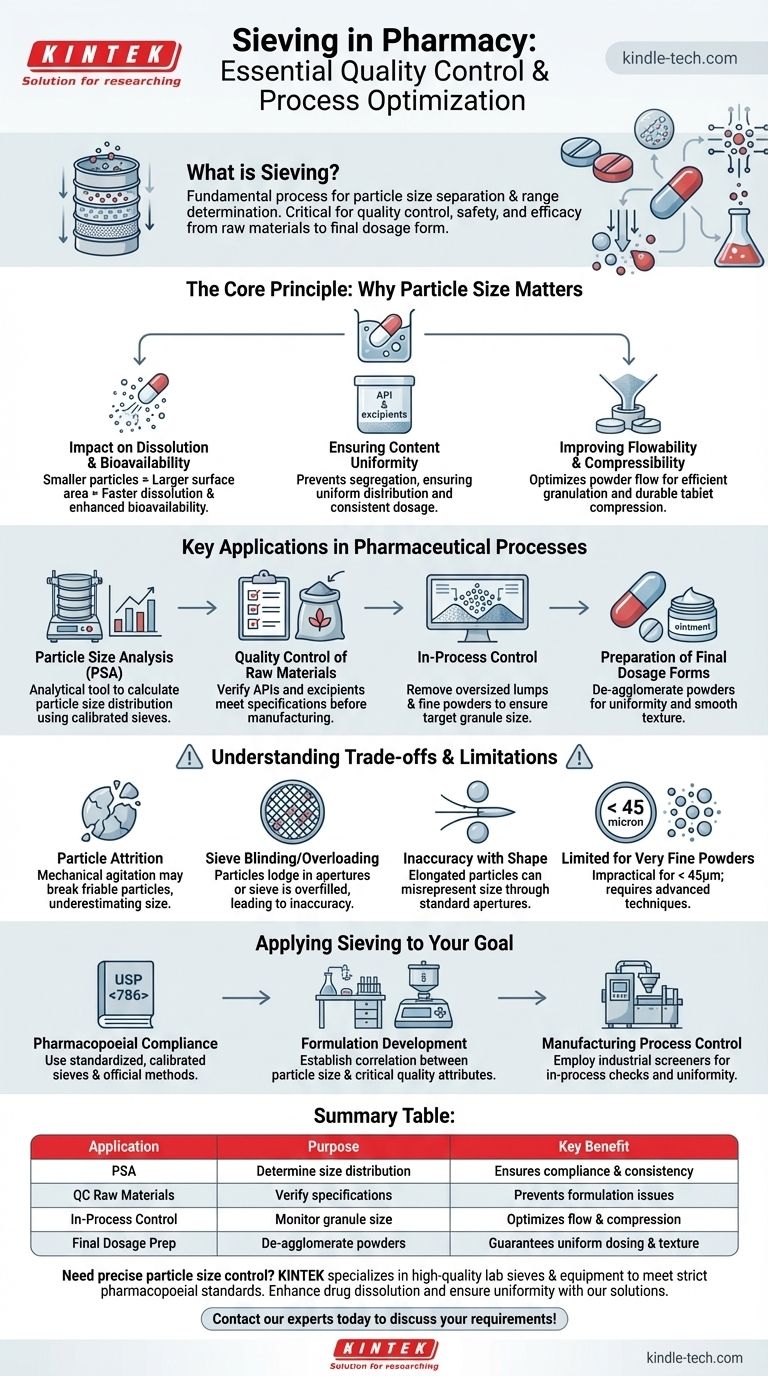
In pharmacy, sieving is a fundamental process used to separate particles based on their size and to determine the range of sizes present in a sample. This technique is not merely for sorting; it is a critical quality control tool that directly ensures the safety, efficacy, and manufacturability of pharmaceutical products, from raw materials to the final dosage form.
The core function of sieving in pharmacy is to control particle size, which is a critical physical attribute that profoundly influences a drug's dissolution rate, bioavailability, content uniformity, and stability. It is a cornerstone of ensuring that each dose of a medication is consistent and performs as intended.

The Core Principle: Why Particle Size Matters
Understanding the application of sieving requires grasping why particle size is one of the most important physical characteristics of a drug substance. Different properties are directly dependent on the size and distribution of particles within a formulation.
Impact on Dissolution and Bioavailability
A drug must dissolve before it can be absorbed by the body. Smaller particles have a larger surface area-to-volume ratio, which allows them to dissolve more quickly in bodily fluids.
By controlling and reducing particle size through processes that are verified by sieving, pharmaceutical scientists can enhance the dissolution rate and, consequently, the bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs.
Ensuring Content Uniformity
Most solid dosage forms, like tablets and capsules, contain a small amount of an Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) mixed with a larger amount of inactive ingredients (excipients).
If the particle sizes of the API and excipients are vastly different, they can segregate during mixing and handling. Sieving ensures all components have a compatible size range, promoting a homogenous blend and guaranteeing that each tablet contains the correct dose.
Improving Flowability and Compressibility
The efficiency of high-speed tablet presses depends on the consistent flow of powder from a hopper into the die cavity.
Particle size and shape significantly influence a powder's flowability. Sieving is used during processes like granulation to produce particles of a defined size that flow smoothly and can be uniformly compressed into durable tablets.
Key Applications of Sieving in Pharmaceutical Processes
Sieving is applied at multiple stages of the research, development, and manufacturing workflow. It is both an analytical tool and a processing step.
Particle Size Analysis (PSA)
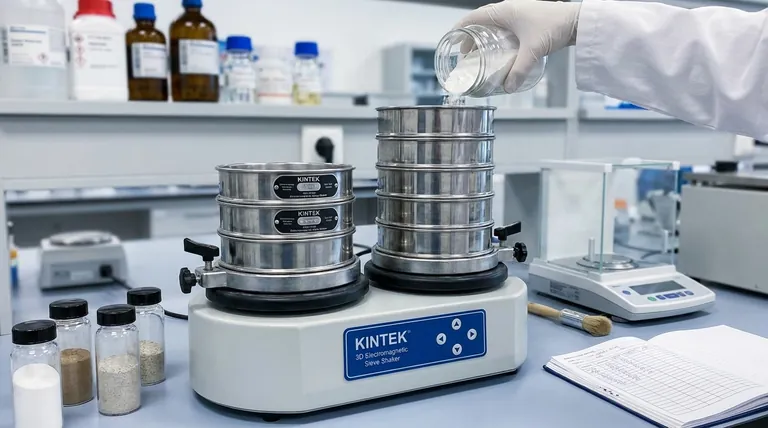
This is the most common analytical application. A stack of calibrated sieves with progressively smaller mesh openings is assembled and placed on a mechanical shaker.
A weighed powder sample is placed on the top sieve, and the shaker agitates the stack for a set time. The weight of the powder retained on each sieve is used to calculate the particle size distribution of the sample, which is a critical quality attribute.
Quality Control of Raw Materials
Before manufacturing begins, both APIs and excipients are tested to ensure they meet specifications. Sieving is a quick and effective method to verify that incoming materials have the correct particle size profile required for the intended formulation.
In-Process Control During Manufacturing
During the production of granules for tablets or capsules, sieving is used to separate out oversized lumps and fine powders. This ensures the granules are within the target size range for optimal performance in the subsequent steps, such as tablet compression.
Preparation of Final Dosage Forms
Sieving is used to de-agglomerate and ensure the uniformity of powders before they are filled into capsules. For topical preparations like ointments and creams, sieving the solid components ensures a smooth, non-gritty texture in the final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While universally applied, the sieving method has inherent limitations that a technical professional must understand to interpret results correctly.
Particle Attrition
The mechanical agitation of a sieve shaker can cause friable or brittle particles to break down (attrition). This can skew results by generating more fine particles than were present in the original sample, leading to an underestimation of the true particle size.
Sieve Blinding and Overloading
Blinding occurs when particles become lodged in the sieve apertures, blocking other particles from passing through. Overloading a sieve with too much powder prevents particles from having an opportunity to pass through the mesh, leading to inaccurate results.
Inaccuracy with Certain Particle Shapes
Standard sieve analysis assumes particles are roughly spherical. Elongated or needle-shaped particles may pass end-on through openings that are smaller than their actual length, leading to a misrepresentation of their size.
Limited Use for Very Fine Powders
Sieving is generally effective for particles larger than approximately 45 microns. For nanoparticles or very fine powders, the method is impractical, and more advanced techniques like laser diffraction or dynamic light scattering are required.
Applying Sieving to Your Pharmaceutical Goal
The specific application of sieving depends on your objective within the pharmaceutical lifecycle.
- If your primary focus is pharmacopoeial compliance: You must use standardized, calibrated test sieves and follow the specific methodology outlined in the official monograph (e.g., USP <786>) for particle size distribution.
- If your primary focus is formulation development: Use analytical sieving to establish a direct correlation between particle size distribution and critical quality attributes like dissolution profiles and tablet hardness.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing process control: Employ industrial-scale sieves (sometimes called screeners) for in-process checks to ensure granule uniformity, improve powder flow, and minimize batch-to-batch variability.
Ultimately, mastering the principles of sieving is fundamental to controlling the quality, safety, and therapeutic performance of nearly every solid dosage form in pharmacy.
Summary Table:
| Application | Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size Analysis (PSA) | Determine particle size distribution | Ensures compliance and batch consistency |
| Quality Control of Raw Materials | Verify API and excipient specifications | Prevents formulation issues before production |
| In-Process Control | Monitor granule size during manufacturing | Optimizes flowability and tablet compression |
| Final Dosage Form Preparation | De-agglomerate powders for capsules/ointments | Guarantees smooth texture and uniform dosing |
Need precise particle size control for your pharmaceutical development or manufacturing? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab sieves and equipment designed to meet strict pharmacopoeial standards. From R&D to QC, our solutions help you enhance drug dissolution, ensure content uniformity, and streamline your production process. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific sieving requirements and achieve superior product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of sieving machines? Choose the Right Motion for Your Material
- What are the applications of sieving machine? From Mining to Pharmaceuticals
- What is powder sieving? A Guide to Accurate Particle Size Separation
- What is the speed of a sieving machine? Optimize Vibration for Maximum Efficiency and Accuracy
- What is the principle of sieving machine? Achieve Accurate Particle Size Separation



















