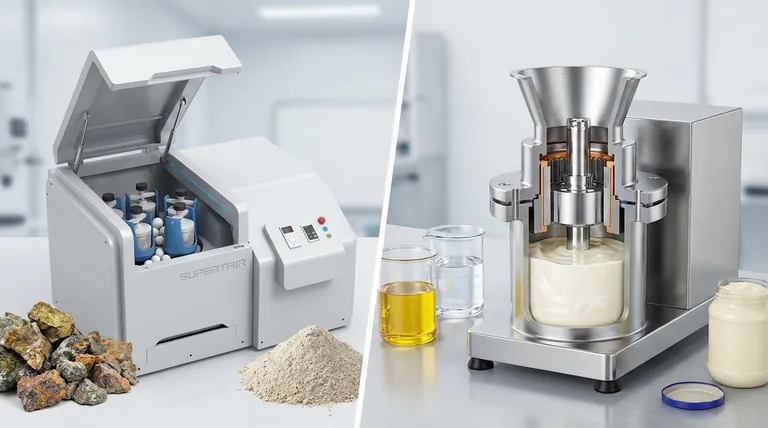
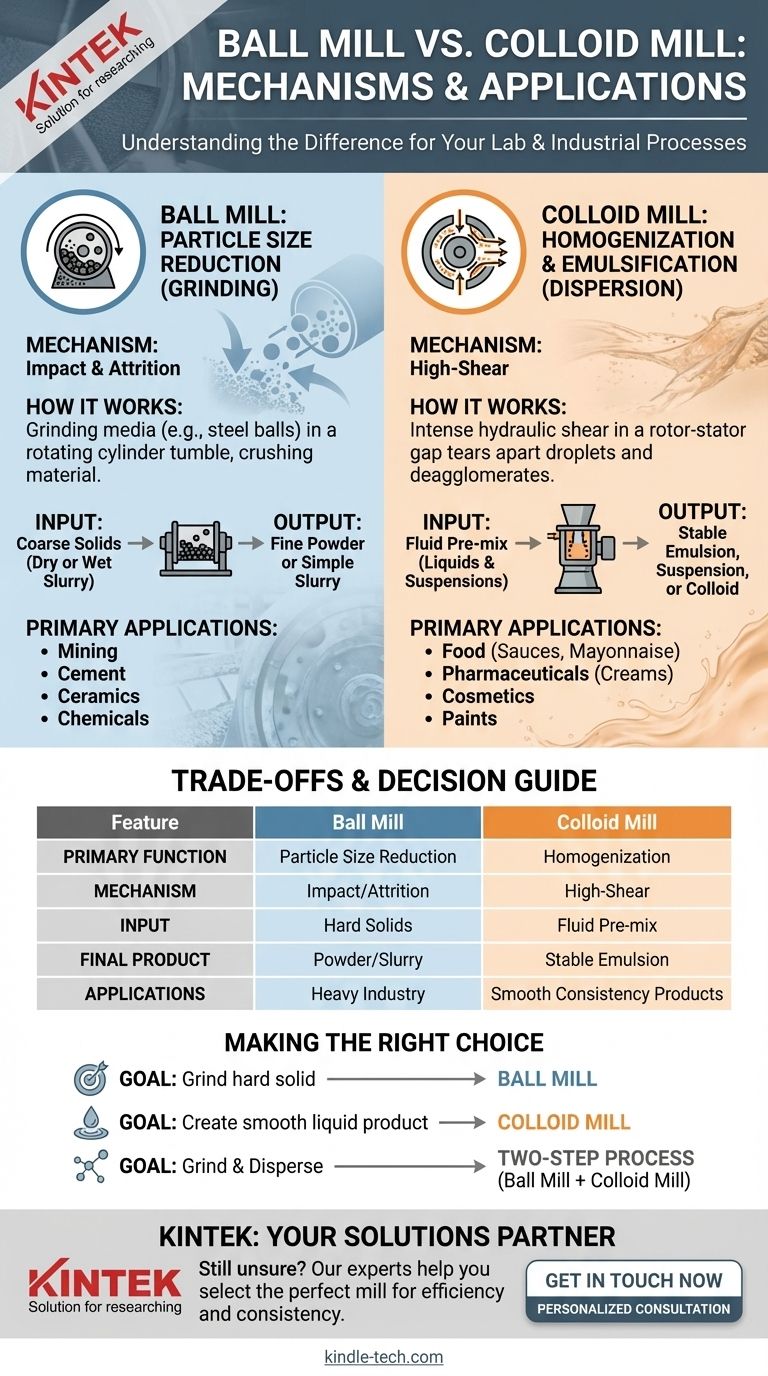
At a fundamental level, the difference between a ball mill and a colloid mill comes down to their mechanism and purpose. A ball mill is a grinder designed to break down hard, solid materials into fine powders through impact and attrition. In contrast, a colloid mill is a homogenizer that uses intense hydraulic shear to create stable emulsions or dispersions within a liquid medium.
The core distinction is this: a ball mill performs particle size reduction on solids, while a colloid mill performs homogenization and emulsification on fluids. They are not interchangeable, as they are engineered to solve entirely different processing challenges.

The Ball Mill: Grinding Through Impact and Attrition
A ball mill is one of the oldest and most reliable tools for comminution, which is the process of reducing the size of solid materials.
How It Works: The Grinding Media
A ball mill consists of a large hollow cylinder that rotates on its horizontal axis. This cylinder is partially filled with the material to be ground, along with a grinding medium—typically steel or ceramic balls.
As the cylinder rotates, the balls are lifted up the side and then cascade or fall back down. This action crushes and grinds the material through two primary forces: impact from the falling balls and attrition as the balls tumble against each other and the cylinder wall.
Input and Output
The input for a ball mill is a coarse solid, which can be processed dry or as a wet slurry. The output is a fine powder or a slurry containing finely ground particles, typically in the micron range.
Primary Applications
Ball mills are workhorses in heavy industry where bulk grinding is required. Common uses include:
- Mining: Grinding metallic ores for mineral extraction.
- Cement Manufacturing: Grinding clinker and gypsum into finished cement.
- Ceramics: Preparing ceramic powders and glazes.
- Pyrotechnics: Milling black powder and other chemical compounds.
The Colloid Mill: Creating Dispersions Through High Shear
A colloid mill operates on a completely different principle. Its function is not to crush hard solids but to disperse and homogenize materials that are already in a liquid phase.
How It Works: The Rotor-Stator Gap
A colloid mill features a high-speed rotor that spins with microscopic clearance relative to a stationary part called the stator. Both the rotor and stator are often cone-shaped and may be toothed or grooved.
The fluid mixture is fed into the gap between the rotor and stator. The extremely high rotation speed (often thousands of RPM) creates intense hydraulic shear and turbulence in the tiny gap, which tears apart droplets and deagglomerates solid particles.
Input and Output
The input must be a fluid pre-mix, such as a solid suspended in a liquid or two immiscible liquids (like oil and water). The output is a highly stable, uniform mixture—an emulsion, suspension, or colloid—where particles are finely dispersed and resistant to separation.
Primary Applications
Colloid mills are essential for creating products that rely on a smooth, stable consistency. Common uses include:
- Food Industry: Making mayonnaise, salad dressings, sauces, and peanut butter.
- Pharmaceuticals: Producing creams, ointments, syrups, and injectable suspensions.
- Cosmetics: Manufacturing lotions, creams, and other emulsions.
- Chemicals: Creating paints, inks, and coatings.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Grinding vs. Homogenizing
Choosing between these mills requires understanding their distinct operational boundaries and outcomes.
Final Product State
This is the most critical difference. A ball mill produces a dry powder or a simple slurry of ground solids. A colloid mill produces a stable liquid emulsion or suspension. You cannot make mayonnaise with a ball mill, and you cannot efficiently grind quartz into powder with a colloid mill.
Energy and Mechanism
A ball mill uses blunt mechanical force (impact and attrition) to shatter crystalline structures. It is a brute-force, often energy-intensive process. A colloid mill uses fluid dynamics and high-velocity shear to rip apart soft droplets or break up particle clumps in a liquid.
Material Constraints
Ball mills are designed to handle hard, abrasive materials. Colloid mills are precision instruments designed only for fluid systems. Feeding large, hard particles into a colloid mill would instantly damage the rotor and stator.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be guided entirely by the final product you need to create.
- If your primary focus is to grind a hard, coarse solid into a fine powder: The ball mill is the correct instrument for this size reduction task.
- If your primary focus is to create a smooth, stable liquid product from a pre-mixed fluid: The colloid mill is the essential tool for homogenization and emulsification.
- If your goal is to both grind a solid and disperse it into a stable liquid: You likely need a two-step process, using a ball mill for primary grinding before introducing the powder into a liquid and processing it with a colloid mill.
Selecting the right mill begins with clearly defining whether your goal is particle size reduction or fluid homogenization.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Ball Mill | Colloid Mill |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Particle Size Reduction (Grinding) | Homogenization & Emulsification |
| Mechanism | Impact & Attrition with Grinding Media | High-Shear in Rotor-Stator Gap |
| Input Material | Hard, Coarse Solids (Dry or Wet Slurry) | Fluid Pre-mix (Liquids & Suspensions) |
| Final Product | Fine Powder or Simple Slurry | Stable Emulsion, Suspension, or Colloid |
| Typical Applications | Mining, Cement, Ceramics, Chemicals | Food (Sauces, Mayonnaise), Pharmaceuticals, Cosmetics |
Still Unsure Which Mill is Right for Your Lab?
Choosing the correct equipment is critical for achieving your desired results, whether you're developing a new pharmaceutical cream or grinding research materials. KINTEK specializes in providing the right lab equipment and consumables for your specific application.
Our experts can help you select the perfect mill to ensure efficiency, consistency, and success in your laboratory processes.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and let us help you optimize your workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- What is a planetary milling machine used for? Achieve Nano-Scale Grinding for Hard & Soft Materials
- What are the effects of ball milling? A Deep Dive into Mechanical Alloying and Material Transformation
- What is the core role of a high-energy planetary ball mill in MCP? Unlock Nanoscale Carbide Synthesis Efficiency
- What are the parameters of a planetary ball mill? Master Speed, Time, and Media for Perfect Grinding
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in evaluating the processing performance of Miscanthus hydrochar?



















