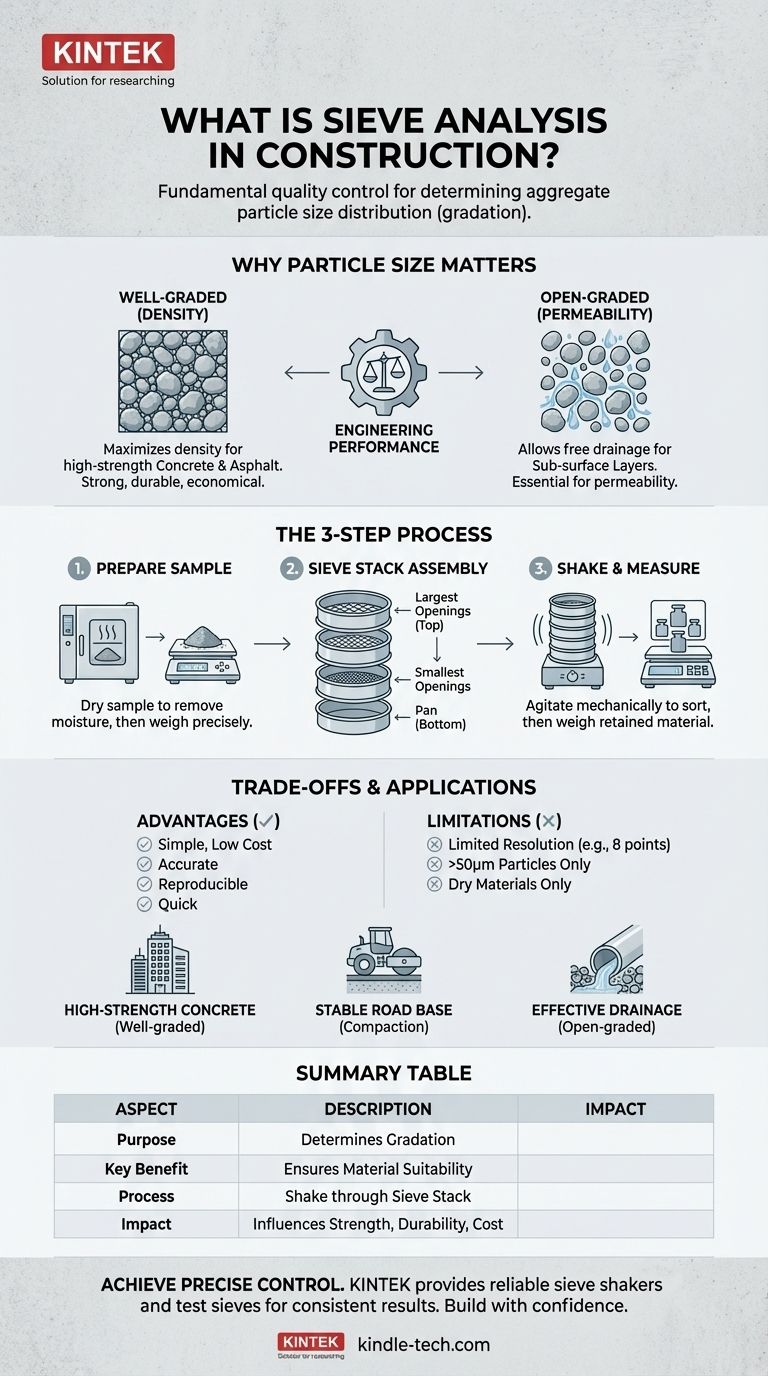
In construction, sieve analysis is the fundamental quality control test used to determine the particle size distribution of granular materials. Also known as a gradation test, this simple process involves passing a sample of aggregate—such as sand, gravel, or crushed rock—through a series of stacked screens with progressively smaller openings to sort the particles by size. The results are critical for ensuring the material's properties are suitable for its intended use, whether in concrete, asphalt, or as a base layer.
Sieve analysis is not simply about sorting materials; it's about engineering the performance of a final product. By controlling the mix of particle sizes (the "gradation"), engineers can precisely manage the strength, durability, workability, and cost-effectiveness of foundational construction materials.

Why Particle Size is Critical in Construction
The distribution of particle sizes within an aggregate sample, known as its gradation, directly influences the physical properties of the final construction material. A project's success often depends on getting this mix right.
The Impact on Concrete and Asphalt
A "well-graded" aggregate contains a balanced mix of particle sizes. Smaller particles fill the voids between larger ones, creating a dense and tightly packed structure.
This density is crucial. It minimizes the amount of empty space that must be filled by expensive cement paste or asphalt binder, leading to a stronger, more durable, and more economical final product.
The Role in Compaction and Drainage
For materials used in foundations or as a road base, gradation determines how well the material can be compacted to create a stable, load-bearing surface.
Furthermore, the gradation dictates the material's permeability. An "open-graded" material with few fine particles allows water to drain freely, which is essential for applications like sub-surface drainage layers.
The Sieve Analysis Process Explained
While the concept is straightforward, the process follows standardized steps to ensure accurate and repeatable results. It is one of the most common and reliable tests performed in the industry.
Preparing the Sample
First, a representative sample of the aggregate is obtained. This sample is typically dried in an oven to remove any moisture, as the test is only effective on dry particles. The dry sample is then weighed precisely.
The Sieve Stack
The core of the test is the sieve stack. This is a set of nesting sieves with wire mesh screens. The sieve at the top has the largest openings, and each subsequent sieve below it has progressively smaller openings. A solid pan is placed at the very bottom to collect the finest particles.
Shaking and Measuring
The prepared sample is poured into the top sieve. The entire stack is then placed in a mechanical shaker, which agitates it for a set period.
This agitation causes the particles to fall through the screens until they are retained on a sieve with openings smaller than their diameter. After shaking, the material retained on each sieve is weighed, and the results are recorded to create a particle size distribution curve.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any testing method, sieve analysis has distinct advantages that make it a cornerstone of quality control, as well as limitations that are important to recognize.
Key Advantages
The primary reasons for its widespread use are its simplicity and low cost. The equipment is inexpensive, the procedure is easy to perform, and it provides accurate, reproducible results relatively quickly.
This accessibility makes it an invaluable tool for quality control on virtually any construction site or in any materials lab.
Inherent Limitations
The main limitation is its resolution. A standard test might use only 8 sieves, meaning the entire particle size distribution is described by just eight data points.
Additionally, the method is generally limited to particles larger than about 50 micrometers (µm) and is only suitable for dry, non-cohesive materials.
Applying Gradation Results to Your Project
The ideal gradation depends entirely on the material's purpose. Understanding your goal is key to interpreting the results of a sieve analysis and selecting the right material.
- If your primary focus is high-strength concrete: You need a "well-graded" aggregate to maximize density and minimize the required amount of cement paste.
- If your primary focus is a drainage layer: You require a "uniformly-graded" or "open-graded" aggregate with minimal fine particles to ensure high permeability.
- If your primary focus is a stable road base: You need a specific gradation that allows for maximum compaction, providing a strong and unyielding foundation.
By mastering the principles of sieve analysis, you gain direct control over the quality, performance, and durability of your most essential construction materials.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Determines particle size distribution (gradation) of aggregates like sand and gravel. |
| Key Benefit | Ensures material properties are suitable for concrete, asphalt, or base layers. |
| Process | Dry sample is shaken through a stack of sieves with progressively smaller openings. |
| Impact | Directly influences strength, durability, workability, and cost-effectiveness of materials. |
Achieve precise quality control on your construction projects.
Accurate sieve analysis is fundamental to material performance. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable laboratory equipment, including robust sieve shakers and high-quality test sieves, to ensure your aggregate testing is consistent and compliant with industry standards.
Let us help you build with confidence. Contact our experts today to find the right sieving solutions for your lab's specific needs in construction materials testing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment
- Why is powder classification using standard sieves essential for SHS reactions? Unlock Superior Nitriding Results
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance



















