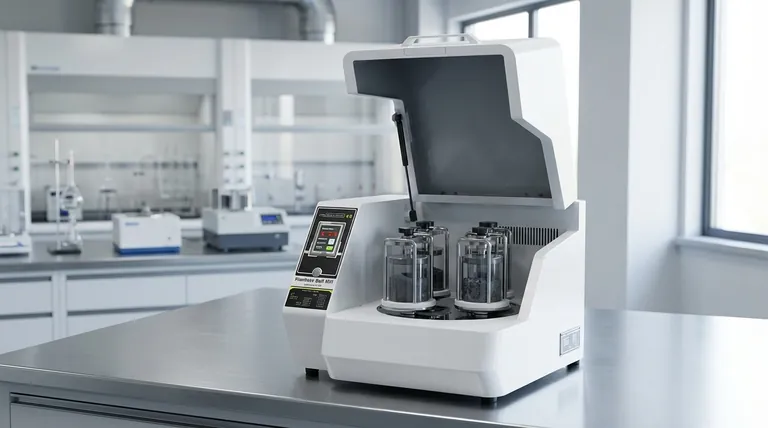
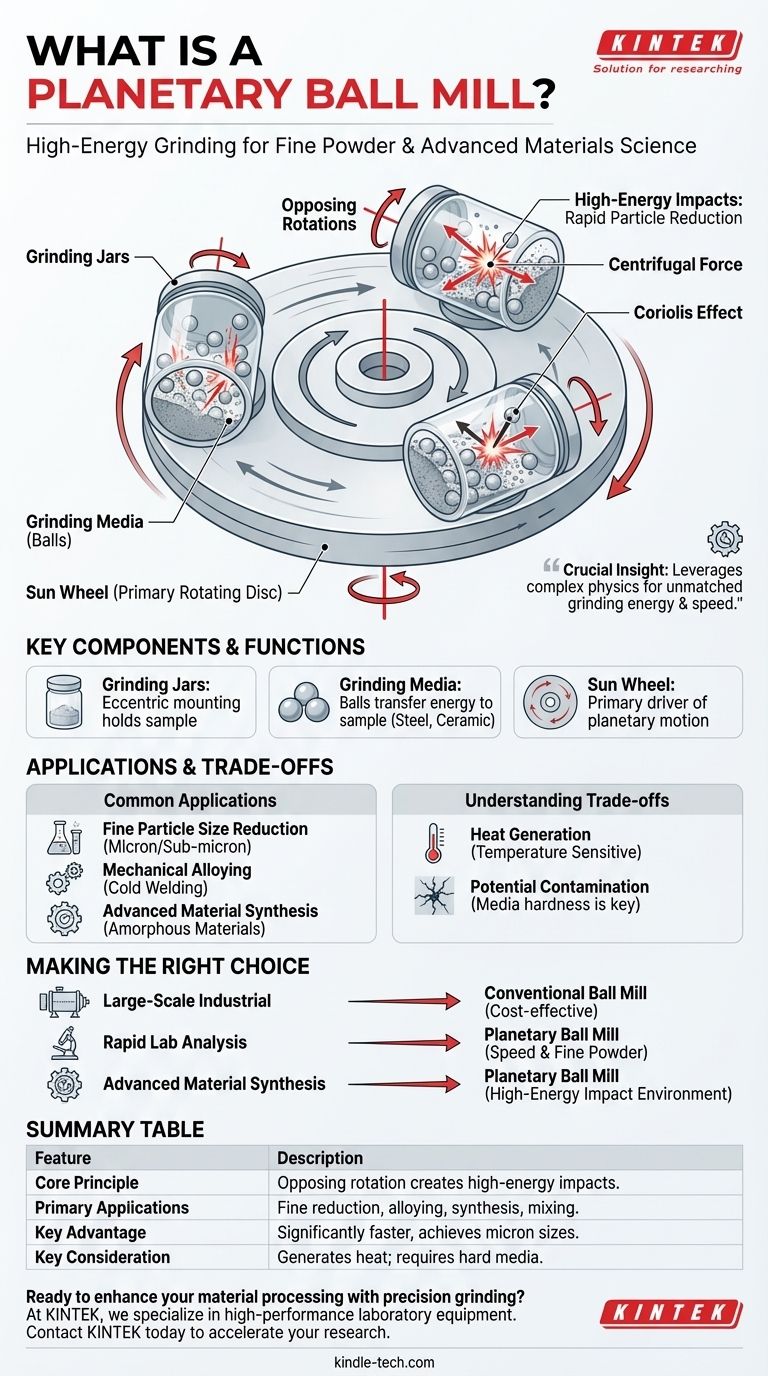
At its core, a planetary ball mill is a high-energy grinding device used to reduce materials to a very fine powder. It achieves this using a unique "sun and planet" rotational system where grinding jars, holding the sample and grinding media, spin on their own axes while simultaneously revolving around a central point in the opposite direction. This opposing motion creates exceptionally high-energy impacts, resulting in rapid and efficient particle size reduction.
The crucial insight is that a planetary ball mill is not just a grinder; it is a specialized instrument that leverages complex physics—specifically centrifugal and Coriolis forces—to achieve a level of grinding energy and speed that conventional ball mills cannot match, making it essential for laboratory and advanced materials science applications.

How Planetary Motion Creates High Energy
The effectiveness of a planetary ball mill comes from its distinct mechanical design, which intentionally generates powerful forces for grinding.
The Sun Wheel and Planets
A planetary ball mill consists of a primary rotating disc, known as the sun wheel. Mounted on this wheel are one or more smaller grinding jars, which act as the planets.
The Principle of Opposing Rotations
The key to the system is the gearing. As the sun wheel turns in one direction, the grinding jars are forced to rotate on their own axes in the opposite direction. This counter-rotation is the fundamental principle that generates immense energy within the jars.
The Physics of Impact
This dual-motion system creates a superposition of forces. The centrifugal forces from both rotations cause the grinding media (balls) inside the jars to detach from the inner wall and travel at high speed across the jar. This movement is compounded by the Coriolis effect, leading to frequent, high-energy collisions between the balls, the material sample, and the jar walls.
Key Components and Their Function
Understanding the parts of the mill clarifies how it achieves its results.
Grinding Jars
These are the containers that hold the material being processed. They are mounted eccentrically (off-center) on the sun wheel.
Grinding Media
These are the balls placed inside the jars along with the sample. They are the actual instruments of grinding. The energy generated by the planetary motion is transferred through these balls, which smash and pulverize the material. The media can be made of various materials, such as steel, ceramic, or tungsten carbide, to match the sample's hardness.
Common Applications and Use Cases
The high energy generated by a planetary ball mill makes it suitable for a wide range of tasks beyond simple grinding.
Fine Particle Size Reduction
This is the most common application. Planetary ball mills are used to grind materials like mining ores, pigments, coal, and ceramics down to micron or even sub-micron sizes.
Mechanical Alloying and Mixing
The intense forces are powerful enough to create mechanical alloys, where different powdered metals are effectively cold-welded together through repeated impacts. It is also used for ultra-thorough mixing of powders.
Advanced Material Science
These mills are critical tools in research and development for creating amorphous materials, changing material properties through mechanical stress, and synthesizing novel powders.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a planetary ball mill is a specific tool for specific jobs, distinct from more conventional grinding methods.
Planetary vs. Standard Ball Mills
A standard ball mill is typically a large horizontal cylinder that tumbles, using gravity to cause balls to cascade and crush material. It is simpler, suited for large industrial volumes, but operates at a much lower energy level. A planetary ball mill is a high-intensity, typically smaller-scale laboratory instrument designed for speed and achieving extremely fine results.
Heat Generation
The immense energy put into the sample inevitably generates significant heat. This can be a major issue for temperature-sensitive materials, potentially altering their chemical or physical properties.
Potential for Contamination
The jar and grinding media must be significantly harder than the material being ground. If not, the media will wear down, and particles from the jar or balls will contaminate the sample.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate grinding method, you must first define your objective.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial processing of raw materials: A conventional horizontal or tumbling ball mill is the standard, cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is rapid particle size reduction for laboratory analysis: The planetary ball mill is the ideal choice for its speed and ability to produce extremely fine powders.
- If your primary focus is advanced material synthesis or mechanical alloying: The unique high-energy impact environment of a planetary ball mill is essential for these applications.
Ultimately, the planetary ball mill is a powerful and precise tool for achieving high-energy material processing where speed and fine particle size are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Opposing rotation of grinding jars creates high-energy impacts via centrifugal and Coriolis forces. |
| Primary Applications | Fine particle size reduction, mechanical alloying, material synthesis, and thorough powder mixing. |
| Key Advantage | Significantly faster and more energetic than conventional ball mills, achieving micron and sub-micron particle sizes. |
| Key Consideration | Generates significant heat; jar and media material must be harder than the sample to avoid contamination. |
Ready to enhance your material processing with precision grinding?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance laboratory equipment, including planetary ball mills, to meet the demanding needs of materials science and research. Our solutions are designed to deliver the rapid, high-energy grinding essential for achieving fine particle sizes, mechanical alloying, and advanced material synthesis.
Let our experts help you select the ideal mill for your specific application. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your requirements and discover how our lab equipment can accelerate your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type Milling Machine
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a planetary high-energy ball mill? Master Mechanical Alloying for Ni-Co-Al Superalloy Powders
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in Al-LLZ lithium garnet preparation? Optimize Solid-State Electrolyte Synthesis
- What role does a planetary ball mill play in SHS? Optimize Powder Activation for Superior Alloy Synthesis
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in the synthesis of Li2S–P2S5 sulfide solid-state electrolytes?
- What is the primary function of a planetary high-energy ball mill? Master Mechanical Alloying for Nickel Nanoparticles



















