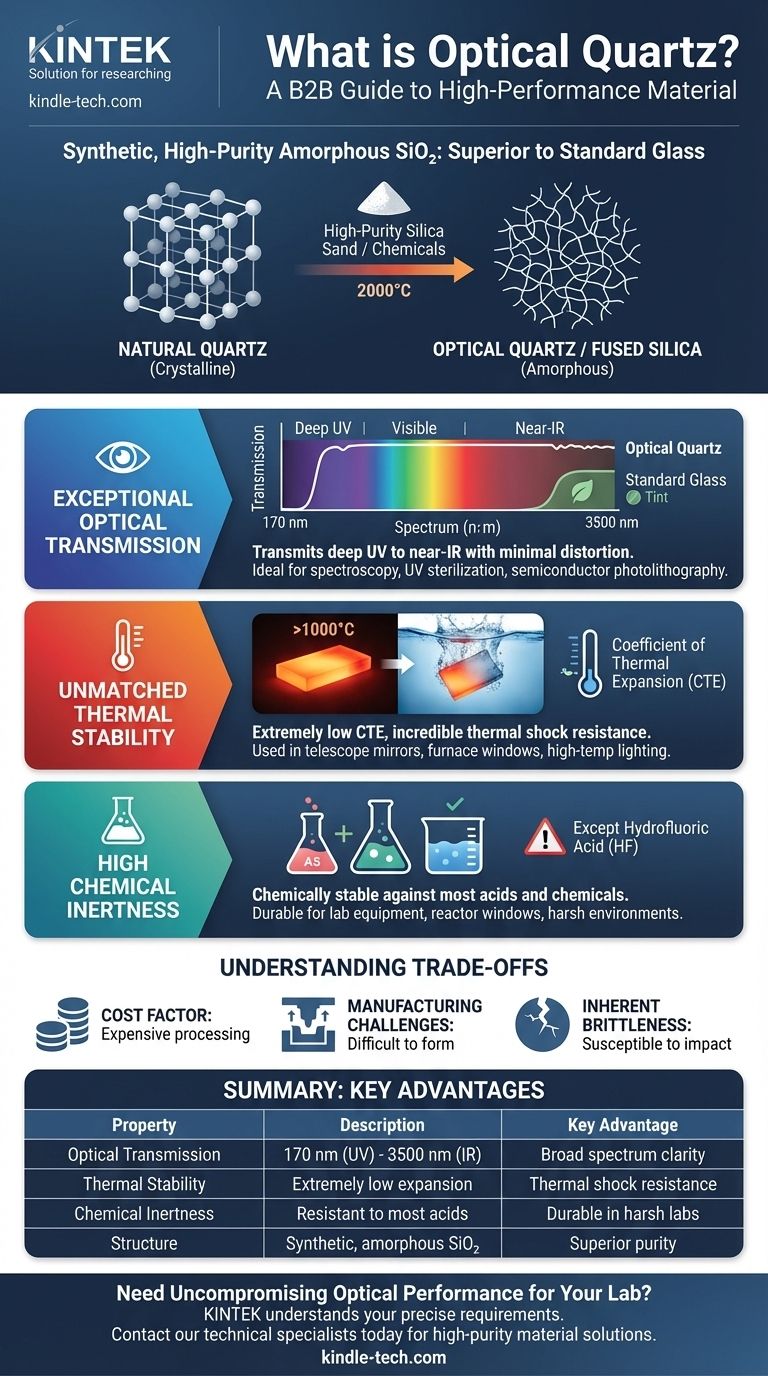
In material science, optical quartz is a specific type of glass renowned for its exceptional purity. Unlike naturally occurring quartz crystal, optical quartz is a synthetic, non-crystalline (amorphous) form of silicon dioxide (SiO₂). Also known as fused quartz or fused silica, its manufacturing process removes nearly all impurities, resulting in optical and thermal properties that are far superior to any standard glass.
The defining characteristic of optical quartz isn't just its composition, but its performance. It transmits light across an incredibly broad spectrum—from deep ultraviolet to near-infrared—with minimal distortion, even when subjected to extreme temperature changes.
The Defining Trait: Purity and Structure
The unique capabilities of optical quartz are a direct result of its chemical purity and amorphous internal structure. Understanding this foundation is key to appreciating its applications.
From Natural Crystal to Amorphous Glass
Natural quartz is a crystalline material, meaning its atoms are arranged in a highly ordered, repeating pattern.
Optical quartz, or fused quartz, is created by melting extremely pure silica sand at high temperatures (around 2000°C) and then cooling it. This process breaks down the crystal lattice, resulting in an amorphous or non-crystalline structure, which is characteristic of glass.
Why Purity is Paramount
Standard glass contains additives and metallic impurities that absorb specific wavelengths of light. For example, the iron content in normal window glass is what gives it a slight green tint and blocks most UV radiation.
The high-purity nature of optical quartz means these light-absorbing elements are absent. This allows it to maintain incredible transparency across a vast range of wavelengths.
Fused Quartz vs. Fused Silica
While the terms are often used interchangeably, there is a technical distinction. Fused quartz is typically made from melting naturally mined, high-purity quartz crystals.
Fused silica is a synthetic product derived from chemical precursors like silicon tetrachloride (SiCl₄). This synthetic process generally results in an even higher level of purity and is often preferred for the most demanding applications, particularly in the deep UV spectrum.
Unpacking the Superior Properties
The combination of purity and amorphous structure gives optical quartz three standout characteristics that engineers and scientists rely on.
Exceptional Optical Transmission
The primary advantage of optical quartz is its ability to transmit light from as low as 170 nm in the deep ultraviolet (UV) up to 3500 nm in the near-infrared (IR) spectrum. Standard glass, by contrast, is opaque to most UV light. This makes it indispensable for optics used in spectroscopy, UV sterilization systems, and semiconductor photolithography.
Unmatched Thermal Stability
Optical quartz has an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE). This means it barely expands or contracts when its temperature changes.
This property provides incredible resistance to thermal shock. You could heat a piece of optical quartz to over 1000°C and plunge it into cold water without it cracking, a test that would instantly shatter normal glass.
High Chemical Inertness
Fused quartz is chemically stable and does not react with most acids, water, or other chemicals. This makes it a durable choice for laboratory equipment, viewing windows on chemical reactors, and components exposed to harsh environments. The notable exception is its reactivity with hydrofluoric acid.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its performance is exceptional, optical quartz is not the right material for every application. Its advantages come with practical limitations that must be considered.
The Cost Factor
The intensive, high-energy process required to purify and melt silica makes optical quartz significantly more expensive than other types of glass like borosilicate or soda-lime glass. Its use is generally reserved for applications where its unique properties are a strict requirement.
Manufacturing Challenges
The very high melting point of silica makes optical quartz much more difficult and costly to form into complex shapes compared to standard glasses. This can limit design possibilities and increase fabrication costs.
Inherent Brittleness
Like all ceramic and glass materials, optical quartz is brittle. While it has high compressive strength, it is susceptible to fracture from sharp impacts or high tensile stress. It does not deform before breaking.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a material always involves balancing performance requirements with practical constraints like budget and manufacturability.
- If your primary focus is broad-spectrum clarity (especially UV): Optical quartz is the essential choice for applications like UV lasers, spectroscopy cuvettes, or semiconductor manufacturing tools.
- If your primary focus is stability under extreme temperature changes: Its near-zero thermal expansion makes it irreplaceable for telescope mirrors, furnace windows, and high-temperature lighting.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for visible-light applications: A different material like BK7 optical glass or borosilicate glass will provide excellent performance in the visible spectrum for a fraction of the cost.
Ultimately, selecting optical quartz is a decision to prioritize uncompromising optical and thermal performance where other materials would fail.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Optical Transmission | Transmits light from 170 nm (Deep UV) to 3500 nm (Near-IR) | Broad spectrum clarity, essential for UV applications |
| Thermal Stability | Extremely low thermal expansion; high resistance to thermal shock | Withstands extreme temperature changes without cracking |
| Chemical Inertness | Resistant to most acids and chemicals (except HF) | Durable in harsh laboratory and industrial environments |
| Structure | Synthetic, amorphous (non-crystalline) SiO₂ | Superior purity and performance over natural crystalline quartz |
Need Uncompromising Optical Performance for Your Lab?
Optical quartz is essential for applications demanding superior UV transmission, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. The experts at KINTEK understand the precise requirements for laboratory equipment and consumables. We can help you select the right materials for your optics, reactor windows, spectroscopy cells, and more.
Let KINTEK provide the solution for your demanding laboratory needs. Contact our technical specialists today to discuss how our high-purity materials can enhance your application's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Resistant Optical Quartz Glass Sheet
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Single Double Sided Coated K9 Quartz Sheet
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Barium Fluoride BaF2 Substrate Window
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
People Also Ask
- What role does an ultrasonic cleaner play in the pretreatment of titanium alloy samples for biological testing?
- What material is used for furnace lining? A Guide to Selecting the Right Refractory
- Why is a multi-position magnetic stirrer necessary for dye degradation? Ensure Uniformity in Photocatalytic Experiments
- How are specialized consumables used to maintain LiMOCl4 stability? Ensure Pure Air-Sensitive Material Processing
- When is it more cost-effective to use a single-stage rotary vane pump? Save 50% on Rough Vacuum Costs
- What does a furnace liner do? Protect Your Home from Chimney Damage and Gas Leaks
- Why Use Zirconia Grinding Media for RPPO Solid Electrolytes? Ensure Purity and Performance
- Why are pressure switches important? Essential for Automation, Safety & Efficiency















