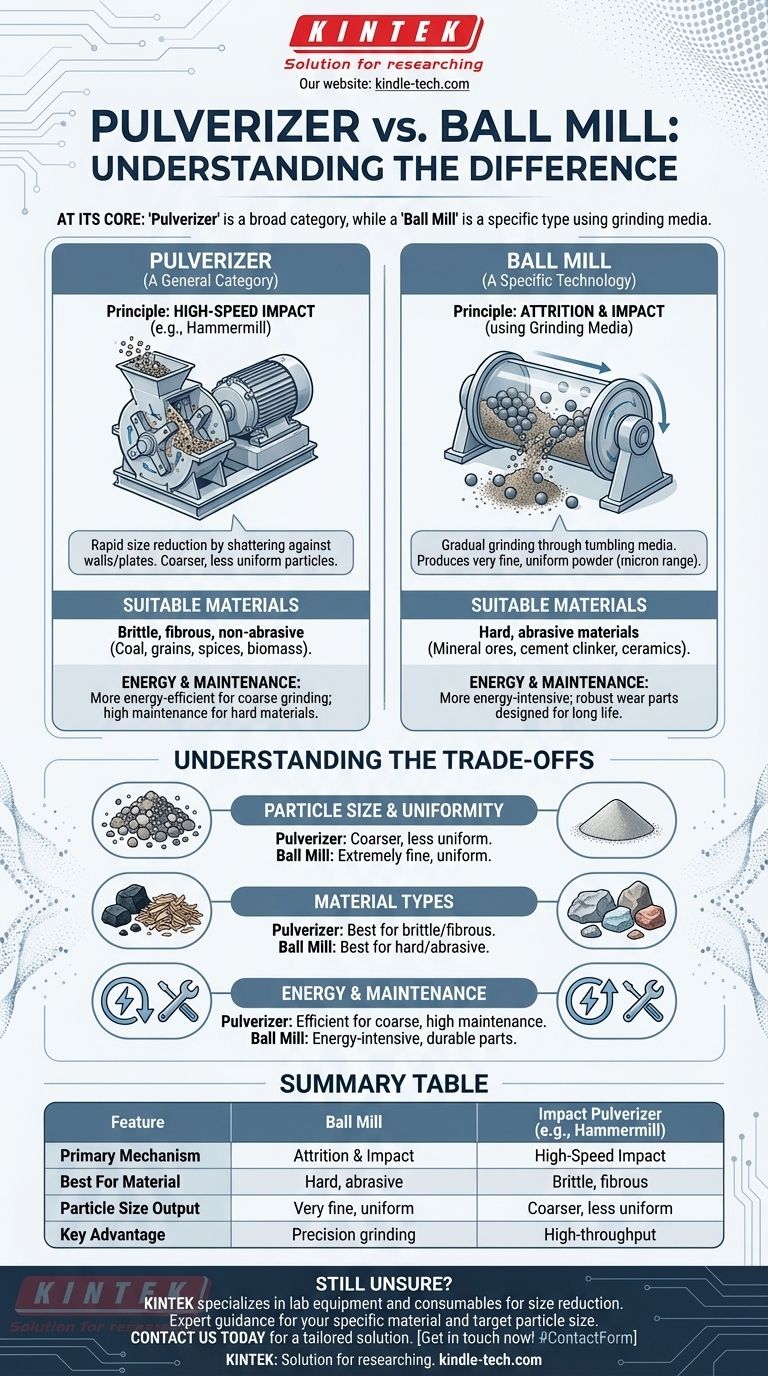
At its core, the term "pulverizer" refers to a broad category of equipment designed for grinding materials, while a "ball mill" is a specific type of pulverizer. The key distinction lies in their mechanism; a ball mill uses grinding media (balls) in a rotating drum for gradual attrition, whereas the term pulverizer is often used to describe machines that rely on high-speed impact, such as a hammermill.
The real question is not "pulverizer vs. ball mill," but rather "which type of pulverizer is right for my material and my target particle size?" The choice between a ball mill and an impact pulverizer like a hammermill depends entirely on this.

The Role of a Pulverizer: A General Overview
A pulverizer is any mechanical device used for comminution, which is the process of reducing the size of solid materials. Its job is to take larger particles and grind them into a fine powder or dust.
A Broad Category of Machines
Think of "pulverizer" as a general classification, similar to the word "vehicle." Just as vehicles include cars, trucks, and motorcycles, pulverizers include ball mills, hammermills, rod mills, and ring mills, among others.
The Principle of High-Speed Impact
Many machines commonly called pulverizers, such as hammermills, operate on the principle of impact. Material is fed into a chamber where it is struck repeatedly by hammers rotating at high speed, shattering it against the chamber walls or breaker plates until it is small enough to pass through a screen.
The Ball Mill: A Specific Grinding Technology
A ball mill is a distinct type of pulverizer renowned for producing very fine powders. It operates on a different principle than high-impact pulverizers.
The Mechanism: Attrition and Impact
A ball mill consists of a hollow cylindrical shell that rotates on its axis. This shell is partially filled with the material to be ground, along with a grinding medium—most commonly steel or ceramic balls.
As the cylinder rotates, the media is lifted up the side of the shell and then cascades or tumbles back down. The size reduction occurs through two actions: impact from the falling balls and attrition as the balls slide and roll over each other and the material.
Key Characteristics
Ball mills are valued for their ability to grind hard, abrasive materials down to a very fine and consistent particle size. The process can be run wet or dry and can operate in either a batch or continuous mode.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Ball Mill vs. Impact Pulverizer
Choosing the correct machine requires understanding the fundamental differences in how they process material and the results they produce. The hammermill, a common type of impact pulverizer, serves as an excellent point of comparison.
Particle Size and Uniformity
A ball mill excels at creating extremely fine and uniform particles, often in the micron or even sub-micron range. The grinding process is slower and more controlled.
An impact pulverizer (like a hammermill) produces a coarser and less uniform particle size distribution. It is designed for rapid, high-throughput size reduction rather than precision finishing.
Suitable Material Types
Ball mills are the industry standard for hard and abrasive materials like mineral ores, cement clinker, and ceramics. The rolling, attritive action is effective on these tough materials without causing excessive wear rates.
Impact pulverizers are better suited for materials that are brittle, fibrous, or less abrasive. This includes coal, grains, spices, wood chips, and certain chemicals. Using one on highly abrasive rock would result in rapid and costly wear on the hammers and internal liners.
Energy and Maintenance
Ball mills are generally more energy-intensive for the amount of size reduction achieved, but their wear parts (liners and grinding media) are robust and designed for long life.
Impact pulverizers can be more energy-efficient for coarse grinding but are high-maintenance when processing hard materials. The hammers and screens are considered consumable parts that require frequent inspection and replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct technology is not about which is "better," but which is best suited for your specific application. Your decision should be guided by your material and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is producing an ultra-fine, uniform powder from hard or abrasive materials (like ores or ceramics): A ball mill is the correct and most effective technology.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput size reduction of brittle, fibrous, or non-abrasive materials (like coal, biomass, or grains): An impact pulverizer like a hammermill is the more efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is simply breaking down bulk material to a coarser, more manageable size for downstream processing: An impact pulverizer or a primary crusher may be the most cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, understanding the properties of your material is the first step toward selecting the right size reduction equipment for the job.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Ball Mill | Impact Pulverizer (e.g., Hammermill) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Mechanism | Attrition & Impact (using grinding media) | High-Speed Impact |
| Best For Material | Hard, abrasive materials (ores, ceramics) | Brittle, fibrous, non-abrasive materials (coal, grains) |
| Particle Size Output | Very fine, uniform (micron/sub-micron) | Coarser, less uniform |
| Key Advantage | Precision grinding for fine powders | High-throughput, rapid size reduction |
Still unsure which grinding equipment is right for your lab or production needs?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with expert guidance on size reduction technology. Whether you're processing abrasive minerals or brittle chemicals, we can help you select the ideal pulverizer or ball mill to achieve your target particle size efficiently.
Contact us today to discuss your material and application—we'll provide a tailored solution to enhance your process. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-energy planetary ball mill preferred over traditional casting for nanocrystalline HEAs?
- What role does a planetary ball mill play in SHS? Optimize Powder Activation for Superior Alloy Synthesis
- How does a planetary ball mill enhance the electrocatalytic activity of La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ? Boost Your Catalyst Performance
- What is the specific role of a high-energy planetary ball mill in the synthesis of Ag-doped sulfide solid-state electrolytes?
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in the synthesis of Li2S–P2S5 sulfide solid-state electrolytes?



















