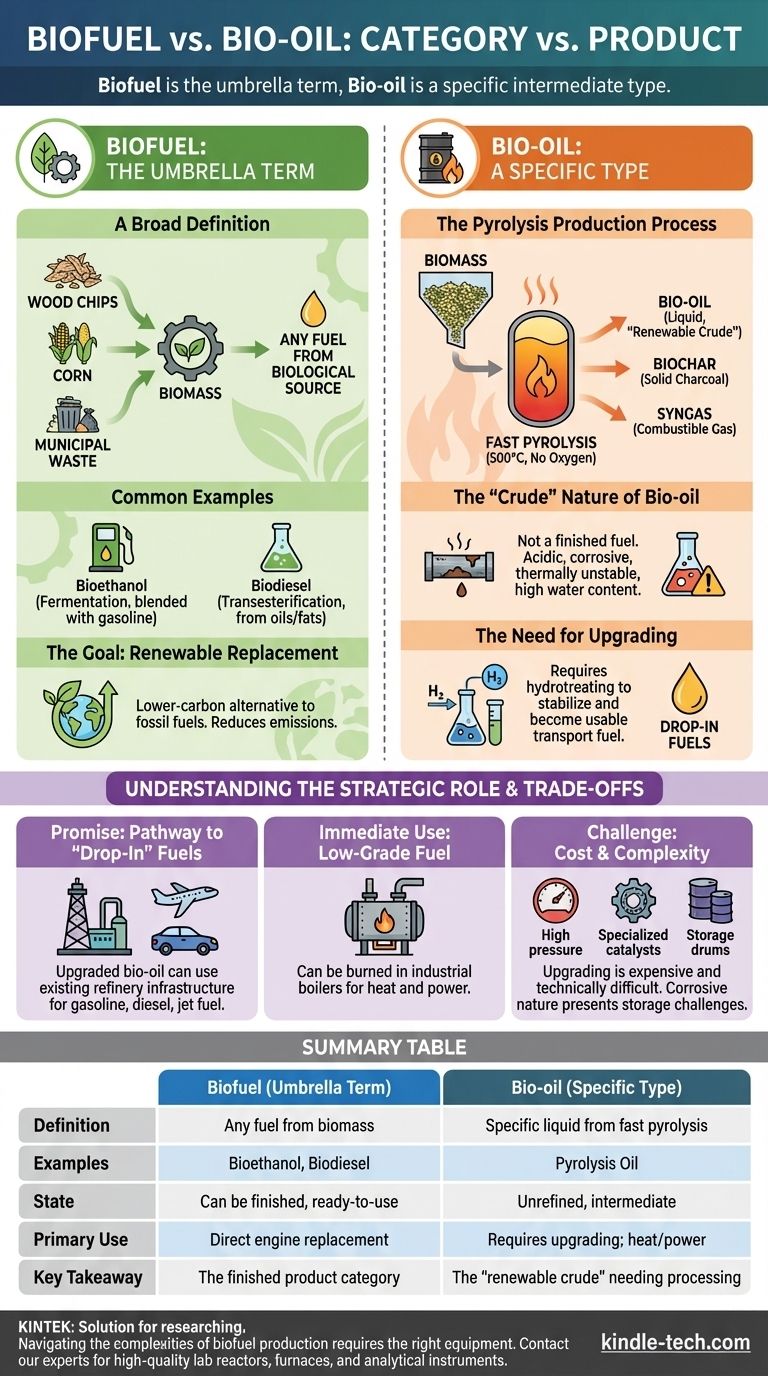
In short, biofuel is the broad category, while bio-oil is a specific type of biofuel. "Biofuel" is an umbrella term for any fuel derived from biological matter (biomass), including well-known examples like bioethanol and biodiesel. Bio-oil, on the other hand, is a specific dark liquid produced from a high-temperature process called pyrolysis and is best understood as a renewable, but unrefined, version of crude oil.
The critical distinction is one of category versus product. "Biofuel" is the all-encompassing term for any fuel from biomass, while "bio-oil" is a specific, unrefined intermediate liquid that requires significant processing before it can be used like conventional gasoline or diesel.

What is a Biofuel? The Umbrella Term
A Broad Definition
A biofuel is any fuel whose energy is obtained from a biological source. This includes a wide range of materials, such as wood, agricultural crops, algae, and even municipal solid waste.
Common Examples
The most common biofuels in use today are bioethanol (an alcohol made via fermentation, often blended with gasoline) and biodiesel (made from vegetable oils or animal fats through a process called transesterification). These are considered "finished" fuels, ready for use in compatible engines.
The Goal: A Renewable Replacement
The primary objective of biofuels is to create a renewable, lower-carbon alternative to fossil fuels. They are a key component in strategies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on finite petroleum resources.
What is Bio-Oil? A Specific Intermediate Product
The Pyrolysis Production Process
Bio-oil, often called pyrolysis oil, is produced through a process called fast pyrolysis. In this process, biomass is rapidly heated to high temperatures (around 500°C or 930°F) in the complete absence of oxygen.
This thermal decomposition breaks the solid biomass down into three things: bio-oil (a liquid), biochar (a solid charcoal), and syngas (a combustible gas).
The "Crude" Nature of Bio-Oil
Unlike bioethanol or biodiesel, bio-oil is not a finished fuel. It is a complex mixture of oxygenated organic compounds, which makes it acidic, corrosive, and thermally unstable. It also has a high water content.
Because of these properties, you cannot simply put raw bio-oil into a standard car or truck engine. It would quickly damage the fuel system and engine components.
The Need for Upgrading
To become a usable transportation fuel, bio-oil must undergo significant secondary processing, known as upgrading. This typically involves hydrotreating, a catalytic process that uses hydrogen to remove oxygen and stabilize the molecules, making them similar to those found in conventional crude oil.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Strategic Role
The Promise: A Pathway to "Drop-In" Fuels
The primary advantage of the bio-oil pathway is its potential. Once upgraded, the resulting hydrocarbon liquid can be processed in traditional petroleum refineries to create "drop-in" fuels like renewable gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel.
This means we could potentially leverage the massive, existing refinery infrastructure instead of building entirely new supply chains from scratch.
The Challenge: Cost and Complexity of Upgrading
The biggest hurdle for bio-oil is the upgrading process. It is technologically complex and expensive, requiring high pressures, hydrogen, and specialized catalysts that can be deactivated by contaminants in the raw bio-oil.
The corrosive nature of bio-oil also presents significant challenges for storage and transportation, requiring specialized materials and handling procedures.
The Immediate Use: A Low-Grade Fuel
While upgrading bio-oil into transportation fuel is the ultimate goal, it can also be used more directly. It can be burned in industrial boilers and furnaces to generate heat and electricity, effectively replacing heavy fuel oil.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this distinction is key to evaluating different renewable energy strategies.
- If your primary focus is on currently available vehicle fuels: You are most likely dealing with bioethanol and biodiesel, which are finished products blended into the existing fuel supply.
- If your focus is on next-generation or advanced renewables: You will frequently encounter bio-oil as a critical intermediate, a "renewable crude" that connects raw biomass to our existing refinery infrastructure.
- When evaluating a new technology: Ask whether it produces a finished, ready-to-use biofuel or an intermediate like bio-oil that requires further capital-intensive upgrading.
Ultimately, all bio-oils are biofuels, but not all biofuels are bio-oils; this simple hierarchy separates a raw ingredient from a potential finished product.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Biofuel (Umbrella Term) | Bio-Oil (Specific Type) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Any fuel derived from biological matter (biomass) | A specific liquid produced from fast pyrolysis of biomass |
| Examples | Bioethanol, Biodiesel | Pyrolysis Oil |
| State | Can be a finished, ready-to-use fuel | An unrefined, intermediate product |
| Primary Use | Direct replacement in engines (e.g., blended gasoline) | Requires upgrading to be a transport fuel; can be used for heat/power |
| Key Takeaway | The finished product category | The "renewable crude" that requires further processing |
Navigating the complexities of biofuel production requires the right equipment. Whether your R&D involves pyrolysis for bio-oil creation or other biomass processing, KINTEK provides the high-quality lab reactors, furnaces, and analytical instruments you need to innovate and scale your renewable energy solutions. Contact our experts today to discuss how our reliable lab equipment can support your biofuel development goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- How do you test for CVD diamonds? Uncover the scientific methods for definitive identification.
- What are the five basic heat treatment processes? A Guide to Metal Hardening & Tempering
- What are the technical advantages of using an industrial electric stirrer for ZrO2 and PMMA? Enhance Shielding Uniformity
- What is the range of KBr in IR? A Guide to Mid-IR Spectroscopy from 4000-400 cm⁻¹
- What is the thermal stability of graphene? A Guide to Temperature Limits and Material Selection
- What is pyrolysis in renewable energy? Converting Biomass and Methane into Clean Fuels
- What is the function of high-temperature thermal treatment equipment in TiO2/G nanocomposites? Optimize Photocatalysts
- What are the conditions for fast pyrolysis? Achieve Maximum Bio-Oil Yield from Biomass















