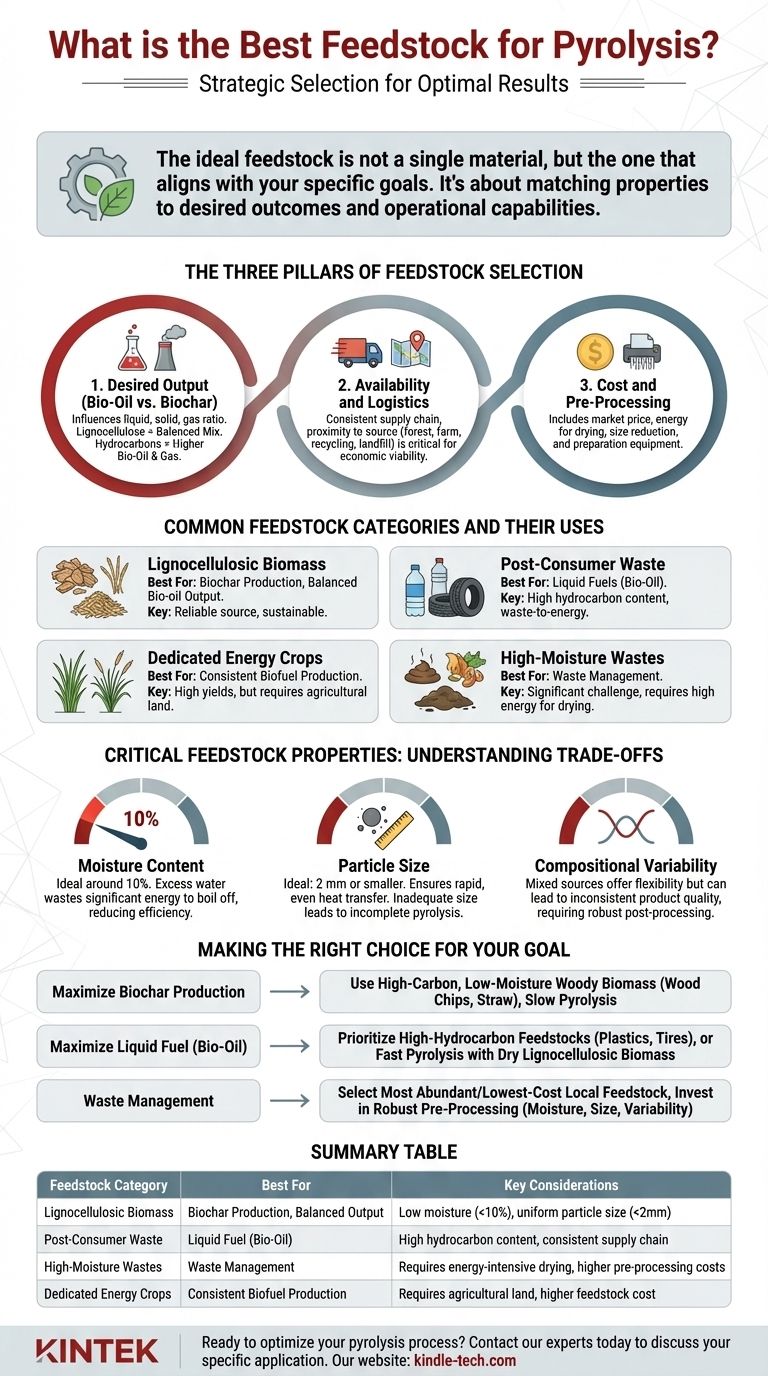
The ideal feedstock for pyrolysis is not a single material, but rather the one that best aligns with your specific goals. While many organic materials can be used, their chemical composition, moisture content, and physical form dictate the efficiency of the process and the quality of the end products. The "best" choice is a strategic decision based on whether you want to maximize liquid fuel, solid biochar, or simply process a particular waste stream.
Choosing the right feedstock isn't about finding one perfect material. It's about matching the feedstock's properties—its composition, cost, and availability—to your desired outcome and operational capabilities.
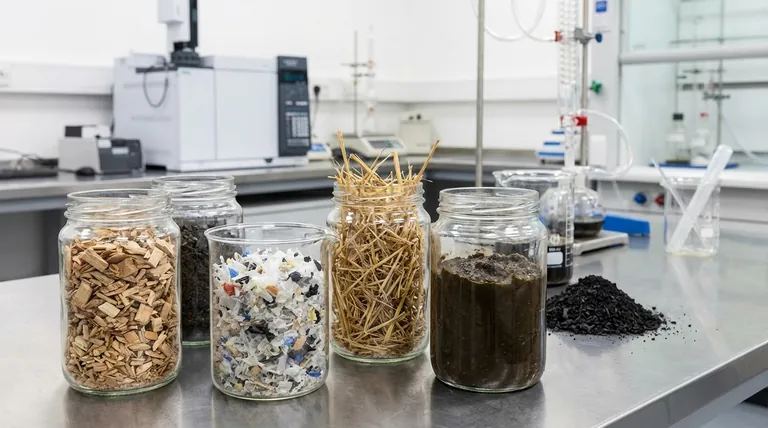

The Three Pillars of Feedstock Selection
The suitability of a pyrolysis feedstock is never absolute. It must be evaluated against three core factors: the products you want to create, the logistics of your supply chain, and the costs of preparation.
Pillar 1: Desired Output (Bio-Oil vs. Biochar)
The chemical makeup of the feedstock directly influences the ratio of liquid (bio-oil), solid (biochar), and gas products.
Materials high in lignocellulose, such as wood and agricultural residues, are versatile. They can produce a balanced mix of bio-oil and biochar. The final yield is heavily influenced by the process conditions; slow pyrolysis of wood, for example, maximizes biochar.
Materials high in hydrocarbons, such as plastics and tires, will inherently yield a much higher percentage of liquid pyrolysis oil and combustible gases, with a smaller fraction of solid residue.
Pillar 2: Availability and Logistics
The most technically suitable feedstock is useless if it is not reliably and affordably available.
A successful pyrolysis operation depends on a consistent supply chain. Proximity to the source—be it a forest, a farm, a recycling facility, or a landfill—is critical to minimizing transportation costs, which can significantly impact your project's economic viability.
Pillar 3: Cost and Pre-Processing
Raw feedstock is almost never ready for direct use. The costs associated with acquiring and preparing the material are a major operational consideration.
This includes the market price of the material itself (if not a waste product) and, more importantly, the energy and capital required for pre-processing steps like drying and size reduction.
Common Feedstock Categories and Their Uses
Different categories of feedstock are better suited for different applications.
Lignocellulosic Biomass (Wood, Agricultural Waste)
This is the most common category and includes wood chips, sawdust, straw, corn stover, and yard waste. It is a reliable source for producing biochar, a valuable soil amendment, and can also yield significant amounts of bio-oil through fast pyrolysis.
Post-Consumer Waste (Plastics, Tires)
This category is ideal for waste-to-energy applications focused on producing liquid fuels. Mixed plastics from municipal solid waste (MSW) or shredded tires can be converted into valuable pyrolysis oil, which can be refined into fuels or chemical feedstocks.
Dedicated Energy Crops
Crops like switchgrass and miscanthus are grown specifically for biofuel production. They offer high yields and consistent quality but require dedicated agricultural land, making their economics different from waste-based feedstocks.
High-Moisture Wastes (Sludge, Food Waste)
Materials like sewage sludge or meat processing waste can be pyrolyzed, but they present a significant challenge. Their high water content must be removed before the process, adding substantial energy costs for drying.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Critical Feedstock Properties
Ignoring key feedstock properties can lead to process inefficiency and poor-quality products. These are non-negotiable prerequisites for successful operation.
Moisture Content: The Energy Killer
The ideal feedstock has a moisture content of around 10%. Any higher, and the pyrolysis process wastes significant energy just to boil off the excess water instead of breaking down the organic material. This reduces your net energy output and overall efficiency.
Particle Size: The Efficiency Driver
Heat must be transferred rapidly and evenly throughout the feedstock. This requires reducing the material to small, uniform particles, typically 2 mm or smaller. Inadequate size reduction leads to incomplete pyrolysis, lowering your yield of desired products.
Compositional Variability: The Consistency Challenge
Using a mixed or variable feedstock source like municipal solid waste offers feedstock flexibility. However, this variability can lead to inconsistent product quality. A plant designed for feedstock flexibility is more robust but may require more sophisticated post-processing to create a uniform final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of feedstock should be a direct reflection of your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing biochar production: Use a high-carbon, low-moisture woody biomass like wood chips or straw and operate under slow pyrolysis conditions.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid fuel (bio-oil): Prioritize high-hydrocarbon feedstocks like waste plastics and tires, or use fast pyrolysis with dry lignocellulosic biomass.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Select the most abundant and lowest-cost local feedstock available, but ensure you invest in robust pre-processing to manage its moisture, size, and variability.
By defining your operational goals first, you can strategically select the most effective feedstock for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Feedstock Category | Best For | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Lignocellulosic Biomass (Wood, Straw) | Biochar Production, Balanced Output | Low moisture (<10%), uniform particle size (<2mm) |
| Post-Consumer Waste (Plastics, Tires) | Liquid Fuel (Bio-Oil) | High hydrocarbon content, consistent supply chain |
| High-Moisture Wastes (Sludge, Food Waste) | Waste Management | Requires energy-intensive drying, higher pre-processing costs |
| Dedicated Energy Crops (Switchgrass) | Consistent Biofuel Production | Requires agricultural land, higher feedstock cost |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process with the right feedstock? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your laboratory's pyrolysis and biomass analysis needs. Whether you're researching bio-oil yields, biochar quality, or waste conversion efficiency, our reliable tools help you achieve accurate and reproducible results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application and enhance your research outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Tweezers
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- How should a glassy carbon sheet be dried and stored? Protect Your Electrode's Pristine Surface
- Which material should not be used inside vacuum chamber? Avoid Outgassing and Contamination
- What can carbon nanotubes be used for? Unlock Superior Performance in Batteries & Materials
- How do you maintain vacuum pressure? Master the balance between gas removal and gas load for stable performance.
- What are the units for vacuum pressure? Torr, mbar, and Pascal Explained











