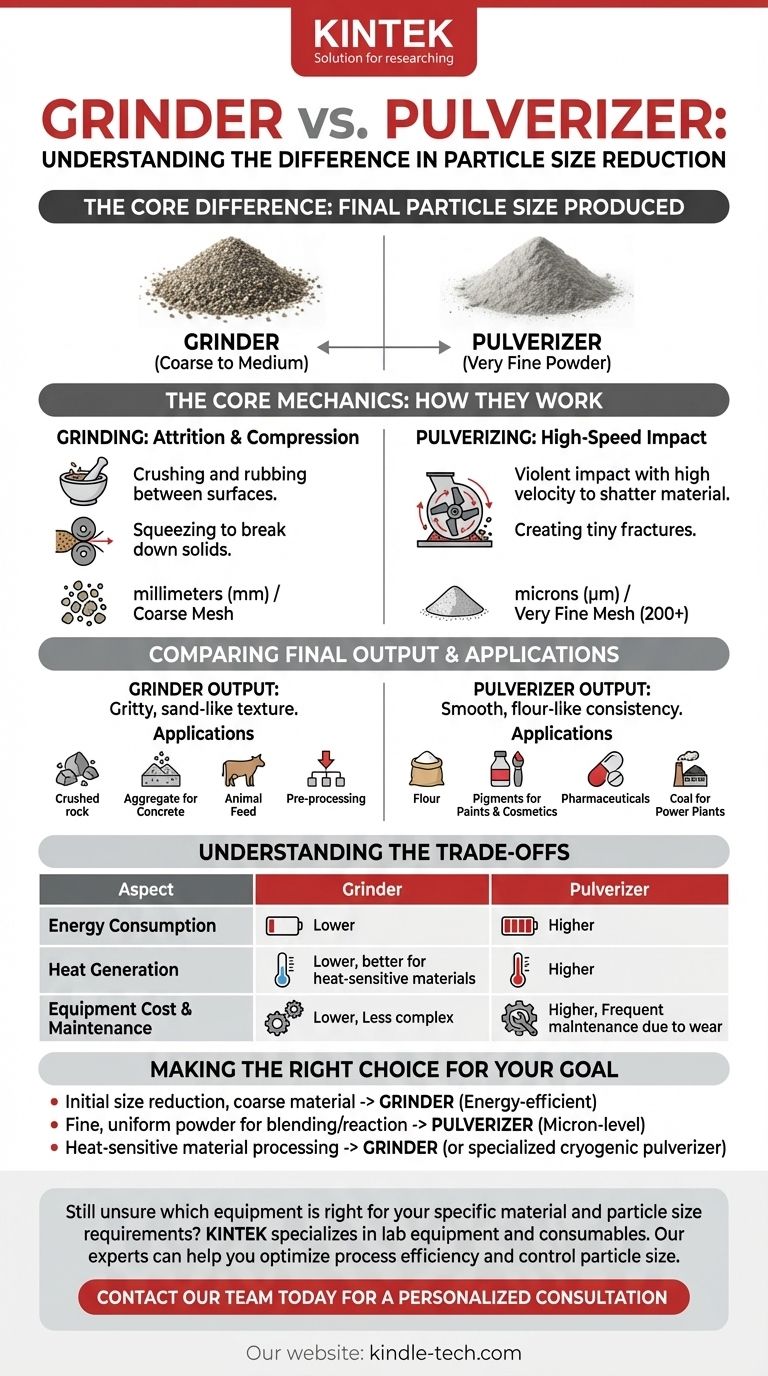
In industrial processing, the core difference between a grinder and a pulverizer is the final particle size they produce. A grinder reduces materials to coarse or medium-sized particles, while a pulverizer takes that process a step further, reducing materials to a very fine, consistent powder. While both tools use force to break down materials, their specific mechanisms, energy requirements, and ideal applications are distinct.
While both grinders and pulverizers reduce material size, the distinction lies in the final output. A grinder is designed to create smaller pieces or coarse powders, whereas a pulverizer is engineered specifically to create extremely fine, flour-like powders measured in microns.

The Core Mechanics: How They Work
Understanding the difference in output begins with understanding the difference in mechanism. Each machine employs a distinct physical force to achieve its goal.
Grinding: Attrition and Compression
A grinder primarily uses attrition (rubbing) and compression (squeezing) to break down materials.
Think of a classic mortar and pestle. The material is crushed and rubbed between two hard surfaces until it breaks apart into smaller granules or a coarse powder.
Industrial grinders, like roller mills or jaw crushers, apply this same principle on a massive scale, using immense pressure to break down solids.
Pulverizing: High-Speed Impact
A pulverizer typically relies on high-speed impact to shatter materials.
Instead of squeezing the material, a pulverizer strikes it with immense force and velocity. In a hammer mill, for example, rotating hammers strike the material at high speed, causing it to shatter against a solid plate.
This violent impact is far more effective at creating the tiny fractures needed to produce an extremely fine, dust-like powder.
Comparing the Final Output
The choice between grinding and pulverizing is almost always determined by the required characteristics of the final product.
Particle Size and Consistency
This is the most critical distinction. A grinder produces particles often measured in millimeters or coarse mesh sizes. The output might feel gritty, like coarse salt or sand.
A pulverizer produces particles measured in microns (a millionth of a meter) or very fine mesh sizes (e.g., 200 mesh or finer). The final product is a true powder with a smooth, flour-like consistency.
Typical Applications for Grinding
Grinding is often used for initial size reduction or when a coarse final product is acceptable.
Common examples include crushing rock into aggregate for concrete, grinding grains for animal feed, or pre-processing raw materials before they are sent for finer pulverization.
Typical Applications for Pulverizing
Pulverizing is essential when a high surface area is needed for reactions, dissolving, or creating a homogenous mixture.
This includes producing flour, creating pigments for paints and cosmetics, manufacturing pharmaceuticals, and pulverizing coal to improve combustion efficiency in power plants.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right equipment isn't just about the final particle size; it also involves practical considerations that impact efficiency and cost.
Energy Consumption
Creating finer particles requires exponentially more energy. Pulverizing a material to a fine powder consumes significantly more power than grinding it to a coarse granule.
Heat Generation
The high-velocity impacts inside a pulverizer generate substantial heat. This can be a major issue for heat-sensitive materials like certain plastics, spices, or pharmaceuticals, as it can degrade or alter their properties. Grinding is a lower-energy process and typically generates less heat.
Equipment Cost and Maintenance
Generally, pulverizers are more complex machines than grinders. The high-speed components, such as hammers and internal liners, are subject to significant wear and require more frequent maintenance and replacement, leading to higher operational costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct process, you must first define your desired outcome with precision.
- If your primary focus is initial size reduction or creating coarse material: A grinder is the correct and more energy-efficient tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is producing a fine, uniform powder for blending, dissolving, or chemical reaction: A pulverizer is necessary to achieve the required micron-level particle size.
- If your primary focus is processing a heat-sensitive material: You must carefully consider the heat generated, especially by high-impact pulverizers, and may need to opt for a low-speed grinder or a specialized cryogenic system.
Ultimately, selecting the right equipment depends entirely on defining the required fineness of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Grinder | Pulverizer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Mechanism | Attrition & Compression | High-Speed Impact |
| Final Particle Size | Coarse to Medium (mm) | Fine Powder (microns) |
| Typical Applications | Initial size reduction, animal feed, aggregates | Pharmaceuticals, flour, pigments, fine chemicals |
| Energy Consumption | Lower | Higher |
| Heat Generation | Lower (better for heat-sensitive materials) | Higher |
Still unsure which equipment is right for your specific material and particle size requirements?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving a wide range of laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect grinder or pulverizer to optimize your process efficiency, control particle size, and protect heat-sensitive materials.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and let us help you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
People Also Ask
- What are cryogenic ground spices? Unlock Maximum Flavor with Advanced Grinding Technology
- What is the process of cold grinding? Achieve Superior Powder Quality for Heat-Sensitive Materials
- What is the temperature of cryogenic grinding? Achieve Superior Particle Size & Preserve Heat-Sensitive Materials
- What is cryogenic machining used for? Process Unmachinable Materials with Extreme Cold
- What was the cryogenic grinding process compared against in the study? Cryogenic vs. Dry Grinding Analysis



















