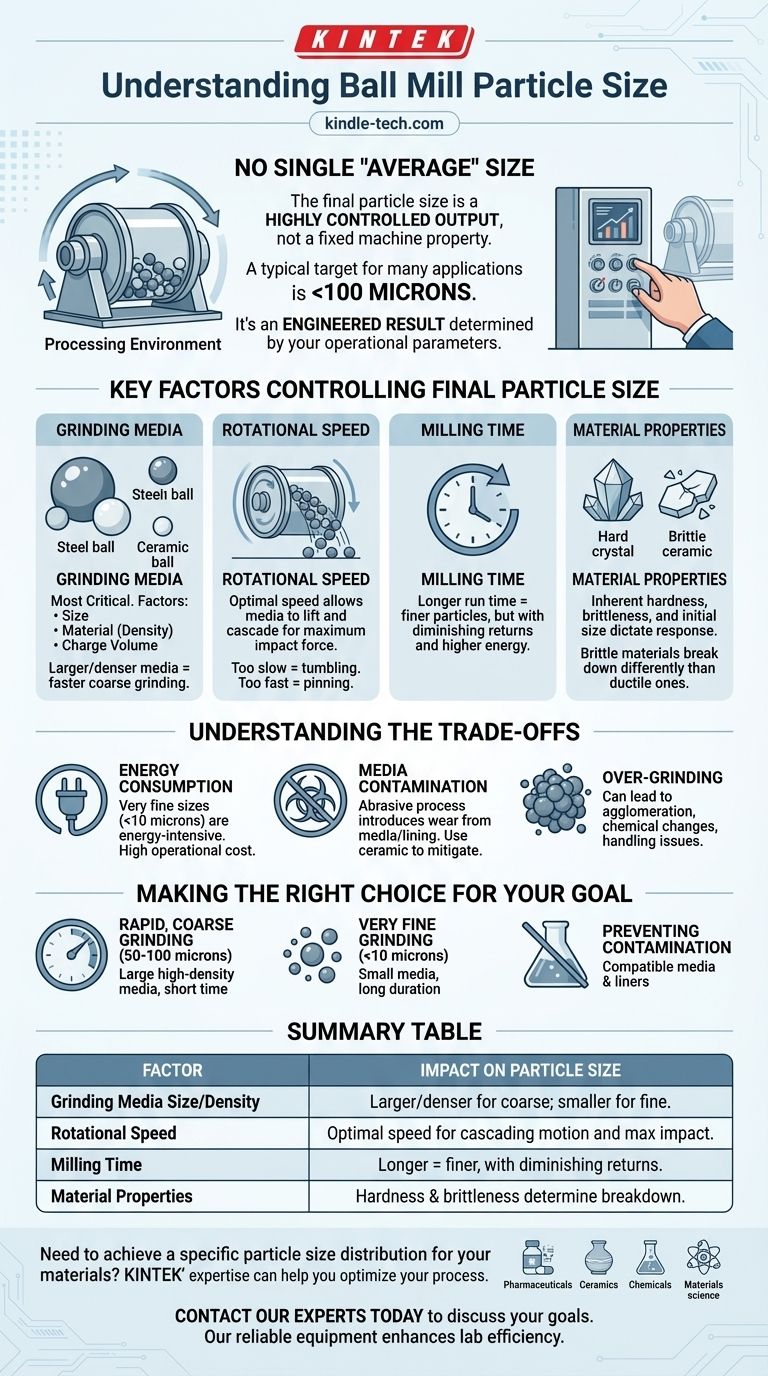
To be direct, there is no single "average" particle size for a ball mill because the final size is a highly controlled output, not a fixed property of the machine. However, a typical target for many applications is a particle size of less than 100 microns. The true purpose of a ball mill is to provide a process where you can manipulate key variables to achieve the precise particle size your specific application requires.
The most critical takeaway is to shift your perspective. Instead of asking what size a ball mill produces, you should define the particle size you need. The ball mill is a system you then configure to meet that specific goal.

Why There Is No Single "Average" Size
A ball mill is not like a sieve with a fixed output. It is a dynamic system designed for size reduction, where the final particle distribution is the result of several interacting factors.
The Machine as a Process
Think of a ball mill as a processing environment rather than a simple tool. The hollow, rotating drum and the grinding media inside create a complex interplay of forces—impact and attrition—that break down particles over time.
An Engineered Outcome
The final particle size is an engineered result. The process begins with a material of a certain size and ends when the desired fineness is achieved. This outcome is determined entirely by the operational parameters you set.
The Key Factors Controlling Final Particle Size
To achieve a specific particle size, you must understand and control the core variables of the milling process. Each one has a direct and significant impact on the final product.
Grinding Media
The balls themselves are the most critical element. Key factors include their size, material (density), and the charge volume (how much of the mill is filled with them). Larger, denser media create higher impact forces, leading to faster size reduction for coarse materials.
Rotational Speed
The speed at which the mill's shell rotates is crucial. If it's too slow, the balls simply tumble and cause grinding through abrasion. If it's too fast, centrifugal force will pin the balls to the shell wall, and no grinding will occur. The optimal speed allows the media to be lifted and then cascade down, creating the maximum impact force for efficient grinding.
Milling Time
This is the most straightforward variable. All else being equal, the longer you run the mill, the finer the resulting particles will be. However, there are diminishing returns, as it takes exponentially more time and energy to break down the smallest particles.
Material Properties
The inherent characteristics of the material you are grinding—its hardness, brittleness, and initial size—will dictate how it responds to the milling process. A brittle ceramic will break down far differently than a ductile metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing for the smallest possible particle size is not always the best strategy. Understanding the limitations and consequences is essential for an efficient and effective process.
Energy Consumption
Achieving very fine particle sizes (e.g., sub-10 micron) is an energy-intensive process. The energy required to grind particles increases dramatically as the target particle size decreases. This has a direct impact on operational cost.
Media Contamination
The grinding process is abrasive by nature, meaning the grinding media (the balls) and the mill lining will wear down over time. This wear introduces minute amounts of contamination into your product. Using ceramic media instead of steel can mitigate this, but it comes at a higher cost.
Over-Grinding
Sometimes, making particles too fine can be detrimental. Over-grinding can lead to issues like particle agglomeration (clumping), changes in the material's chemical properties, or difficulty in downstream handling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational settings should be a direct reflection of your desired outcome. By adjusting the key variables, you can tune the ball mill to produce exactly what you need.
- If your primary focus is rapid, coarse grinding (e.g., 50-100 microns): Use larger, high-density media and a relatively short milling time to maximize impact forces.
- If your primary focus is very fine grinding (e.g., <10 microns): Utilize smaller media to increase surface area contact and run the mill for significantly longer durations.
- If your primary focus is preventing product contamination: Select grinding media and liners made of a material (like ceramic or stainless steel) that is compatible with your final product.
Ultimately, a ball mill gives you the control to produce the precise particle size your process demands.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Particle Size |
|---|---|
| Grinding Media Size/Density | Larger, denser media for coarse grinding; smaller media for fine grinding. |
| Rotational Speed | Optimal speed creates a cascading motion for maximum impact and efficient grinding. |
| Milling Time | Longer milling times produce finer particles, but with diminishing returns. |
| Material Properties | Hardness and brittleness of the feedstock determine how it breaks down. |
Need to achieve a specific particle size distribution for your materials?
KINTEK's expertise in lab milling solutions can help you optimize your process. We provide high-quality ball mills and the technical support to select the right grinding media and operational parameters for your application—whether you're in pharmaceuticals, ceramics, chemicals, or materials science.
Contact our experts today to discuss your particle size goals and discover how KINTEK's reliable equipment can enhance your lab's efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of polyurethane ball mill jars for silicon nitride? Ensure Purity & Prevent Metal Contamination
- Why are zirconia (ZrO2) milling jars recommended for sulfide electrolytes? Ensure Purity in Li6PS5Cl Synthesis
- What is the benefit of using tungsten carbide (WC) milling jars and balls? Achieve High-Energy Milling Efficiency
- How do stainless steel grinding jars and balls contribute to mechanical alloying? Optimize HEA Powder Synthesis
- Why are silicon nitride or zirconia preferred for milling iodo-vanadate-lead precursors? Ensure High Purity Results



















