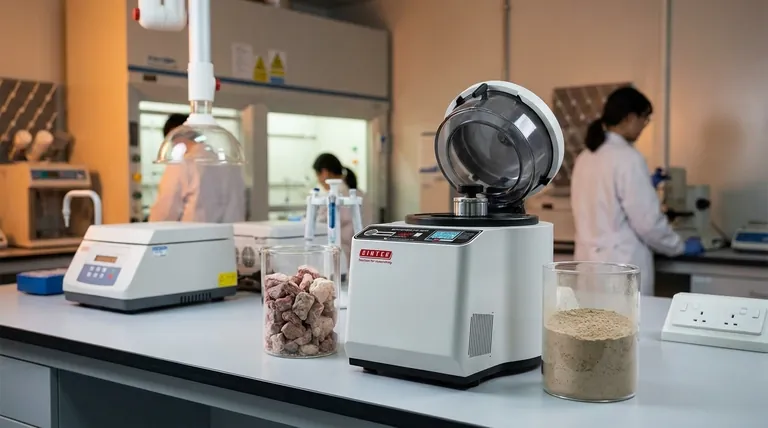
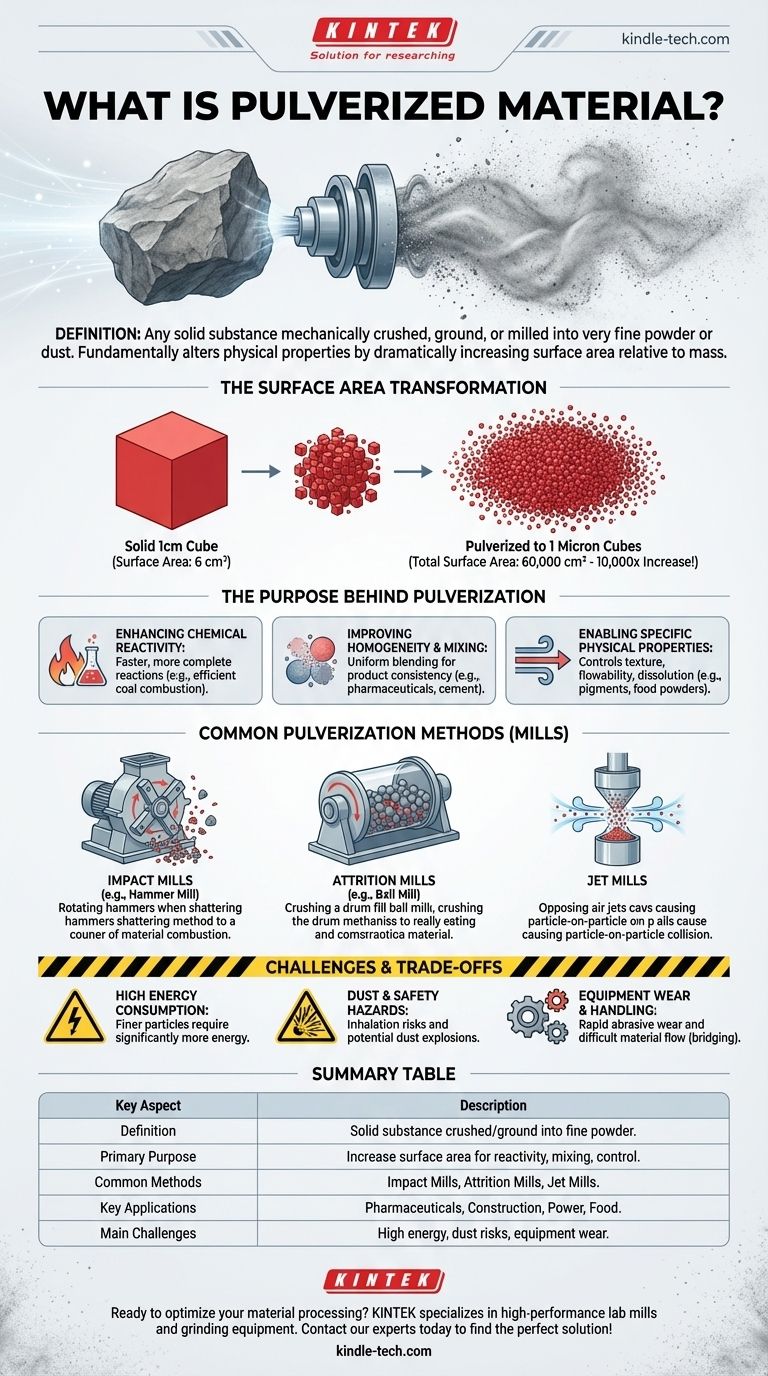
In simple terms, pulverized material is any solid substance that has been mechanically crushed, ground, or milled into the form of a very fine powder or dust. This process fundamentally changes the material's physical properties, most notably by dramatically increasing its surface area relative to its mass. This transformation is not merely about making something smaller; it is a critical step for unlocking its potential for a wide range of industrial applications.
Pulverization is a foundational engineering process designed to alter a material's physical state to enhance its chemical reactivity, improve its ability to be mixed, and control its behavior in a final product. Understanding the purpose behind creating a powder is key to grasping its industrial significance.

The Purpose Behind Pulverization
The decision to pulverize a material is driven by the need to manipulate its core properties. By breaking down its structure, we gain precise control over how it behaves and interacts with its environment.
Maximizing Surface Area
Breaking a solid chunk of material into billions of tiny particles massively increases the total surface area that is exposed. This is the single most important consequence of pulverization.
For example, a solid one-centimeter cube has a surface area of 6 cm². If pulverized into cubes that are one micron on each side, the total surface area increases to 60,000 cm²—a 10,000-fold increase.
Enhancing Chemical Reactivity
With more surface area exposed, chemical reactions can occur much faster and more completely. This principle is vital in many processes.
In a coal-fired power plant, pulverized coal dust burns almost as efficiently and quickly as a flammable gas, releasing energy far more effectively than burning large lumps of coal.
Improving Homogeneity and Mixing
Fine powders can be blended together far more uniformly than larger, irregular granules. This is essential for ensuring product consistency.
In pharmaceuticals, active ingredients are pulverized to ensure every tablet contains the exact same dose. In construction, cement is a pulverized powder that must mix evenly with sand, gravel, and water to create strong concrete.
Enabling Specific Physical Properties
The size and shape of pulverized particles directly influence the final product's characteristics, such as texture, flowability, and dissolution rate.
Pigments for paints are pulverized to achieve a specific particle size that determines color opacity and finish. In food production, the fine texture of flour or cocoa powder is a direct result of controlled pulverization.
Common Pulverization Methods
The machinery used for pulverization is chosen based on the material's hardness, the desired particle size, and the required production volume. These machines are broadly known as mills.
Impact Mills
These mills, such as a hammer mill, use high-speed rotating hammers or bars to shatter material upon impact. They are effective for brittle materials and are often used for high-volume, coarse-to-medium grinding.
Attrition Mills
An attrition mill, such as a ball mill, uses a rotating drum filled with hard grinding media (e.g., steel balls or ceramic cylinders). The material is crushed and ground between the colliding media, making this method ideal for very hard and abrasive substances.
Jet Mills
In a jet mill, high-velocity streams of compressed air or gas are used to accelerate particles, causing them to collide with each other. This particle-on-particle impact creates extremely fine, uniform powders with minimal contamination, a process often required for high-purity applications like pharmaceuticals and electronics.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While incredibly useful, pulverization is a process with significant operational considerations and inherent risks.
High Energy Consumption
Grinding solids into fine powders is an energy-intensive process. The finer the target particle size, the more energy is required, often representing a major operational cost.
Dust and Safety Hazards
Fine powders present two major risks. First is the inhalation hazard for workers. Second, many organic or metallic powders are highly combustible and can cause a devastating dust explosion if ignited while suspended in air.
Difficult Material Handling
Ultra-fine materials can be challenging to store and transport. They may clump together, refuse to flow smoothly from hoppers (a phenomenon known as "bridging"), or become easily airborne, leading to product loss and contamination.
Equipment Wear and Maintenance
The constant impact and abrasion wear down milling equipment rapidly, especially when processing hard materials like minerals or ceramics. This leads to high maintenance costs and production downtime.
Matching the Process to the Goal
Choosing the right approach to pulverization depends entirely on the desired outcome for the material and the acceptable operational trade-offs.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical reactivity: Aim for the smallest, most consistent particle size possible, often using energy-intensive methods like jet milling for applications in power generation or advanced catalysis.
- If your primary focus is consistent mixing and dosage: Prioritize tight control over the particle size distribution, a critical factor in the pharmaceutical, food, and chemical industries where product uniformity is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective volume processing: Use robust, high-throughput methods like impact or jaw crushing, which are suitable for the initial stages of mineral processing, recycling, or aggregate production.
Ultimately, pulverization is a transformative process that strategically tailors a material's fundamental properties to meet a specific industrial need.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Solid substance crushed/ground into a fine powder or dust. |
| Primary Purpose | Increase surface area to enhance reactivity, mixing, and control. |
| Common Methods | Impact Mills, Attrition Mills (e.g., Ball Mills), Jet Mills. |
| Key Applications | Pharmaceuticals, Construction, Power Generation, Food Production. |
| Main Challenges | High energy consumption, dust explosion risks, equipment wear. |
Ready to optimize your material processing? The right pulverization equipment is critical for achieving the desired particle size, reactivity, and mixability in your lab or production line. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab mills and grinding equipment tailored to your specific material challenges. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Throughput Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill with Screw Feeder
- Laboratory Jar Ball Mill with Alumina Zirconia Grinding Jar and Balls
- Low-Temperature Water-Cooled Touchscreen Vibratory Ultrafine Pulverizer
People Also Ask
- What does a grinder do in a laboratory? Achieve Homogeneous Sample Preparation for Accurate Analysis
- What is the role of laboratory grinding equipment and high-precision sieving systems? | Boost Sludge Pretreatment
- Can zirconia be milled? Mastering the Green-State vs. Sintered Milling Process
- Why is an agate mortar and pestle preferred for melamine condensates? Achieve Molecular Purity in Nanomaterial Synthesis
- What laboratory apparatus is used for grinding? Match the Right Mill to Your Sample Material
- What are the advantages of ball milling process? Achieve Nanoscale Materials & Alloying
- Why is it important to grind the sample finely and pack it tightly before performing a melting point determination? Ensure Accurate and Sharp Melting Points
- What is the primary function of vibration milling in Heusler alloy preparation? Achieve High-Reactivity Fine Powders



















