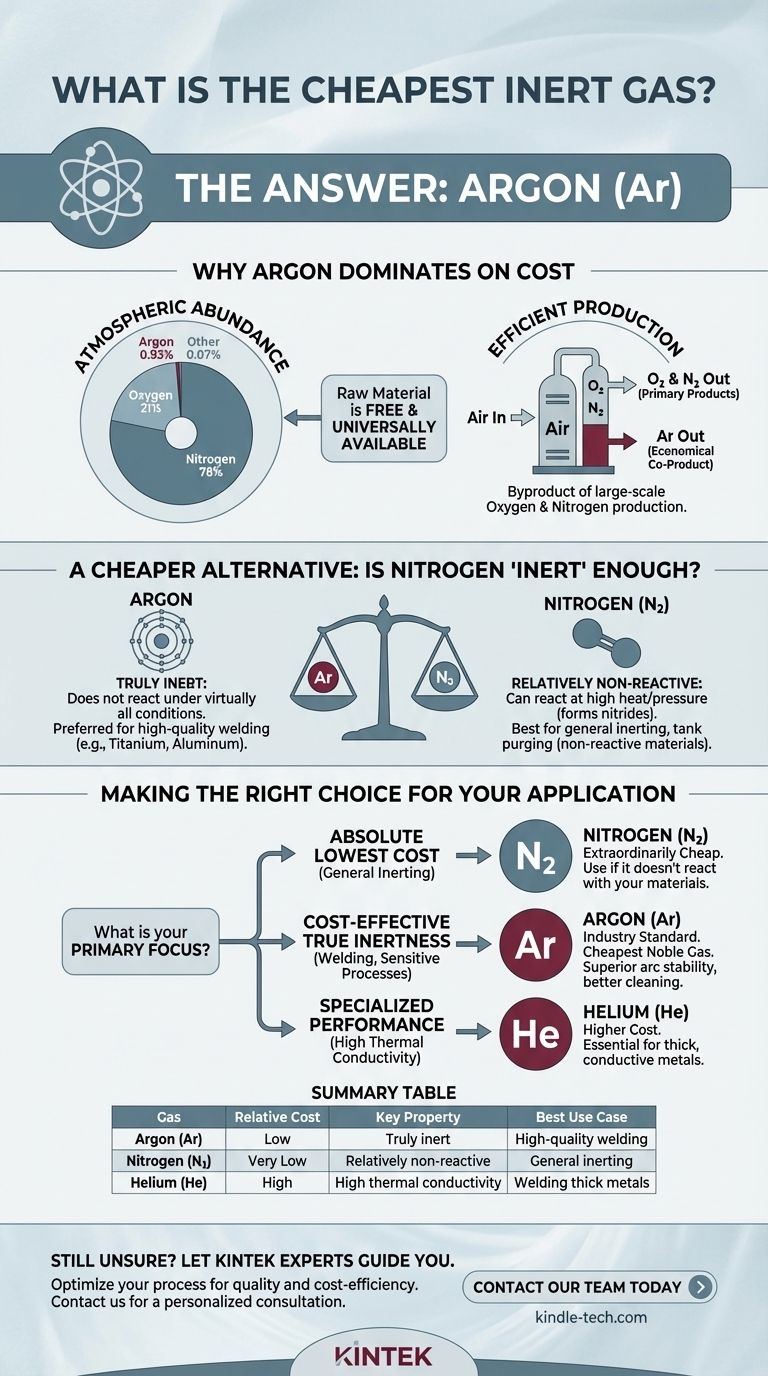
By a significant margin, the cheapest and most commonly used true inert gas is Argon (Ar). Its low cost is a direct result of its relative abundance in the Earth's atmosphere, making it simple and economical to produce compared to other noble gases.
The core reason for Argon's cost-effectiveness is not its inherent properties, but its source. Because it makes up nearly 1% of the air we breathe, it can be efficiently harvested as a byproduct of large-scale industrial processes that separate air to produce oxygen and nitrogen.

Why Argon Dominates on Cost
The price of any industrial gas is fundamentally tied to its availability and the complexity of its extraction process. Argon has a natural advantage on both fronts.
Sourced Directly from the Air
Argon is the third most abundant gas in our atmosphere, comprising approximately 0.93%. While this sounds small, it is vastly more plentiful than any other noble gas.
This atmospheric abundance means the raw material for producing argon is free and universally available.
The Efficiency of Fractional Distillation
Argon is produced commercially through the fractional distillation of liquid air. This is the same process used to produce massive quantities of liquid nitrogen and oxygen for industrial and medical use.
Because the infrastructure for air separation plants already exists on a global scale, argon is essentially an economical co-product. The primary cost is energy, not sourcing a rare material.
Comparing Abundance to Other Gases
The cost of other noble gases skyrockets because of their extreme rarity. Helium, for example, is primarily extracted from natural gas deposits and is a finite resource. Neon, Krypton, and Xenon exist in the atmosphere in mere parts-per-million, making their extraction far more energy-intensive and expensive.
A Cheaper Alternative: Is Nitrogen "Inert" Enough?
While Argon is the cheapest noble gas, it's important to consider Nitrogen (N₂), which is often used for its inert properties and is even cheaper.
The Unbeatable Cost of Nitrogen
Nitrogen makes up 78% of the atmosphere, making it extraordinarily cheap to produce via the same air separation process as Argon. If an application simply requires displacing oxygen and the gas does not need to be truly non-reactive, Nitrogen is the most economical choice.
The Critical Distinction: True Inertness vs. Reactivity
The key difference is that Argon is a noble gas, meaning it is chemically inert under virtually all conditions. Its outer electron shell is full, so it does not want to react with other elements.
Nitrogen, however, is not a noble gas. While it is relatively non-reactive at standard temperatures, it can and will react with certain materials under conditions of high heat and pressure, forming compounds called nitrides. This can be detrimental in processes like the welding of titanium, magnesium, or certain stainless steels.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When "Cheapest" Isn't Best
Choosing an inert gas is not just about price; it's about matching the gas's properties to the technical requirements of the application.
Argon for Superior Welding
In many MIG and TIG welding applications, Argon is preferred over cheaper Nitrogen. It provides a highly stable arc, better cleaning action, and produces a higher quality, more precise weld bead on metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium.
Density and Arc Characteristics
Argon is significantly denser than air. This allows it to effectively shield the weld pool from atmospheric contamination with a lower flow rate compared to lighter gases like Helium.
When to Use More Expensive Gases
Despite its high cost, Helium is sometimes required. Its high thermal conductivity creates a hotter, more fluid weld puddle, which is essential for welding thick sections of conductive metals like aluminum or copper. Often, a more expensive Argon/Helium mix is used to balance cost and performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must balance budget against the specific chemical and physical properties required for a successful outcome.
- If your primary focus is the absolute lowest cost for general inerting: Nitrogen is your most economical choice for applications like purging tanks or blanketing, provided it does not react with your materials.
- If your primary focus is a cost-effective and truly non-reactive gas for welding or sensitive processes: Argon is the industry standard and the cheapest of the noble gases.
- If your primary focus is a specialized technical requirement like high thermal conductivity or low density: You must look beyond cost to gases like Helium, where performance justifies the higher price.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental properties of each gas is the key to selecting the most effective solution for your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Gas | Relative Cost | Key Property | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Argon (Ar) | Low | Truly inert (noble gas) | High-quality welding, sensitive processes |
| Nitrogen (N₂) | Very Low | Relatively non-reactive | General inerting, tank purging (non-reactive materials) |
| Helium (He) | High | High thermal conductivity | Welding thick, conductive metals (e.g., aluminum) |
Still Unsure Which Inert Gas is Right for Your Lab?
The choice between cost and performance is critical. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance to help you select the perfect gas for your specific application—whether it's for welding, material processing, or creating an inert atmosphere.
**Let our experts help you optimize your process for both quality and cost-efficiency. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Sterile Slapping Type Homogenizer for Tissue Mashing and Dispersing
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What type of instruments Cannot be autoclaved? Protect Your Equipment from Heat and Moisture Damage
- How should solid materials in bags be prepared for decontamination? Master Steam Penetration for Safe Sterilization
- What are the advantages of using a laboratory ultrasonic homogenizer for PHA extraction? Faster Physical Cell Disruption
- What is the significance of using an ultrasonic homogenizer to treat cells on NCD films? Optimize Protein Extraction
- Which instrument Cannot be autoclaved? Protect Your Lab Equipment from Sterilization Damage












