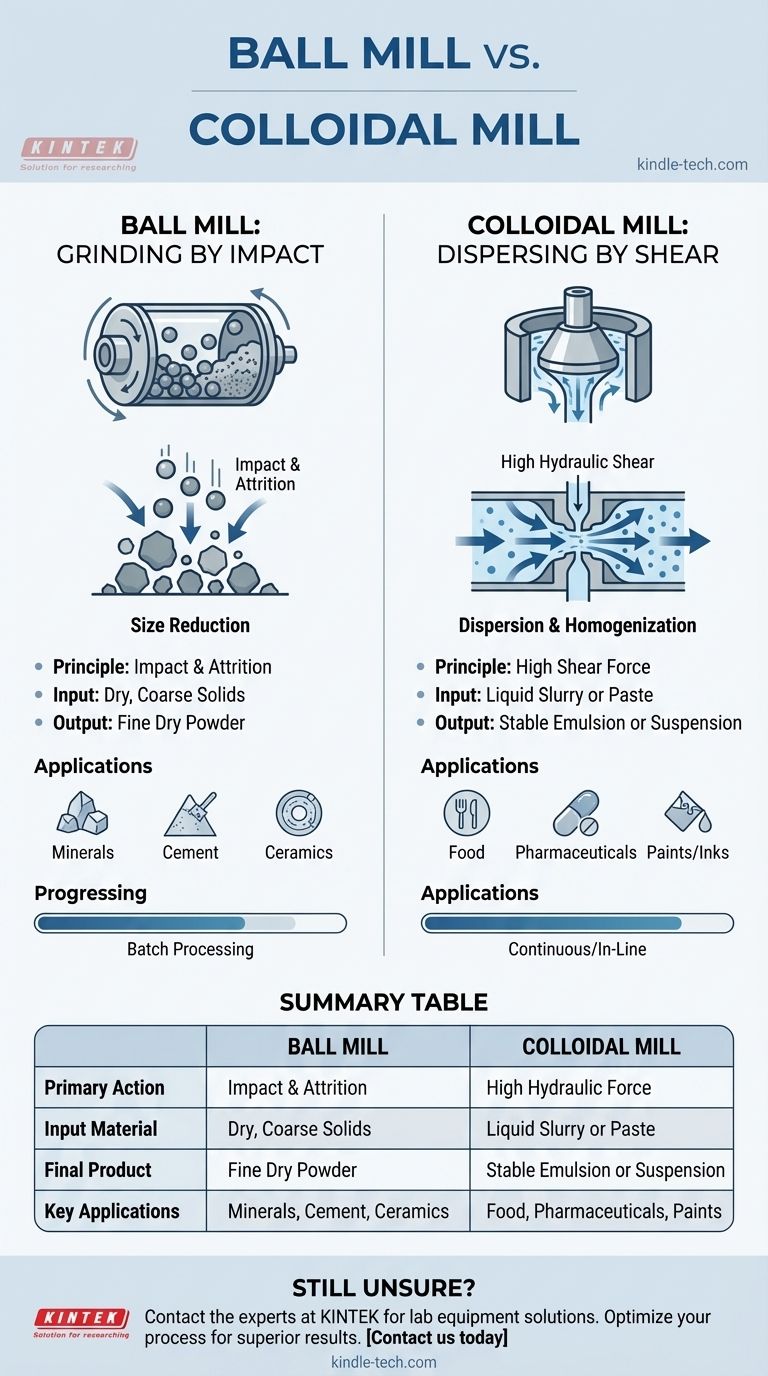
The fundamental difference is in their mechanical action and intended purpose. A ball mill is a grinder that uses the physical impact of grinding media to break down solid particles into smaller pieces, typically creating a dry powder. A colloidal mill is a high-shear homogenizer that disperses or emulsifies particles within a liquid by forcing the fluid through a narrow gap between a rotor and a stator.
The core distinction is simple: a ball mill grinds solids, while a colloidal mill disperses particles in a liquid. Choosing between them depends entirely on whether your goal is to pulverize a solid material or to create a stable liquid emulsion or suspension.

How a Ball Mill Works: Grinding by Impact
A ball mill is designed for one primary purpose: reducing the particle size of solid materials through impact and attrition.
The Principle of Operation
A ball mill consists of a hollow cylindrical shell that rotates on its axis. This shell is partially filled with the material to be ground, along with grinding media—typically steel or ceramic balls.
As the shell rotates, the balls are lifted up the side of the shell and then cascade or fall back down.
The Force of Impact and Attrition
The size reduction happens in two ways. Impact occurs when the balls fall and crush the material trapped between them. Attrition occurs as the balls tumble and rub against each other and the inner surface of the mill, grinding the material down.
Key Applications and Output
Ball mills are workhorses in industries that need to produce fine powders from coarse, hard materials.
Common applications include mineral processing, cement production, pyrotechnics, and ceramic manufacturing. The final product is typically a fine, dry powder measured in microns.
How a Colloidal Mill Works: Dispersing by Shear
A colloidal mill does not rely on impact. Its function is to create extremely stable mixtures by subjecting fluids to intense mechanical stress.
The Principle of Operation
A colloidal mill uses a rotor-stator mechanism. A cone-shaped rotor spins at very high speeds (thousands of RPM) with a minute clearance—often less than a millimeter—from a stationary outer element, the stator.
The material, which must be in a liquid or semi-liquid form, is fed into the gap between these two components.
The Force of High Shear
As the fluid is forced through this tiny, high-velocity gap, it is subjected to immense hydraulic shear. This force tears apart droplets and deagglomerates solid particles, dispersing them uniformly throughout the liquid medium.
Key Applications and Output
Colloidal mills are essential for creating emulsions (mixing immiscible liquids like oil and water) and suspensions (dispersing fine solid particles in a liquid).
They are critical in the food industry for products like mayonnaise and salad dressings, in pharmaceuticals for creams and ointments, and in chemical manufacturing for producing paints, inks, and lubricants. The goal is a smooth, stable, and homogenous liquid product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is a direct replacement for the other; they solve different problems and come with distinct considerations.
Starting Material Condition
A ball mill is your tool for starting with dry, coarse solids. A colloidal mill requires the material to already be in a liquid slurry or paste form.
Energy and Heat
Ball milling can be a highly energy-intensive and slow process, especially for achieving very fine particle sizes.
Colloidal mills generate significant heat due to the intense shear forces. For heat-sensitive products, a cooling jacket is often a non-negotiable component.
Contamination Risk
In ball milling, the grinding media and the mill lining can wear down over time, potentially introducing small amounts of contamination into the final product. This is a critical consideration in high-purity applications.
Process Type
Ball mills are most often used for batch processing. As noted in development, the mill's diameter dictates grinding performance, while its length primarily affects the batch capacity.
Colloidal mills are easily integrated into continuous or in-line processes, making them highly efficient for large-scale liquid production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct mill requires a clear understanding of your input material and desired final product.
- If your primary focus is creating a fine, dry powder from a hard solid (e.g., ore, ceramic): The ball mill is the correct and necessary tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is creating a stable liquid emulsion (e.g., salad dressing, cosmetic cream): The colloidal mill is the industry standard for achieving the required high shear.
- If your primary focus is dispersing a pre-milled powder into a liquid (e.g., paint, ink): The colloidal mill is designed specifically to break apart clumps and ensure a smooth, homogenous suspension.
- If you are developing a complex multi-step process: You might use a ball mill first to produce a fine powder, which is then mixed into a liquid and processed through a colloidal mill for final homogenization.
Ultimately, choosing the right mill is about matching the machine's fundamental mechanical force to the physical transformation you need to achieve.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Ball Mill | Colloidal Mill |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Action | Impact & Attrition (Grinding) | High Shear (Dispersion/Homogenization) |
| Input Material | Dry, Coarse Solids | Liquid Slurry or Paste |
| Final Product | Fine Dry Powder | Stable Liquid Emulsion or Suspension |
| Key Applications | Minerals, Cement, Ceramics | Food, Pharmaceuticals, Paints, Inks |
Still unsure which mill is right for your lab's specific needs? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions for all your laboratory grinding and homogenization challenges. Contact us today for a personalized consultation to optimize your process and achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why use zirconia ball milling jars for SiC/ZTA composite powders? Ensure High Purity & Efficient Particle Refinement
- Why is a ball mill jar lined with Y-ZrO2 required for Na3PS4 synthesis? Ensuring Purity in Sulfide Electrolytes
- What is the benefit of using tungsten carbide (WC) milling jars and balls? Achieve High-Energy Milling Efficiency
- What is the ball mill based on the principle of? Impact and Attrition for Efficient Grinding
- What are the advantages of polyurethane ball mill jars for silicon nitride? Ensure Purity & Prevent Metal Contamination



















