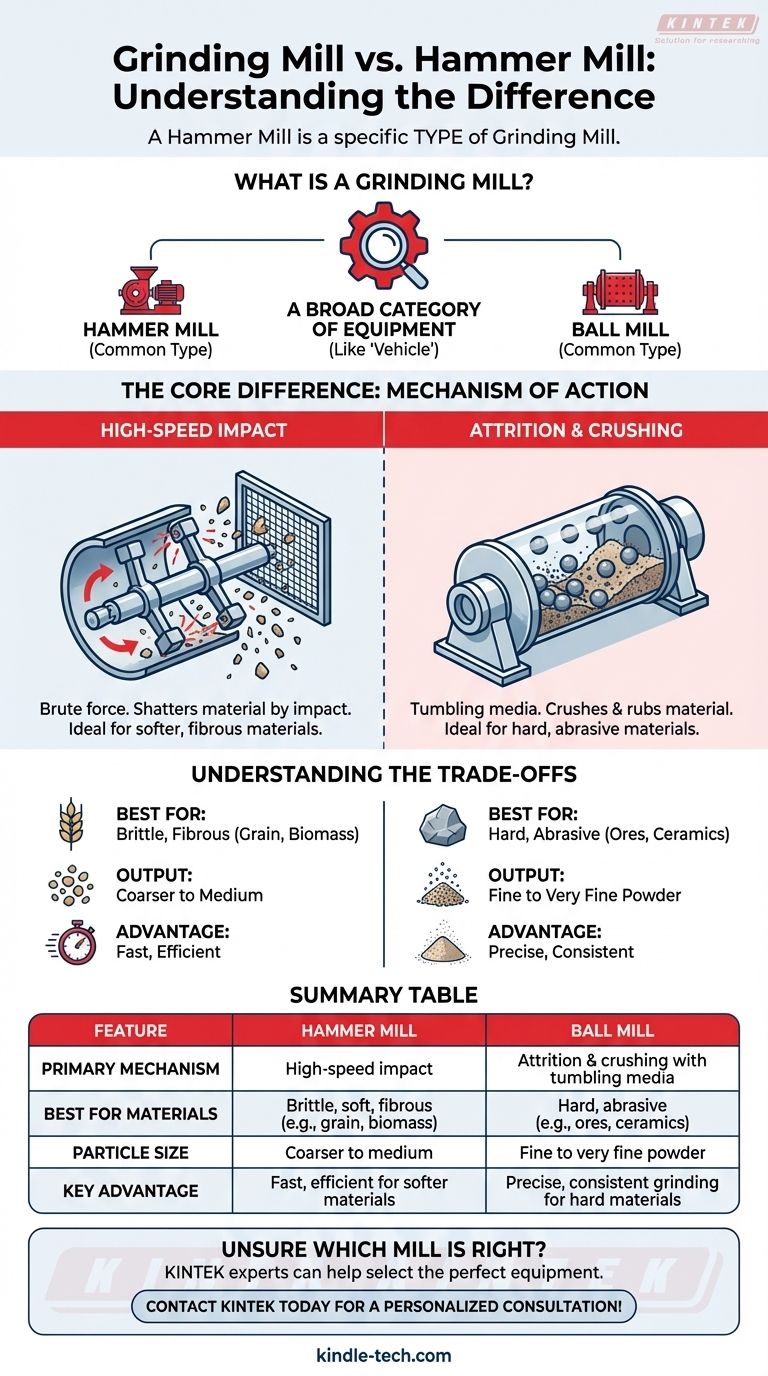
The primary difference is that a hammer mill is a specific type of grinding mill. The term "grinding mill" is a broad category for equipment that breaks down solid material, and the two most common types are hammer mills and ball mills. The key distinction lies in how they reduce particle size: hammer mills use high-speed impact, while ball mills use a combination of impact and attrition.
The core distinction is not "grinding mill vs. hammer mill," but understanding the different mechanisms within the grinding mill family. Hammer mills shatter material with brute force impact, making them ideal for softer materials, whereas ball mills use tumbling media to crush and grind, excelling with harder materials and finer outputs.

What is a Grinding Mill?
A grinding mill is not a single machine but a class of equipment designed for size reduction. The goal is to break down large particles into smaller ones, creating powders or granules.
A Broad Category of Equipment
Think of "grinding mill" as the overarching category, similar to the term "vehicle." Just as vehicles can be cars, trucks, or motorcycles, grinding mills can be hammer mills, ball mills, or other designs, each suited for a different task.
The Two Common Types
As the references indicate, the two most common types of grinding mills you will encounter are ball mills and hammer mills. Understanding the functional difference between these two archetypes will cover the vast majority of industrial and laboratory applications.
The Core Difference: Mechanism of Action
The most important distinction between a hammer mill and a ball mill is the physical principle they use to break down material. This fundamental difference dictates what materials they can process and the characteristics of the final product.
Hammer Mills: High-Speed Impact
A hammer mill operates on the principle of brute force. It uses a rotating shaft with swinging hammers that strike material at high speeds. The particles are shattered upon impact with these hammers, as well as by colliding with the walls of the chamber, until they are small enough to pass through a screen.
Ball Mills: Attrition and Crushing
A ball mill uses a completely different method. It is a rotating cylinder filled with grinding media, typically steel or ceramic balls. As the cylinder tumbles, the balls cascade from the top of the mill, crushing and grinding the material trapped between them. This process involves both impact (from the falling balls) and attrition (rubbing and shearing forces).
The references mention several variations, such as planetary, mixer, and horizontal rolling ball mills, which all use this same core principle of tumbling media but vary in their motion and capacity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong type of mill for your material can lead to inefficiency, excessive wear, or an inability to achieve the desired particle size.
When to Choose a Hammer Mill
Hammer mills excel at processing materials that are brittle or fibrous. Their high-impact action is perfect for quickly shattering things like grain, biomass, or softer minerals. They are generally less effective on very hard, abrasive materials, which can cause rapid wear on the hammers.
When to Choose a Ball Mill
Ball mills are the standard for grinding hard, abrasive materials down to a very fine powder. The constant crushing and grinding action is highly effective for things like ores, cement clinker, and ceramics. The process can be slower than a hammer mill but allows for much finer and more consistent particle sizes.
Scaling and Testing
As noted in the references, mill design affects its use. The length of a ball mill primarily affects its capacity (throughput), while its diameter dictates grinding performance. This is why smaller versions, like "Slice Mills," can be used to test formulations and processes with little concern for scale-up.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice depends entirely on your starting material and your desired final product.
- If your primary focus is processing softer, brittle, or fibrous materials: A hammer mill is likely the correct and more efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is grinding hard, abrasive materials to a fine, uniform powder: A ball mill is the industry standard and the superior tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is initial R&D or testing a formulation: You can use a smaller laboratory-scale mill, such as a slice mill or planetary ball mill, to validate your process before investing in larger equipment.
Ultimately, selecting the right mill begins with a clear understanding of your material's properties and the specific particle size you need to achieve.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hammer Mill | Ball Mill |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Mechanism | High-speed impact | Attrition and crushing with tumbling media |
| Best For Materials | Brittle, soft, fibrous (e.g., grain, biomass) | Hard, abrasive (e.g., ores, ceramics) |
| Particle Size | Coarser to medium | Fine to very fine powder |
| Key Advantage | Fast, efficient for softer materials | Precise, consistent grinding for hard materials |
Unsure which mill is right for your lab's materials? The experts at KINTEK can help you select the perfect equipment—from hammer mills to ball mills—to achieve your specific particle size goals efficiently. Let's optimize your grinding process together.
Contact KINTELK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do stainless steel grinding jars and balls contribute to mechanical alloying? Optimize HEA Powder Synthesis
- Why are zirconia (ZrO2) milling jars recommended for sulfide electrolytes? Ensure Purity in Li6PS5Cl Synthesis
- Why are silicon nitride or zirconia preferred for milling iodo-vanadate-lead precursors? Ensure High Purity Results
- Why use zirconia ball milling jars for SiC/ZTA composite powders? Ensure High Purity & Efficient Particle Refinement
- Why are tungsten carbide grinding jars and balls preferred for high-purity lithium ceramic powders? Ensure Peak Purity.



















