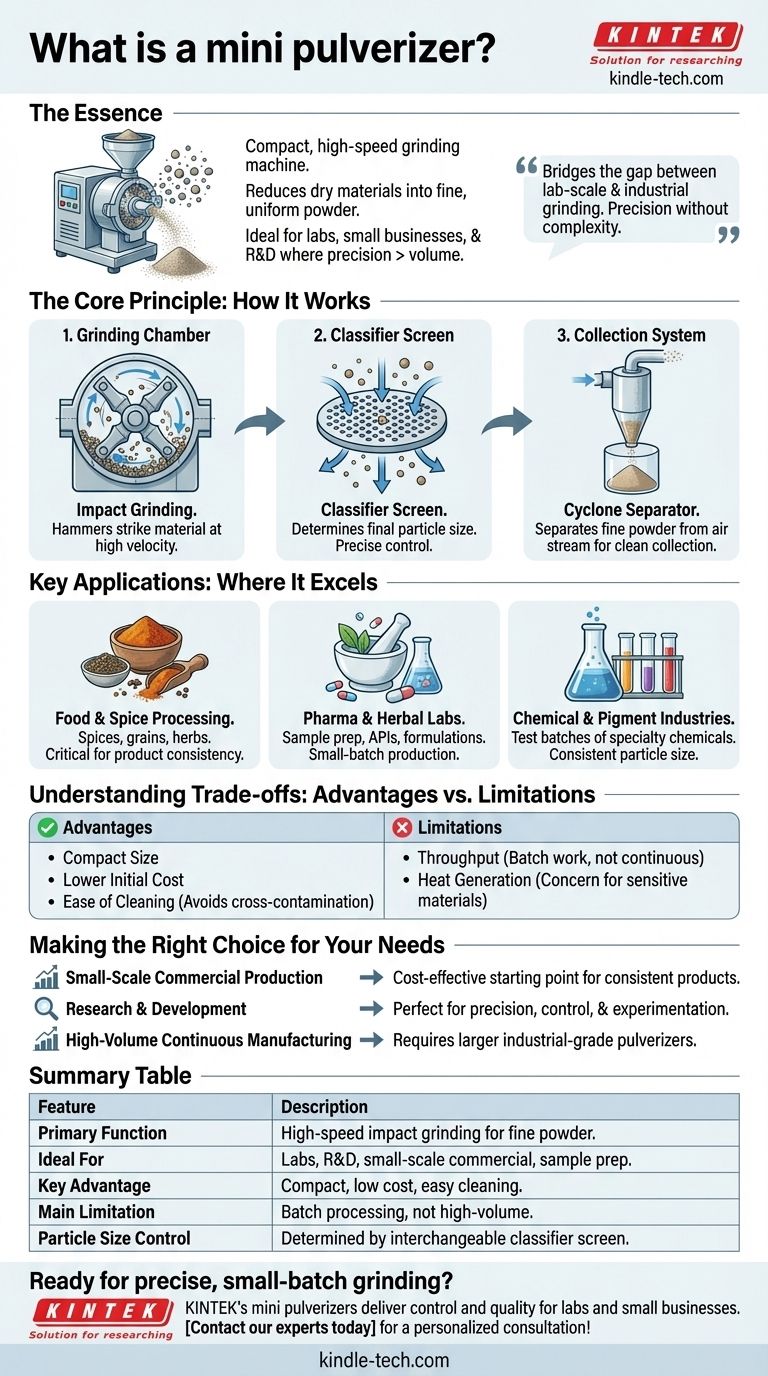
In essence, a mini pulverizer is a compact, high-speed grinding machine designed to reduce a wide range of dry materials into a fine, uniform powder. Unlike large industrial grinders, it operates on a smaller scale, making it a crucial tool for laboratories, small businesses, and research applications where precision and batch processing are more important than massive volume.
A mini pulverizer bridges the gap between lab-scale milling and industrial grinding. It offers the precision needed for specialized applications without the footprint, cost, or complexity of full-scale production machinery.

The Core Principle: How a Mini Pulverizer Works
A mini pulverizer operates on the principle of impact grinding. Material is shattered by being struck repeatedly at high velocity rather than being compressed or abraded. This process is remarkably efficient and consistent.
The Grinding Chamber
The heart of the machine is the grinding chamber, which houses a set of rotating hammers. As material is fed into the chamber, these hammers, spinning at several thousand RPM, strike the particles, causing them to shatter.
The Classifier Screen
The material remains in the chamber until it is small enough to pass through a perforated screen at the bottom. The size of the holes in this classifier screen directly determines the final particle size of the powder, allowing for precise control over the output.
The Collection System
Once the particles pass through the screen, they are typically drawn into a cyclone separator. This device uses centrifugal force to separate the fine powder from the air stream, depositing the finished product into a collection bag or container in a clean and efficient manner.
Key Applications: Where Mini Pulverizers Excel
The versatility and compact size of mini pulverizers make them indispensable in a variety of fields. They are not intended for bulk processing but for tasks requiring quality and control.
Food and Spice Processing
These machines are widely used by small-scale businesses for grinding spices like turmeric and chili, as well as grains, sugar, and herbs. The ability to control fineness is critical for product consistency.
Pharmaceutical and Herbal Labs
In research and development, mini pulverizers are essential for preparing samples and formulations. They can grind active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and herbal compounds into fine powders for testing and small-batch production.
Chemical and Pigment Industries
For creating test batches of specialty chemicals, pigments, or minerals, a mini pulverizer provides a reliable method for achieving a consistent particle size distribution without committing large amounts of raw material.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Advantages and Limitations
Choosing a mini pulverizer means understanding what it does well and where its limits are. Objectivity is key to selecting the right tool for the job.
The Clear Advantages
The primary benefits are its compact size, lower initial cost, and ease of cleaning between batches. This makes it ideal for environments where multiple different materials are processed and cross-contamination must be avoided.
The Inherent Limitations
The most significant limitation is throughput. A mini pulverizer is designed for batch work, not for continuous, high-volume production. It can also generate heat, which may be a concern for heat-sensitive materials if the machine is run for extended periods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
Selecting the correct equipment depends entirely on your operational goals. A mini pulverizer is a specialized tool, not a one-size-fits-all solution.
- If your primary focus is small-scale commercial production: A mini pulverizer is a cost-effective and highly capable starting point for creating consistent, high-quality powdered products.
- If your primary focus is research and development: The machine's precision, control over particle size, and suitability for small batches make it the perfect tool for experimentation and sample preparation.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous manufacturing: You must invest in larger, industrial-grade pulverizers designed for sustained output and greater capacity.
Ultimately, the mini pulverizer is a powerful tool for anyone who needs to produce high-quality powders on a manageable and controlled scale.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | High-speed impact grinding to reduce dry materials into a fine powder. |
| Ideal For | Laboratories, R&D, small-scale commercial production, and sample preparation. |
| Key Advantage | Compact size, lower cost, and easy cleaning for processing multiple materials. |
| Main Limitation | Designed for batch processing, not for high-volume, continuous production. |
| Particle Size Control | Determined by the interchangeable classifier screen. |
Ready to achieve precise, small-batch grinding?
Whether you're in a lab developing new formulations or a small business creating consistent powdered products, KINTEK's mini pulverizers deliver the control and quality you need. Our equipment is designed for efficiency, ease of use, and reliable performance.
Let us help you find the perfect grinding solution for your specific materials and goals. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Laboratory Disc Cup Vibratory Mill for Sample Grinding
- Low-Temperature Water-Cooled Touchscreen Vibratory Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Lab Vibration Mill
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill with Screw Feeder
People Also Ask
- How much balls should be loaded in a ball mill for working? Optimize Grinding with the Correct Ball Charge
- What are the different types of grinding mills? Match the Mechanism to Your Material for Optimal Size Reduction
- Why is grinding important in sample preparation? Ensure Accurate & Reliable Analytical Results
- What are the five methods of synthesis of nanoparticles? A Guide to Top-Down & Bottom-Up Approaches
- How many balls are needed for a ball mill? Optimize grinding with the right charge volume.



















